Abstract
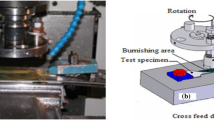
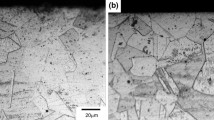
This work aims at the improvement of surface quality and wear resistance of AISI 316L stainless steel, used in different industrial sectors including orthopedic applications. Ball-burnishing treatment, considered as a very efficient mechanical finish process, was applied with respect to the response surface method. Surface roughness parameter Ra was minimized by using a mathematical model based on Box–Behnken model and expressing Ra as a function of applied charge, feed rate, and ball diameter. After optimization, the selected regime was fixed and the number of passes was increased by up to 5. Ra was measured again and tribological behavior was studied. Results show that surface roughness of best burnished sample can be decreased to a value much less by 93.4% and correspondingly, its wear loss can be improved by 53.4%, but with respect to fix 3 passes during ball burnishing. Morphologies of wear scars analyzed by scanning electron microscopy specify that adhesive wear occurred in both untreated and burnished surfaces. The coefficient of friction, measured under dry conditions, was reduced only for the smoothest surface, while other specimens had elevated coefficient of friction compared to turned surface.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BB:
-
Ball burnishing
- COF:
-
Coefficient of friction
- D :
-
Ball diameter [mm]
- f :
-
Burnishing feed rate[mm/rev]
- f t :
-
Turning feed rate [mm/rev]
- i:
-
Number of burnishing passes
- N:
-
Rotational frequency [rev/min]
- p:
-
Depth of pass [mm]
- Px :
-
Burnishing force [N]
- Ra:
-
Arithmetical surface roughness average [μm]
- RSM:
-
Response surface method
- SS:
-
Stainless steel
References
Fellah M, Labaïz M, Assala O, Iost A, Dekhil L (2013) Tribological behaviour of AISI 316L stainless steel for biomedical applications. Tribol Mater Surf Interfaces 7:135–149. https://doi.org/10.1179/1751584X13Y.0000000032
Yazıcı M, Kovacı H, Yetim AF, Çelik A (2018) Structural, mechanical and tribological properties of Ti and TiN coatings on 316L stainless steel. Ceram Int 44:14195–14201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.05.022
Teoh S (2000) Fatigue of biomaterials: a review. Int J Fatigue 22:825–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-1123(00)00052-9
St John K (ed) (1992) Particulate debris from medical implants: mechanisms of formation and biological consequences. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Ahmed AA, Mhaede M, Wollmann M, Wagner L (2014) Effect of surface and bulk plastic deformations on the corrosion resistance and corrosion fatigue performance of AISI 316L. Surf Coat Technol 259:448–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.10.052
Attabi S, Mokhtari M, Taibi Y, Abdel-Rahman I, Hafez B, Elmsellem H (2019) Electrochemical and tribological behavior of surface-treated titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. J Bio- Tribo-Corros. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-018-0193-5
Laouar L, Hamadache H, Saad S, Bouchelaghem A, Mekhilef S (2009) Mechanical surface treatment of steel-optimization parameters of regime. Phys Proc 2:1213–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2009.11.084
Hassan AM (1997) The effects of ball- and roller-burnishing on the surface roughness and hardness of some non-ferrous metals. J Mater Process Technol 72:385–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00199-4
Hassan AM, Al-Wahhab OMA (1998) Surface characteristics of some roller burnished non-ferrous components. Mater Manuf Processes 13:505–515. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426919808935272
Dimitrov DM, Slavov SD, Dimitrov Z (2017) Experimental research on the effect of the ball burnishing process, using new kinematical scheme on hardness and phase composition of surface layer of AISI 304L stainless steel. MATEC Web Conf 112:02001. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201711202001
Amdouni H, Bouzaiene H, Montagne A, Van Gorp A, Coorevits T, Nasri M, Iost A (2017) Experimental study of a six new ball-burnishing strategies effects on the Al-alloy flat surfaces integrity enhancement. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90:2271–2282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9529-9
López de Lacalle LN, Rodríguez A, Lamikiz A, Celaya A, Alberdi R (2011) Five-axis machining and burnishing of complex parts for the improvement of surface roughness. Mater Manuf Process 26(8):997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2010.529589
Hamadache H, Laouar L, Zeghib NE, Chaoui K (2006) Characteristics of Rb40 steel superficial layer under ball and roller burnishing. J Mater Process Technol 180:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.05.013
Gu Y, Zheng X, Liu Q, Ma H, Zhang L, Yang D (2018) Investigating corrosion performance and corrosive wear behavior of Sol–gel/MAO-Coated Mg alloy. Tribol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1052-8
El-Tayeb NSM, Low KO, Brevern PV (2008) Enhancement of surface quality and tribological properties using ball burnishing process. Mach Sci Technol 12:234–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/10910340802067536
Abrão AM, Denkena B, Breidenstein B, Mörke T (2014) Surface and subsurface alterations induced by deep rolling of hardened AISI 1060 steel. Prod Eng Res Devel 8:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-014-0539-x
Gharbi F, Sghaier S, Morel F, Benameur T (2015) Experimental investigation of the effect of burnishing force on service properties of AISI 1010 steel plates. J Mater Eng Perform 24:721–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1349-1
Lee SSG, Tam SC, Loh NH n.d. Ball burnishing of 316L stainless steel 11
