Abstract
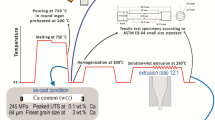
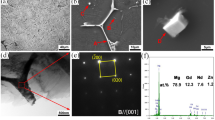
The present investigation highlights the creep deformation and rupture behavior of indigenously produced as-cast Mg-10 wt.%Sn-3 wt.%Al-1 wt.%Zn (TAZ1031) and Mg-10 wt.%Sn (T10) alloys. Conventional creep tests were conducted at 423 K (150 °C) in the stress range of 30-45 MPa and at 45 MPa in the temperature range of 423-453 K (150-180 °C) for both the alloys. The nature of creep curves was found to be identical for both the alloys with short primary and secondary creep regime, followed by extended tertiary creep region. The creep resistance of the TAZ1031 alloy was better than the T10 alloy. The former exhibited reduced minimum creep rate and enhanced creep rupture life under identical creep test conditions with respect to the latter. The change of minimum creep rate (έmin) followed a power-law relationship with a change in applied stress (σ) for both the alloys with a significant change in stress exponent (n) value. Activation energy for creep deformation of TAZ1031 alloy (~ 117 kJ/mol) was found to be higher than T10 alloy (~ 105 kJ/mol). Fine secondary Mg2Sn precipitates within the α-Mg matrix and primary Mg2Sn, Mg17Al12 and MgZn2 precipitates along the grain boundaries improved the creep properties of TAZ1031 alloy. On the contrary, the threshold stress required for creep deformation was found to be significantly low in TAZ1031 alloy due to the presence of Mg17Al12. Both creep damage analysis and dimpled fracture surfaces revealed necking dominated creep deformation for the alloys. SEM studies revealed the absence of creep cavities along grain/dendritic boundaries for the investigated alloys, which substantiated the formation of dimpled fracture surfaces during creep deformation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Liu, Y. Chen, Y. Tang, S. Wei, and G. Niu, The Microstructure, Tensile Properties, and Creep Behavior of As-Cast Mg-(1–10)% Sn Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2007, 440, p 122–126
S. Wei, Y. Chen, Y. Tang, H. Liu, S. Xiao, G. Niu, X. Zhang, and Y. Zhao, Compressive Creep Behavior of As-Cast and Aging-Treated Mg-5wt% Sn Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 492, p 20–23
C.L. Mendis, C.J. Bettles, M.A. Gibson, S. Gorsse, and C.R. Hutchinson, Refinement of Precipitate Distributions in an Age-Hardenable Mg-Sn Alloy Through Microalloying, Philos. Mag. Lett., 2006, 86, p 443–456
J.F. Nie, Precipitation and Hardening in Magnesium Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43, p 3891–3939
Y. Huang, H. Dieringa, K.U. Kainer, and N. Hort, Understanding Effects of Microstructural Inhomogeneity on Creep Response—New Approaches to Improve the Creep Resistance in Magnesium Alloys, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2014, 2, p 124–132
C.L. Mendis, C.J. Bettles, M.A. Gibson, and C.R. Hutchinson, An Enhanced Age Hardening Response in Mg-Sn Based Alloys Containing Zn, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 435, p 163–171
M.A. Gibson, X.Y. Fang, C.J. Bettles, and C.R. Hutchinson, The Effect of Precipitate State on the Creep Resistance of Mg-Sn Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2010, 63(8), p 899–902
F.R. Elsayed, T.T. Sasaki, C.L. Mendis, T. Ohkubo, and K. Hono, Compositional Optimization of Mg-Sn-Al Alloys for Higher Age Hardening Response, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 566, p 22–29
C. Praveen, J. Christopher, V. Ganesan, G.V. Prasad Reddy, G. Sasikala, and S.K. Albert, Constitutive Modelling of Transient and Steady State Creep Behaviour of Type 316LN Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mech. Mater., 2019, 137, p 103122
S.D. Yadav, T. Scherer, G.V. Prasad Reddy, K. Laha, G. Sasikala, S.K. Albert, and C. Poletti, Creep Modelling of P91 Steel Employing a Microstructural Based Hybrid Concept, Eng. Fract. Mech., 2018, 200, p 104–114
