Abstract
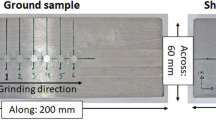
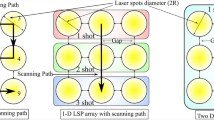
The paper describes an experimental study aimed at suppressing stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of machined 304L stainless steel specimens through laser shock peening. The study also evaluates a new approach of oblique laser shock peening to suppress stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of internal surface of type 304L stainless steel tube. The results of the study, performed with an indigenously developed 2.5 J/7 ns Nd:YAG laser, demonstrated that laser shock peening effectively suppresses chloride stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of machined surface of type 304L stainless steel. In the investigated range of incident laser power density (3.2-6.4 GW/cm2), machined specimens peened with power density of 4.5 and 6.4 GW/cm2 displayed lower stress corrosion cracking susceptibility considerably than those treated with 3.2 and 3.6 GW/cm2 in boiling magnesium chloride test. Oblique laser shock peening, performed on machined internal surface of a type 304L stainless steel tube (OD = 111 mm; ID = 101 mm), was successful in introducing residual compressive surface stresses which brought about significant suppression of its stress corrosion cracking susceptibility. The technique of oblique laser shock peening, in spite of its inherent limitations on the length of peened region being limited by tube internal diameter and the need for access from both the sides, presents a simplified approach for peening internal surface of small tubular components.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Davis, Ed., Stainless Steels, ASM Specialty Handbook, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1999, p 169–173
Z. Feng, X. Cheng, C. Dong, L. Xu, and X. Li, Passivity of 316L Stainless Steel in Borate Buffer Solution Studied by Mott-Schottky Analysis, Atomic Absorption Spectrometry and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(11), p 3646–3653
X. Cheng, Z. Feng, C. Li, C. Dong, and X. Li, Investigation of Oxide Film Formation on 316L Stainless Steel in High-Temperature Aqueous Environments, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56(17), p 5860–5865
H.S. Khatak and B. Raj, Ed., Corrosion of Austenitic Stainless Steels: Mechanism, Mitigation and Monitoring, Woodhead Publishing, Cambirdige, 2002, p 74–139
D. Féron and J.-M. Olive, Ed., Corrosion Issues in Light Water Reactors—Stress Corrosion Cracking, 1st ed., Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 2007
Stress Corrosion Cracking in Light Water Reactors: Good Practices and Lessons Learned, IAEA Nuclear Energy Series, NP-T-3.13, 2011, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna.
M. Nakahara, Preventing Stress Corrosion Cracking of Austenitic Stainless Steels in Chemical Plants, NiDi Technical Series 10066, Nickel Development Institute, http://www.nickelinstitute.org/~/Media/Files/TechnicalLiterature/PreventingStress_CorrosionCrackingofAusteniticStainlessSteelsinChemicalPlants_10066_.pdf, Accessed on 20.01.2014.
J. Esmacher, Stress Corrosion Cracking in Boilers and Cooling Water Systems, Stress Corrosion Cracking—Theory and Practice, V.S. Raja and T. Shoji, Ed., Woodhead Publishing, Philadelphia, 2011, p 537–607
J. Isselin, A. Kai, K. Sakaguchi, and T. Shoji, Assessment of the Effects of Cold Work on Crack Initiation in a Light Water Environment Using the Small-Punch Test, Metall. Mater. Trans., 2008, 39A, p 1099–1108
P.L. Andresen and M.M. Morra, IGSCC of Non-sensitized Stainless Steels in High Temperature Water, J. Nucl. Mater., 2008, 383, p 97–111
R. Ishibashi and H. Anzai, CD Proceeding of Environment Assisted Cracking, December 17-19, Sendai, 2007
Y. Sueishi, A. Kohyama, H. Kinoshita, M. Narui, and K. Fukumoto, Microstructure and Nano-hardness Analyses of Stress Corrosion Cracking Utilizing 316L Core Shroud of BWR Power Reactors, Fusion Eng. Des., 2006, 81, p 1099–1103
M. Koshiishi, J. Kuniya, and Z. Sagawa, CD Proceeding of Environment Assisted Cracking, December 17–19, Sendai, 2007.
S. Ghosh, V.P.S. Rana, V. Kain, V. Mittal, and S.K. Baveja, Role of Residual Stresses Induced by Industrial Fabrication on Stress Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 3823–3831
K.R. Trethewey, Some Observations on the Current Status in the Understanding of Stress-Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels, Mater. Des., 2008, 29, p 501–507
Effect of Surface Working on the Microstructure and Electrochemical Behaviour of Stainless Steel, http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/11620/11/11_chapter%206.pdf, Accessed on 25.11.2014.
