Abstract
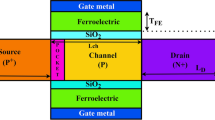
The present study proposes an approach to enhance the DC and RF performance parameters of a double-gate tunnel field-effect transistor (DGTFET). The approach integrates an extended source with stacked drain layers of varying doping concentrations. This integration results in a drain-engineered extended source double-gate tunnel FET (DE-ES-DGTFET), demonstrating low ambipolarity and abrupt switching. The source and drain engineering enable the device to increase the ON-current while simultaneously reducing ambipolarity due to the large tunneling area with different drain doping concentrations. The optimization of the device's performance parameters was carried out by varying the doping concentration of the stacked drain, source length, and thickness of the drain. The proposed device achieved significant improvements compared to conventional DGTFETs, including a two-decade reduction in ambipolar current, an order of improvement in the ON-current (ION) of ~ 10−5 A/µm, two orders of reduction in ambipolarity (IAmb) 5.91 × 10−17 A/µm, two orders of enhancement in ratio ION/IOFF of − 1013, a subthreshold swing (SS) of 23.3 mV/dec, and nearly a two-fold increase in cut-off frequency (fT), and a transit time (\(\tau\)) ~ 80 ps have been accomplished.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.J. Frank, R.H. Dennard, E. Nowak, P.M. Solomon, Y. Taur, and S.P. Wong, Device scaling limits of Si MOSFETs and their application dependencies. Proc. IEEE 89, 259 (2001).
C.W. Pearce and D.S. Yaney, Short-channel effects in MOSFET’s. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 6, 326–328 (1985).
K.K. Young, Short-channel effect in fully depleted SOI MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36, 399 (1989).
Y. Taur, D. Buchanan, W. Chen, D. Frank, K. Ismail, S.H. Lo, G. Sai-Halasz, R. Viswanathan, H.J. Wann, S. Wind, and H.S. Wong, CMOS scaling into the nanometer regime. Proc. IEEE 85, 486 (1997).
S.A. Loan, S. Qureshi, and S.S.K. Iyer, A novel partial-ground plane based MOSFET on selective buried oxide: a 2-D simulation study. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 57, 671 (2010).
E. Goel, S. Kumar, B. Singh, K. Singh, and S. Jit, Two-dimensional model for the subthreshold current and subthreshold swing of graded-channel dual-material double-gate (GCDMDG) MOSFETs. Superlattices Microstruct. 106, 147 (2017).
K.P. Pradhan, S.K. Mohapatra, P.K. Sahu, and D.K. Behera, Impact of high-k gate dielectric on analog and RF performance of nanoscale DG-MOSFET. Microelectron. J. 45, 144 (2014).
J. Appenzeller, Y.M. Lin, J. Knoch, and P. Avouris, Band-to-band tunneling in carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93(196), 805–811 (2004).
K. Boucart and A.M. Ionescu, Double-gate tunnel FET with high-gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54, 1725 (2007).
A.M. Ionescu and H. Riel, Tunnel field-effect transistors as energy-efficient electronic switches. Nature 479, 329 (2011).
S. Saurabh and M.J. Kumar, Fundamentals Tunnel Field-Effect Transistors (Boca Raton, FL USA: CRC Press, 2016).
Y. Zhu and M.K. Hudait, Low-power tunnel field effect transistors using mixed As and Sb based heterostructures. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2, 637 (2013).
F. Horst, A. Parokhnejad, B. Iñíguez, and A. Kloes, An area equivalent WKB approach to calculate the B2B tunneling probability for a numerical robust implementation in TFET compact models. 2018 25th International Conference "Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and System" (MIXDES) (2018), p. 45
R. Pandey and S. Mookerjea, Opportunities and challenges of tunnel FETs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 63, 2128 (2016).
U.E. Avci, D.H. Morris, and I.A. Young, Tunnel field-effect transistors: prospects and challenges. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 3, 88 (2015).
S.H. Kim, H. Kam, C. Hu, and T.-J.K. Liu, Germanium-source tunnel field-effect transistors with record high Ion/Ioff. Symposium on VLSI Technology (2009), p. 178
S. Chen, H. Liu, S. Wang, W. Li, X. Wang, and L. Zhao, Analog/RF performance of t-shape gate dual-source tunnel field-effect transistor. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13, 321 (2018).
M.A. Tajally and M.A. Karami, TFET performance optimization using gate work function engineering. Indian J. Phys. 93, 1123 (2019).
W.Y. Choi and W. Lee, Hetero-gate-dielectric tunneling field effect transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 57, 2317 (2010).
T. Joshi, Y. Singh, and B. Singh, Extended-source double-gate tunnel FET with improved DC and analog/RF performance. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 67, 1873 (2020).
A. Kaur and G. Saini, Design and analysis of a novel asymmetric source dual-material DG-TFET with germanium pocket. Silicon 15, 2889 (2023).