B. Xiao, X. Lianyong, L. Zhao, H. Jing, and Y. Han, Deformation-Mechanism-Based Creep Model and Damage Mechanism of G115 Steel Over a Wide Stress Range, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 743, p 280–293
P. Poddar, K.L. Sahoo, S. Mukherjee, and A.K. Ray, Creep Behaviour of Mg-8% Sn and Mg-8% Sn-3% Al-1% Si alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 545, p 103–110
F.H. Norton, The Creep of Steel at High Temperatures, McGraw-Hill, NewYork, 1929
R.W. Bailey, Creep of Steel Under Simple and Compound Stress, Engineering, 1930, 121, p 265
J.S. Lee, H.G. Armaki, K. Maruyama, T. Muraki, and H. Asahi, Causes of Breakdown of Creep Strength in 9Cr-1.8W-0.5Mo-VNb Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 428, p 270–275
W.-G. Kim, J.-Y. Park, I.M.W. Ekaputra, S.-J. Kim, M.-H. Kim, and Y.-W. Kim, Creep Deformation and Rupture Behavior of Alloy 617, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2015, 58, p 441–451
G. Nayyeri and R. Mahmudi, Enhanced Creep Properties of a Cast Mg-5Sn Alloy Subjected to Aging-Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 4613–4618
R. Lagneborg and B. Bergman, The Stress/Creep Rate Behaviour of Precipitation-Hardened Alloys, Met. Sci., 1976, 10, p 20–28
N.Q. Vo, C.H. Liebscher, M.J.S. Rawlings, M. Asta, and D.C. Dunand, Creep Properties and Microstructure of a Precipitation-Strengthened Ferritic Fe-Al-Ni-Cr alloy, Acta Mater., 2014, 71, p 89–99
B. Xiao, L. Xu, L. Zhao, H. Jing, Y. Han, and Y. Zhang, Creep Properties, Creep Deformation Behaviour, and Microstructural Evolution of 9Cr-3W-3Co-1CuVNbB Martensite Ferritic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 711, p 434–447
S.-H. Song, J. Wu, X.-J. Wei, D. Kumar, S.-J. Liu, and L.-Q. Weng, Creep Property Evaluation of a 2.25Cr-1Mo Low Alloy Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2010, 527, p 2398–2403
F.C. Monkman and N.J. Grant, An Empirical Relationship Between Rupture Life and Minimum Creep Rate in Creep-Rupture Tests, Proc. Am. Soc. Test. Mater., 1956, 56, p 593–620
F. Dobes and K. Milicka, The Relation Between Minimum Creep Rate and Time to Fracture, Met. Sci., 1976, 10, p 382–384
W.G. Kim, S.H. Kim, and W.S. Ryu, Evaluation of Monkman–Grant Parameters for type 316LN and Modified 9Cr-1Mo Stainless Steels, KSME Int. J., 2002, 16, p 1420–1427
B.K. Choudhary, Tertiary Creep Behaviour of 9Cr-1Mo Ferritic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 585, p 1–9
B.K. Choudhary, C. Phaniraj, and R. Baldev, Interesting Relationships for Creep Deformation and Damage and Their Applicability for 9Cr-1Mo Ferritic Steel, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2010, 63, p 675–680
B.K. Choudhary, S. Saroja, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, and S.L. Mannan, Creep-Rupture Behaviour of Forged Thick Section 9Cr-1Mo Ferritic Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 1999, 30, p 2825–2834
C. Phaniraj, B.K. Choudhary, K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, and R. Baldev, Relationship Between Time to Reach Monkman–Grant Ductility and Rupture Life, Scr. Mater., 2003, 48, p 1313–1318
T. Shrestha, M. Basirat, I. Charit, G.P. Potirniche, and K.K. Rink, Creep Rupture Behavior of Grade 91 Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 565, p 382–391
B.F. Dyson and T.B. Gibbons, Tertiary Creep in Nickel-Base Superalloys: Analysis of Experimental Data and Theoretical Synthesis, Acta Met., 1987, 35, p 2355–2369
Acknowledgment
Authors are grateful to Dr. Mainak Ghosh, Principal Scientist, Materials Engineering Division, CSIR-National Metallurgical Laboratory, Jamshedpur, for his valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagui, S., Murugesan, A.P. & Poddar, P. Creep Behavior of As-Cast Mg-10 wt.%Sn and Mg-10 wt.%Sn-3 wt.%Al-1 wt.%Zn Alloys: A Comparative Study. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 7616–7628 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04513-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04513-1