Abstract
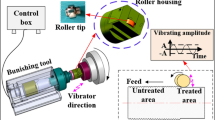
A set of ultrasonic burnishing equipment with two different burnishing tips was designed and manufactured, with which a series of experiments were performed to explore the effects of process parameters and burnishing tips on the surface integrity of austenitic stainless steel material being treated by ultrasonic burnishing (UB). Based on the experiment data, the two surface treatments, i.e. UB with ball tip and UB with roller tip, were comparatively assessed together with the other two surface machining methods of fine turning and grinding. As a further study, a microscopic FE model was built to investigate the three-dimensional transient stress and strain field inside the being treated material. It was found that parameter combination is determinative to surface finishing in UB process, and static pressure and burnishing pass are supposed to be the two most significant parameters for surface integrity of the treated sample. On the whole, roller tip is more preferable to achieve good surface enhancement than ball tip. The superposition of ultrasonic vibration leads to the dynamic change of the stress and strain field in UB, resulting in the oscillating propagation of stress wave inside the material, which gives explanation for the good performance of UB than that of conventional burnishing without ultrasonic.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nalbant M, Yildiz Y. Effect of cryogenic cooling in milling process of AISI 304 stainless steel. Trans Nonferrous Meter Soc China (Engl Ed). 2011;21:72–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60680-8.
Lu K, Lu J. Surface nanocrystallization (SNC) of metallic materials-presentation of the concept behind a new approach. J Mater Sci Technol. 1999;15:193–7.
Wu J, Zou S, Zhang Y, Gong S, Sun G, Ni Z, Cao Z, Che Z, Feng A. Microstructures and mechanical properties of β forging Ti17 alloy under combined laser shock processing and shot peening. Surf Coatings Technol. 2017;328:283–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.08.069.
Bin Tang C, Xin Liu D, Tang B, Hua Zhang X, Qin L, Song Liu C. Influence of plasma molybdenizing and shot-peening on fretting damage behavior of titanium alloy. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;390:946–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.08.146.
Mizunuma S, Iizuka T, Mitsui K, Okumura H, Kohzu M. Grain refinement of magnesium alloy AZ31 under torsion extrusion with a square-hole die. Mater Sci Forum. 2010;654–656:711–4. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.654-656.711.
Jahedi M, Paydar MH. Study on the feasibility of the torsion extrusion (TE) process as a severe plastic deformation method for consolidation of Al powder. Mater Sci Eng A. 2010;527:5273–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.04.088.
Pu Z, Yang S, Song GL, Dillon OW, Puleo DA, Jawahir IS. Ultrafine-grained surface layer on Mg–Al–Zn alloy produced by cryogenic burnishing for enhanced corrosion resistance. Scr Mater. 2011;65:520–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.06.013.
Low KO, Wong KJ. Influence of ball burnishing on surface quality and tribological characteristics of polymers under dry sliding conditions. Tribol Int. 2011;44:144–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2010.10.005.
Joo SH, Kim HS. Comparison of deformation and microstructural evolution between equal channel angular pressing and forward extrusion using the dislocation cell mechanism-based finite element method. J Mater Sci. 2010;45:4705–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4465-9.
Chen H, Tang J, Lang X, Huang Y, He Y. Influences of dressing lead on surface roughness of ultrasonic-assisted grinding. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2014;71:2011–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5636-7.
Li K, He Y, Cho IS, Shin K. Effect of ultrasonic nanocrytalline surface modification on hardness and microstructural evolution of Cu–Sn alloy. Defect Diffus Forum. 2015;364:157–64. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/DDF.364.157.
Dong Z, Liu Z, Li M, Luo JL, Chen W, Zheng W, Guzonas D. Effect of ultrasonic impact peening on the corrosion of ferritic-martensitic steels in supercritical water. J Nucl Mater. 2015;457:266–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2014.11.028.
Qinjian Z, Jianguo C, Huiying W. Ultrasonic Surface Strengthening of train axle material 30CrMoA. Procedia CIRP. 2016;42:853–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.03.007.
Amanov A, Cho IS, Kim DE. Effectiveness of high-frequency ultrasonic peening treatment on the tribological characteristics of Cu-based sintered materials on steel substrate. Mater Des. 2013;45:118–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.08.073.
Vilhauer B, Bennett CR, Matamoros AB, Rolfe ST. Fatigue behavior of welded coverplates treated with ultrasonic impact treatment and bolting. Eng Struct. 2012;34:163–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.09.009.
Yang Z, Qi L, Wang J, Ma Z, Wang Y, Wang D. Effect of ultrasonic impact treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of diffusion-bonded TC11 alloy joints. Arch Civ Mech Eng. 2019;19:1431–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2019.09.006.
Wu B, Zhang L, Zhang J, Murakami RI, Pyoun YS. An investigation of ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification machining process by numerical simulation. Adv Eng Softw. 2015;83:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.01.011.
Kayumov R, Sik Pyun Y, Suh CM, Murakami R. Mechanical and fatigue characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V extra low interstitial and solution-treated and annealed alloys after ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification treatment. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014;14:9430–5. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2014.10164.
Teimouri R, Amini S, Bami AB. Evaluation of optimized surface properties and residual stress in ultrasonic assisted ball burnishing of AA6061-T6. Meas J Int Meas Confed. 2018;116:129–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.11.001.