Yilmaz H, Sadeler R (2018) Effect of ball burnishing treatment on the fatigue behavior of 316L stainless steel operating under anodic and cathodic polarization potentials. Metall Mater Trans A 49:5393–5401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4889-4
Yilmaz H, Sadeler R (2019) Impact wear behavior of ball burnished 316L stainless steel. Surf Coat Technol 363:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.02.022
Tanaka H, Ishii W, Yanagi K (2011) Optimal burnishing conditions and mechanical properties of surface layerby surface modification effect induced of applying burnishing processto stainless steel and aluminum alloy. J Jpn Soc Technol Plast 52:726–730. https://doi.org/10.9773/sosei.52.726
Goupy J (1999) Plans d’expériences pour surfaces de réponse. Dunod, Paris
Amanov A, Cho I-S, Kim D-E, Pyun Y-S (2012) Fretting wear and friction reduction of CP titanium and Ti–6Al–4V alloy by ultrasonic nanocrystalline surface modification. Surf Coat Technol 207:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.06.046
Marteau J, Bigerelle M, Mazeran P-E, Bouvier S (2015) Relation between roughness and processing conditions of AISI 316L stainless steel treated by ultrasonic shot peening. Tribol Int 82:319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.07.013
Bourebia M, Laouar L, Hamadache H, Dominiak S (2017) Improvement of surface finish by ball burnishing: approach by fractal dimension. Surf Eng 33:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670844.2016.1232778
El-Taweel TA, El-Axir MH (2009) Analysis and optimization of the ball burnishing process through the Taguchi technique. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1485-6
Hassan AM, Al-Jalil HF, Ebied AA (1998) Burnishing force and number of ball passes for the optimum surface finish of brass components. J Mater Process Technol 83:176–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(98)00058-2
Li FL, Xia W, Zhou ZY, Zhao J, Tang ZQ (2012) Analytical prediction and experimental verification of surface roughness during the burnishing process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2012.06.001
Zhao J, Zhanqiang L (2020) Plastic flow behavior for machined surface material Ti-6Al-4V with rotary ultrasonic burnishing. J Mater Res Technol 9(2):2387–2401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.12.071
Bounezour H, Laouar L, Bourbia M, Ouzine B (2019) Effects of work hardening on mechanical metal properties—experimental analysis and simulation by experiments. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 101:2475–2485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3071-x
López de Lacalle LN, Lamikiz A, Sanchez JA, Arana JL (2007) The effect of ball burnishing on heat-treated steel and Inconel 718 milled surfaces. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32:958–968
Branko T, Petar MT, Ognjan L, Dragomir M, Branislav MJ, Bojan B, Djordje V (2012) Using specially designed high-stiffness burnishing tool to achieve high-quality surface finish. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67:601–611
El-Axir MH, Othman OM, Abodiena AM (2008) Study on the inner surface finishing of aluminum alloy 2014 by ball burnishing process. J Mater Process Technol 202:435–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.10.040
Lin N, Li D, Zou J, Guo J, Yuan S, Wang Z, Tang B (2018) Tribological behavior of electrochemically etched AISI 316 stainless steel with a textured surface. J Mater Eng Perform 27:6616–6628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3748-1
Revankar GD, Shetty R, Rao SS, Gaitonde VN (2017) Wear resistance enhancement of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) by ball burnishing process. J Mater Res Technol 6:13–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2016.03.007
Sedlaček M, Podgornik B, Vižintin J (2009) Influence of surface preparation on roughness parameters, friction and wear. Wear 266:482–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2008.04.017
Dogan H, Findik F, Morgul O (2002) Friction and wear behaviour of implanted AISI 316L SS and comparison with a substrate. Mater Des 23:605–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-3069(02)00066-3
Keller J, Fridrici V, Kapsa Ph, Huard JF (2009) Surface topography and tribology of cast iron in boundary lubrication. Tribol Int 42:1011–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2009.02.008
Rao DS, Suresh HH, Komaraiah M, Kempaiah UN (2008) Investigations on the effect of ball burnishing parameters on surface hardness and wear resistance of HSLA dual-phase steels. Mater Manuf Process 23:295–302
Godse RS, Gawande SH, Keste AA (2016) Tribological behavior of high fraction carbon steel alloys. J Bio- Tribo-Corros 2:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-016-0034-3
QinW KJ, Li J, Yue W, Liu Y, She D, MaoQ LY (2018) Tribological behavior of the 316L stainless steel with heterogeneous lamella structure. Materials 11:1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101839
Kuznetsov VP, Makarov AV, Psakhie SG, Savrai RA, Malygina IYu, Davydova NA (2014) Tribological aspects in nanostructuring burnishing of structural steels. Phys Mesomech 17:250–264. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102995991404002X
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the response of Mechanics and Structures (LMS) Research Laboratory, University of 8th May 1945, Guelma, Algeria, for their involvement in our study.
Funding
Not applicable for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attabi, S., Himour, A., Laouar, L. et al. Effect of Ball Burnishing on Surface Roughness and Wear of AISI 316L SS. J Bio Tribo Corros 7, 7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-020-00437-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-020-00437-9