A. Turnbull, K. Mingard, J.D. Lord, B. Roebuck, D.R. Tice, K.J. Mottershead, N.D. Fairweather, and A.K. Bradbury, Sensitivity of Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steel to Surface Machining and Grinding Procedure, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, p 3398–3415
S. Suzuki, K. Takamori, K. Kumagai, A. Sakashita, N. Yamashita, C. Shitara, and Y. Okamura, Stress Corrosion Cracking in Low Carbon Stainless Steel Components in BWRs, E-J. Adv. Maint., 2009, 1, p 1–29
S. Ghosh and V. Kain, Microstructural Changes in AISI, 304 Stainless Steel Due to Surface Machining: Effect on Its Susceptibility to Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking, J. Nucl. Mater., 2010, 402, p 62–67
S. Ghosh and V. Kain, Effect of Surface Machining and Cold Working on the Ambient Temperature Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of AISI, 304L Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 679–683
S.G. Acharyya, A. Khandelwal, V. Kain, and I. Samajdar, Surface Working of 304L Stainless Steel: Impact on Microstructure, Electrochemical Behaviour and SCC Resistance, Mater. Charact., 2012, 72, p 68–76
T.M. Yue, C.F. Dong, L.J. Yan, and H.C. Man, The Effect of Laser Surface Treatment on Stress Corrosion Cracking Behaviour of 7075 Aluminium Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58, p 630–635
T.M. Yue, L.J. Yan, and C.P. Chan, Stress Corrosion Cracking Behavior of Nd:YAG Laser-Treated Aluminum Alloy 7075, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 252, p 5026–5034
Jeong-Hun Suh, Jin-Koog Shin, Suk-Joong L. Kang, Yun-Soo Lim, Il-Hiun Kuk, and Joung-Soo Kim, Investigation of IGSCC Behavior of Sensitized and Laser-Surface-Melted Alloy 600, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 254, p 67–75
R.K. Gupta, R. Sundar, B.S. Kumar, P. Ganesh, R. Kaul, K. Ranganathan, K.S. Bindra, V. Kain, S.M. Oak, and L.M. Kukreja, A Hybrid Laser Surface Treatment Scheme for Rejuvenation of Stress Corrosion Cracking Damaged Type 304L Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perf., 2015, 24, p 2569–2576
R. Fabbro, P. Peyre, L. Berthe, and X. Scherpereel, Physics and Applications of Laser Shock Processing, J. Laser. Appl., 1998, 10, p 265–279
L. Berthe, P. Peyre, X. Scherpereel, R. Fabbro, and M. Jeandin, Laser Shock Surface Processing of Materials, Laser in Surface Engineering, Surface Engineering Series, Vol 1, N.B. Dahotre, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1998, p 465–504
Y. Zhang, J. You, J. Lu, C. Cui, Y. Jiang, and X. Ren, Effects of Laser Shock Processing on Stress Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2010, 204, p 3947–3953
P. Peyre, X. Scherpereel, L. Berthe, C. Carboni, R. Fabbro, G. Béranger, and C. Lemaitre, Surface Modifications Induced in 316L Steel by Laser Peening and Shot-Peening. Influence on Pitting Corrosion Resistance, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 280, p 294–302
J.Z. Lu, K.Y. Luo, D.K. Yang, X.N. Cheng, J.L. Hu, F.Z. Dai, H. Qi, L. Zhang, J.S. Zhong, Q.W. Wang, and Y.K. Zhang, Effects of Laser Peening on Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) of ANSI, 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2012, 60, p 145–152
Y. Sano, M. Obata, T. Kubo, N. Mukai, M. Yoda, K. Masaki, and Y. Ochi, Retardation of Crack Initiation and Growth in Austenitic Stainless Steels by Laser Peening Without Protective Coating, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 417, p 334–340
M. Yoda and B. Newton, Underwater Laser Peeing, Welding and Repair Technology for Power Plants, Eighth Int. EPRI Conf., June 18-20, Fort Myers, Florida, 2008
A.D. Evans, A. King, T. Pirling, G. Bruno, and P. J. Withers, The Effect of Incidence Effect of Incidence Angle on Residual Stress State in Laser-Peened Ti-6AI-4V Plate, Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on Shot Peening: ICSP9, Sept. 6-9, 2005, Paris, 454-459, Document No. 2005124.
