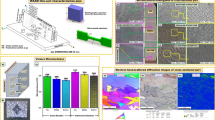
Abstract
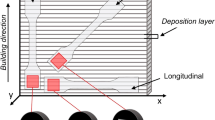
The inhomogeneous microstructures and mechanical properties in thickness direction are clearly present for extra-thick ultra-high-strength steel, due to the cross section effect. In this work, multi-level structure and its effect on strength and yield ratio for extra-thick steel are investigated, and the relationship between the microstructures and strength was discussed by the Hall-Petch formula. The results show that the size of prior austenite grain, martensite packet, block and lath are all gradually increasing from the surface to the center, and corresponding strength and yield ratio are decreasing. Simultaneously, the high-angle boundary of the martensite block and the low angle boundaries of the martensite lath have a stacking effect on the dislocation movement, and they act as the “effective grain size” to control the strength and yield ratio. Furthermore, the strain hardening rate is high and decreases rapidly in the first stage in the work hardening behavior, whereas, it is low and reaches a dynamic equilibrium in the second stage.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.Y. Wang, Study on the Hardenability and Strength & Toughness of High Strength Low Alloyed Ultra-Heavy Plate Steels for Marine Engineering, China Iron and Steel Research Institute, China, 2013.
X.J. Sun, S.F. Yuan, Z.J. Xie, L.L. Dong, C.J. Shang and R.D.K. Misra, Microstructure-Property Relationship in a High Strength-High Toughness Combination Ultra-Heavy Gauge Offshore Plate Steel: The Significance of Multiphase Microstructure, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 689(24), p 212-219.
B.B. Wu, S. Huang, Z.Q. Wang, J.X. Zhao, C.S. Wang, C.J. Shang and R.D.K. Misra, Crystallography Analysis of Toughness in High Strength Ultra-Heavy Plate Steel, Mater. Lett., 2019, 250(1), p 55-59.
Rules for the Material and Qualification Procedures for Ships, Lloyd’s Register, 2014
Z.Y. Gao, T. Pan, Z. Wang, G.Q. Liu and H. Su, Hot Deformation Behavior of a Novel Ni-Cr-Mo-B Ultra-Heavy Plate Steel by Hot Compression Test, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2015, 22(9), p 818-826.
X.Y. Wang, T. Pan, H. Wang, H. Su, X.Y. Li and X.Z. Cao, Investigation of the Toughness of Low Carbon Tempered Martensite in the Surface of Ni-Cr-Mo-B Ultra-Heavy Plate Steel, Acta Metall. Sin., 2012, 48(4), p 401-406.
S.Q. Zhang, X.F. Hu, Y.B. Du, H.C. Jiang, H.Y. Pang and L.J. Rong, Cross-Section Effect of Ni-Cr-Mo-B Ultra-Heavy Steel Plate for Offshore Platform, Acta Metall. Sin., 2020, 56(9), p 1227-1238.
W.G. Huang, H.S. Fang and Y.K. Zheng, Strength and Strengthening Mechanism of C-Si-Mn-B Bainitic Steel, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2003, 15(1), p 38-41.
A.J. Kaijalainen, P.P. Suikkanen, T.J. Limnell, L.P. Karjalainen, J.I. Kömi and D.A. Porter, Effect of Austenite Grain Structure on the Strength and Toughness of Direct-Quenched Martensite, J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 577(1), p S642-S648.
B. Chhajed, K. Mishra, K. Singh and A. Singh, Effect of Prior Austenite Grain Size on the Tensile Properties and Fracture Toughness of Nano-Structured Bainite, Mater. Charact., 2022, 192, p 112214.
S. Morito, H. Saito, T. Ogawa, T. Furuhara and T. Maki, Effect of Austenite Grain Size on the Morphology and Crystallography of Lath Martensite in Low Carbon Steels, ISIJ Int., 2005, 45(1), p 91-94.
S. Morito, H. Tanaka, R. Konishi, T. Furuhara and T. Maki, The Morphology and Crystallography of Lath Martensite in Fe-C Alloys, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(6), p 1789-1799.
C.F. Wang, M.Q. Wang, J. Shi, W.J. Hui and H. Dong, Effect of Microstructure Refinement on the Strength and Toughness of Low Alloy Martensitic Steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2007, 23(5), p 659-664.