Liu Y, Zhao X, Wang D. Determination of the plastic properties of materials treated by ultrasonic surface rolling process through instrumented indentation. Mater Sci Eng A. 2014;600:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.096.
Mordyuk BN, Prokopenko GI. Ultrasonic impact peening for the surface properties’ management. J Sound Vib. 2007;308:855–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2007.03.054.
Liu X, Wu D, Zhang J, Hu X, Cui P. Analysis of surface texturing in radial ultrasonic vibration-assisted turning. J Mater Process Technol. 2019;267:186–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.12.021.
Bozdana AT, Gindy NNZ. Comparative experimental study on effects of conventional and ultrasonic deep cold rolling processes on Ti–6Al–4V. Mater Sci Technol. 2008;24:1378–84. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328408x302431.
Zhang M, Deng J, Liu Z, Zhou Y. Investigation into contributions of static and dynamic loads to compressive residual stress fields caused by ultrasonic surface rolling. Int J Mech Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105144.
Cheng M, Zhang D, Chen H, Qin W. Development of ultrasonic thread root rolling technology for prolonging the fatigue performance of high strength thread. J Mater Process Technol. 2014;214:2395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.05.019.
Jerez-Mesa R, Travieso-Rodriguez JA, Gomez-Gras G, Lluma-Fuentes J. Development, characterization and test of an ultrasonic vibration-assisted ball burnishing tool. J Mater Process Technol. 2018;257:203–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.02.036.
Travieso-Rodriguez JA, Gomez-Gras G, Dessein G, Carrillo F, Alexis J, Jorba-Peiro J, Aubazac N. Effects of a ball-burnishing process assisted by vibrations in G10380 steel specimens. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2015;81:1757–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7255-3.
Huuki J, Hornborg M, Juntunen J. Influence of ultrasonic burnishing technique on surface quality and change in the dimensions of metal shafts. J Eng (USA). 2014;2014:5–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/124247.
Zhao W, Liu D, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Zhang R, Zhang H, Ye C. Improving the fretting and corrosion fatigue performance of 300M ultra-high strength steel using the ultrasonic surface rolling process. Int J Fatigue. 2019;121:30–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.11.017.
Shen X, Gong X, Zhang J, Su G. An investigation of stress condition in vibration-assisted burnishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2019;105:1189–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04128-9.
Jerez-Mesa R, Gomez-Gras G, Travieso-Rodriguez JA. Surface roughness assessment after different strategy patterns of ultrasonic ball burnishing. Procedia Manuf. 2017;13:710–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2017.09.116.
Bozdana AT, Gindy NNZ, Li H. Deep cold rolling with ultrasonic vibrations—a new mechanical surface enhancement technique. Int J Mach Tools Manuf. 2005;45:713–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2004.09.017.
Jinchun S, Zhiqiang JIA, Minxin Z, Engineering M. Influence of ultrasonic rolling and finishing processing parameters on surface roughness and hardness of 45 steel. Manuf Technol Mach Tool. 2016;2016:85–9.
Stalin John MR, Vinayagam BK. Investigation of roller burnishing process on aluminium 63400 material. Aust J Mech Eng. 2011;8:47–544. https://doi.org/10.1080/14484846.2011.11464594.
Habibnejad-Korayem M, Mahmudi R, Ghasemi HM, Poole WJ. Tribological behavior of pure Mg and AZ31 magnesium alloy strengthened by Al2O3 nano-particles. Wear. 2010;268:405–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.08.031.
Amanov A, Umarov R. The effects of ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification temperature on the mechanical properties and fretting wear resistance of Inconel 690 alloy. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;441:515–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.293.
Nestler A, Schubert A. Effect of machining parameters on surface properties in slide diamond burnishing of aluminium matrix composites. Mater Today Proc. 2015;2:S156–S161161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2015.05.033.
Babu P, Ankamma K, Prasad T. Optimization of burnishing parameters by DOE and surface roughness, microstructure and micro hardness characteristics of AA6061 aluminium alloy in T6 condition. Int J Eng Res Appl. 2012;2:1139–1146. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.416.8697&rep=rep1&type=pdf. Accessed 3 Nov 2019.
Ritchie RO. The conflicts between strength and toughness. Nat Mater. 2011;10:817–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3115.
Warren AW, Guo YB. The impact of surface integrity by hard turning versus grinding on rolling contact fatigue—part I: comparison of fatigue life and acoustic emission signals. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct. 2007;30:698–711. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2695.2007.01144.x.
Liu Y, Wang L, Wang D. Finite element modeling of ultrasonic surface rolling process. J Mater Process Technol. 2011;211:2106–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.07.009.
Lee CS, Park IG, Pyoun YS, Cho IS, Cho IH, Park J. Rolling contact fatigue characteristics of SAE52100 by ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification technology. Int J Mod Phys B. 2010;24:3065–70. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217979210066094.
Teimouri R, Amini S. Analytical modeling of ultrasonic surface burnishing process: Evaluation of through depth localized strain. Int J Mech Sci. 2019;151:118–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.11.008.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grand numbers 51775285]; Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province of China [grand number 2019GGX104093]; Project for the Innovation Team of Universities and Institutes in Jinan [grand number 2018GXRC005]; National Natural Science Foundation of China [grand numbers 51675289].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 2130 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, YL., Shen, XH., Xu, GF. et al. Surface integrity enhancement of austenitic stainless steel treated by ultrasonic burnishing with two burnishing tips. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 20, 79 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00074-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00074-6