Abstract
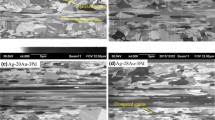
Ion migration and corrosion behavior in Ag-4Pd alloy wires with fine and coarse grains in the outer regions were evaluated with water drop tests. The results from the in situ observations and measurements of Ag ion migration in both Ag-4Pd bonding wires indicated that the fine-grained wire had much shorter times of dendrite contact and short circuit than those of coarse-grained wire for various wire spaces. It was obvious that grain refinement in Ag-4Pd alloy wires accelerated the ion migration of Ag-4Pd alloy wires. Electrochemical polarization tests confirmed that the passive film on fine-grained Ag-4Pd wire was easily broken down, leading to a higher Ag dissolution tendency than that of coarse-grained wire. Although an annealing twin-rich Ag-4Pd alloy wire was shown to enhance the thermal stability of the grain structure and mechanical properties, the large number of twins had no influence on the formation of Ag dendrites on the cathode and Ag2O oxide on the anode of the coarse-grained Ag-4Pd wire couple during ion migration.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Chung, Y.S. Choi, J.G. Kim, Y.M. Kim, and J.C. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 366, 282 (2004).
R.J. Hellmig, M. Janecek, B. Hadzima, O.V. Gendelman, M. Shapiro, X. Molodova, A. Springer, and Y. Estrin, Mater. Trans. 49, 31 (2008).
M. Niikura, M. Fujioka, Y. Adachi, A. Matsukura, T. Yokota, Y. Shirota, and Y. Hagiwara, J., Mater. Process. Technol. 117, 341 (2001).
K.D. Ralston, and N. Birbilis, Corrosion 66, 075005–075013 (2010).
W.R. Osorio, C.M. Freire, and A. Garcia, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 402, 22 (2005).
R. Ambat, N.N. Aung, and W. Zhou, Corros. Sci. 42, 1433 (2000).
S. Tao, and D.Y. Li, Nanotechnology 17, 65 (2006).
G. Ben Hamu, D. Eliezer, and L. Wagner, J. Alloys Compd. 468, 222 (2009).
G. Ben Hamu, D. Eliezer, and C.E. Cross, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 452, 210 (2007).
S. J. Krumbein, IEEE Trans. Components, Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 11, 5 (1988).
J. Kim, and S.D. Park, Eng. Fail. Anal. 28, 252 (2013).
P. Bojta, P. Nemeth, and G. Harsanyi, Microelectron. Reliabili. Microelectron. Reliabili. 42, 1213 (2002).
M. Chen, X. Shan, T. Geske, J. Li, and Z. Yu, ACS Nano 11, 6312 (2017).
C.H. Tsai, C.H. Chuang, H.H. Tsai, J.D. Lee, Dennis Chang, H.J. Lin, and T.H. Chuang, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packaging Manuf. Technol. 6, 298 (2016).
T.H. Chuang, C.C. Chang, C.H. Chuang, J.D. Lee, and H.H. Tsai, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packaging Manuf. Technol. 3, 3 (2013).
T.H. Chuang, H.C. Wang, C.H. Chuang, H.J. Lin, J.D. Lee, and T.H. Chuang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44, 5106 (2013).
T.H. Chuang, H.J. Lin, C.H. Chuang, Y.Y. Shiue, F.S. Shieu, Y.L. Huang, P.C. Hsu, J.D. Lee, and H.H. Tsai, J. Alloys Compd. 615, 891 (2014).
C.H. Chuang, Y.C. Lin, Y.Z. He, C.H. Tsai, J.D. Lee, S.C. Wang, and H.H. Tsai, Mater. Sci. Forum, Mater. Sci. Forum 863, 95 (2016).
Y.C. Lin, C.H. Chen, Y.Z. He, S.C. Chen, and T.H. Chuang, J. Electronic Mater. 47, 3634 (2018).
C.H. Chen, Y.C. Lin, Y.T. Shih, S.C. Chen, C.H. Tsai, S.C. Wang, and T.H. Chuang, Evaluation of corrosion resistance of Ag-alloy bonding wires for electronic packaging IEEE Trans. Compon. Packaging Manuf. Technol. 8, 146 (2018).
Kim. Vu, Silver migration–The mechanism and effects on thick-film conductors. (CiteSeerX, 2003), http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.516.6359, Accessed 26 June 2021.
ASTM F1996-01, Standard test method for silver migration for membrane switch circuitry, 1996.
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by the industrial and academic cooperation program of Wire Technology Co., LTD. and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under Grant No. MOST 108-2622-E002-009-CC2, and by the Hsinchu Science Park R & D program of Ag Materials Technology Co., LTD. and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under Grant No. 109A18A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YC., Lee, PI., Wu, PC. et al. Effects of Grain Size on the Ag Dissolution and Ion Migration of Ag-4Pd Alloy Wires. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 5955–5964 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09119-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09119-9