C.F. Wang, M.Q. Wang, J. Shi, W.J. Hui and H. Dong, Effect of Microstructure on the Toughness of Low Alloy Martensitic Steel, Scripta Mater., 2008, 58(6), p 492-495.
Z.M. Shi, K. Liu, M.Q. Wang, J. Shi, H. Dong, J. Pu, B. Chi, Y.S. Zhang and J. Li, Effect of Tensile Deformation of Austenite on the Morphology and Strength of Lath Martensite, Met. Mater. Int., 2012, 18(2), p 317-320.
Z.J. Luo, J.C. Shen, H. Su, Y.H. Ding, C.F. Yang and X. Zhu, Effect of Substructure on Toughness of Lath Martensite/Bainite Mixed Structure in Low-Carbon Steels, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2010, 17(11), p 40-48.
H.W. Luo, X.H. Wang, Z.B. Liu and Z.Y. Yang, Influence of Refined Hierarchical Martensitic Microstructures on Yield Strength and Impact Toughness of Ultra-High Strength Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 51, p 130-136.
S.L. Long, Y.L. Liang, Y. Jiang, Y. Liang, M. Yang and Y.L. Yi, Effect of Quenching Temperature on Martensite Multi-Level Microstructures and Properties of Strength and Toughness in 20CrNi2Mo Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 676(31), p 38-47.
T. Zhou, H. Yu and S.Y. Wang, Effect of Microstructural Types on Toughness and Microstructural Optimization of Ultra-Heavy Steel Plate: EBSD Analysis and Microscopic Fracture Mechanism, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 658(21), p 150-158.
T. Zhou, H. Yu, J.L. Hu and S.Y. Wang, Study of Microstructural Evolution and Strength-Toughness Mechanism of Heavy-Wall Induction Bend Pipe, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 615(6), p 436-446.
X.H. Li, Y.C. Liu, K.F. Gan, J. Dong and C.X. Liu, Acquiring a Low Yield Ratio Well Synchronized with Enhanced Strength of HSLA Pipeline Steels Through Adjusting Multiple-Phase Microstructures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 785(21), p 139350.
M.W. Tong, P.K.C. Venkatsurya, W.H. Zhou, R.D.K. Misra, B. Guo, K.G. Zhang and W. Fan, Structure-Mechanical Property Relationship in a High Strength Microalloyed Steel with Low Yield Ratio: The Effect of Tempering Temperature, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 609(15), p 209-216.
S. Morito, X. Huang, T. Furuhara, T. Maki and N. Hansen, The Morphology and Crystallography of Lath Martensite in Alloy Steels, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(19), p 5323-5331.
Y.L. Liang, S.L. Long, P.W. Xu, Y.M. Lu, Y. Jiang, Y. Liang and M. Yang, The Important Role of Martensite Laths to Fracture Toughness for the Ductile Fracture Controlled by the Strain in EA4T Axle Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 695(17), p 154-164.
R.W. Hertzberg, R.P. Vinci and J.L. Hertzberg, Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, John Wiley & Sons, USA, 2012.
S.M. Hasan, A. Mandal, S.B. Sign and D. Chakrabarti, Work Hardening Behaviour and Damage Mechanisms in Carbide-Free Bainitic Steel during Uni-Axial Tensile Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 751(28), p 142-153.
R. Song, D. Ponge and D. Raabe, Mechanical Properties of an Ultrafine Grained C-Mn Steel Processed by Warm Deformation and Annealing, Acta Mater., 2005, 50(53), p 4881-4892.
M. Umemoto, K. Tsuchiya, Z.G. Liu and S. Sugimoto, Tensile Stress-Strain Analysis of Single-Structure Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, 31(7), p 1785-1794.
D. Raabe, S. Sandlöbes, J. Millán, D. Ponge and P.P. Choi, Segregation Engineering Enables Nanoscale Martensite to Austenite Phase Transformation at Grain Boundaries: A Pathway to Ductile Martensite, Acta Mater., 2013, 61(16), p 6132-6152.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A20279), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M700875), and Subject innovation and talent introduction program in Colleges and universities (111 program)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Shi, Y., Hu, L. et al. Impact of Multi-Level Microstructures on the Strength and Yield Ratio of Extra-Thick Ultra-High-Strength Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 10344–10353 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-07854-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-07854-0