P. Ganesh, R. Sunder, H. Kumar, R. Kaul, K. Ranagnathan, P. Hedaoo, P. Tiwari, L.M. Kukreja, S.M. Oak, S. Dasari, and G. Raghavendra, Studies on Laser Peening of Spring Steel for Automotive Applications, Opt. Laser. Eng., 2012, 50, p 678
R. Sundar, R.H. Kumar, R. Kaul, K. Ranganathan, P. Tiwari, L.M. Kukreja, and S.M. Oak, Studies on Laser Peening Using Different Sacrificial Coatings, Surf. Eng., 2012, 28(8), p 564–568
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 2nd ed., Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1978
I.C. Noyan and J.B. Cohen, Residual Stress, Springer, New York, 1987
N.S. Rossini, M. Dassisti, K.Y. Benyounis, and A.G. Olabi, Methods of Measuring Residual Stresses in Components, Mater. Des., 2012, 35, p 572–588
ASTM G36 (94), Standard Practice for Evaluating Stress-Corrosion-Cracking Resistance of Metals and Alloys in Magnesium Chloride Solution, ASTM International, Pennsylvania, 2013.
Y. Fan, J. Zhou, S. Huang, J. Fan, B. Gao, and W. Zhu, Residual Stress Induced by Multi-micro Laser Shock Peening Under Overlapping Process, China Opt. Lett., 2012, 10(1), p S11408
P. Peyre, R. Fabbro, P. Merrien, and H.P. Lieurade, Laser Chock Processing of Aluminum Alloys: Application to High Cycle Fatigue Behavior, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 210, p 102–113
C.S. Montross, T. Wei, L. Ye, G. Clark, and Yiu-Wing Mai, Laser Shock Processing and Its Effects on Microstructure and Properties of Metals and Alloys: A Review, Int. J. Fatigue, 2002, 24, p 1021–1036
J.E. Scheel, D.J. Hornbach, and N. Jayaraman, Preventing Stress Corrosion Cracking of Nuclear Weldments via Low Plasticity Burnishing, http://www.lambdatechs.com/documents/278.pdf, Accessed on 17.06.2015.
D.Y. Jang, T.R. Watkins, K.J. Kozaczek, C.R. Hubbard, and O.B. Cavin, Surface Residual Stresses in Machined Austenitic Stainless Steel, Wear, 1996, 194, p 168–173
R. Fabbro, J. Fournier P. Ballard, D. Devaux, and J. Virmont, Physical Study of Laser-Produced Plasma in Confined Geometry, J. Appl. Phys., 1990, 68(2), p 775-784.
A.W. Warren, Y.B. Guo, and S.C. Chen, Massive Parallel Laser Shock Peening: Simulation Analysis and Validation, Int. J. Fatigue, 2008, 30, p 188–197
W. Zhang, Y.L. Yao, and I.C. Noyan, Microscale Laser Shock Peening of Thin Films, Part I: Experiment, Modelling and Simulation, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2004, 126, p 10–17
P. Peyre, R. Fabbro, L. Bethe, X. Scherpereel, and E. Bartnicki, Laser Shock Processing of Materials and Related Phenomenon, Proc. Int. Conf. High-Power Laser Ablation, SPIE 3343, Ed. Claude R. Phipps, 1998, Santa Fe, NM, Paper ID 183.
P.S. Prevéy, The Effect of Cold Work on the Thermal Stability of Residual Compression in Surface Enhanced IN718, Proc. 20th ASM Materials Solutions Conf. & Expo., St. Louis, Missouri, October 10-12, 2000.
Acknowledgment
Technical assistance of Mr. Ram Nihal Ram in metallographic specimen preparation is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundar, R., Ganesh, P., Kumar, B.S. et al. Mitigation of Stress Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of Machined 304L Stainless Steel Through Laser Peening. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 3710–3724 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2220-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2220-3