P. Pandey, R. Vishnoi, and M.J. Kumar, A full range dual material gate tunnel field effect transistor drain current model considering both source and drain depletion region band-to-band tunneling. J. Comput. Electron. 14, 280 (2015).
S. Singh and B. Raj, Design and analysis of a heterojunction vertical t-shaped tunnel field effect transistor. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 6253 (2019).
Ashita, S.A. Loan, and M. Rafat, A high-performance inverted-c tunnel junction FET with source–channel overlap pockets. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65, 763 (2018).
S. Garg and S. Saurabh, Suppression of ambipolar current in tunnel FETs using drain-pocket: proposal and analysis. Superlattices Microstruct. 113, 261 (2018).
M.R.U. Shaikh, and S.A. Loan, Drain-engineered TFET with fully suppressed ambipolarity for high-frequency application. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 66, 1628 (2019).
D.B. Abdi and M.J. Kumar, controlling ambipolar current in tunneling FETs using overlapping gate-on-drain. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2, 187 (2014).
S. Sahay and M.J. Kumar, Controlling the drain side tunnelling width to reduce ambipolar current in tunnel FETs using heterodielectric box. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 62, 3882 (2015).
V. Vijayvargiya and S. Kumar Vishvakarma, Effect of drain doping profile on double-gate tunnel field-effect transistor and its influence on device RF performance. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 13, 974 (2014).
J. Li, Q. Xie, A. Huang, and Z. Wang, Effects of drain doping profile and gate structure on an ambipolar current of TFET. IEEE 3rd International Conference Electronics Technology (2020), p. 20
S. Ashish, D. Sharma, N.B.Y. Kumar, and M.H. Vasantha, Performance enhancement of novel InAs/Si hetero double-gate tunnel FET using Gaussian doping. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 63, 288295 (2016).
N. Bagga, N. Chauhan, S. Banchhor, D. Gupta, and S. Dasgupta, Demonstration of a novel tunnel FET with channel sandwiched by drain. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 35, 015008 (2020).
S. Sahoo, S. Dash, S. Ranjan Routray, and G.P. Mishra, Impact of drain doping engineering on ambipolar and high-frequency performance of ZHP line-TFET. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 35, 065003 (2020).
Synopsys Inc., Sentauras’s Performance Device User Guide (Mountain View: Synopsys Inc, 2020).
E.P. Gusev, C. Cabral, M. Copel, C. D’Emic, and M. Gribelyuk, Ultrathin HfO2 films grown on silicon by atomic layer deposition for advanced gate dielectrics applications. Microelectron. Eng. 69, 145 (2003).
D.W. McNeill, S. Bhattacharya, H. Wadsworth, F.H. Ruddell, S.J.N. Mitchell, B.M. Armstrong, and H.S. Gamble, Atomic layer deposition of hafnium oxide dielectrics on silicon and germanium substrates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19, 119–123 (2008).
P.C. Jamison, T. Tsunoda, T.A. Vo, J. Li, H. Jagannathan, S.R. Shinde, V.K. Paruchuri, and D. Gall, SiO2 free HfO2 gate dielectrics by physical vapor deposition. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 62, 2878 (2015).
K. Kumar, A. Kumar, V. Kumar, A. Jain, and S.C. Sharma, Ambipolarity suppression of band gap and gate dielectric engineered novel Si0.2Ge0.8/GaAs JLTFET using gate overlap technique. Silicon 15, 7837 (2023).
A. Acharya, S. Dasgupta, and A. Bulusu, A novel VDSAT extraction method for tunnel FETs and its implication on analog design. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 64, 629 (2016).
R. Narang, M. Saxena, R.S. Gupta, and M. Gupta, Impact of temperature variations on the device and circuit performance of tunnel FET: a simulation study. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 12, 951 (2013).
W. Cao, C.J. Yao, G.F. Jiao, D. Huang, H.Y. Yu, and M.F. Li, Improvement in reliability of tunneling field-effect transistor with p-n-i-n structure. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 2122 (2011).
S.C. Kang, D.W. Lim, S.J. Kang, S.K. Lee, C.H. Choi, D.S. Lee, and B.H. Lee, Hot-carrier degradation estimation of a silicon-on insulator tunneling FET using ambipolar characteristics. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 40, 1716 (2019).
T. Chawla, M. Khosla, and B. Raj, Extended gate to source overlap heterojunction vertical TFET: design, analysis, and optimization with process parameter variations. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 145, 106643 (2022).
G. Singh, S.I. Amin, S. Anand, and R.K. Sarin, Design of Si0.5Ge0.5 based tunnel field effect transistor and its performance evaluation. Superlattices Microstruct. 92, 143 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, A., Saini, G. Drain Source-Engineered Double-Gate Tunnel FET for Improved Performance. J. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11109-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11109-6