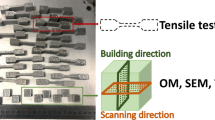
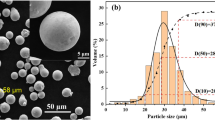
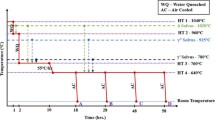
Abstract
Inconel718 (IN718) superalloy is one of the most widely employed high-temperature materials. How to improve its working temperature limit is a challenging but rewarding task. In this study, we have proved that by simply mechanical blending pre-alloyed IN718 powder with elemental Al powder, one can successfully add extra Al to the IN718 alloy. The Al-added IN718 alloys developed by this study show homogenous distribution of Al in the as-printed microstructure produced by selective laser melting (SLM), and only a slight loss of the Al amount is detected due to SLM in situ alloying. Excellent relative density of > 99.5 pct has been achieved, and after the standard heat treatment, the IN718 + 0.5Al alloy shows good mechanical properties, achieving a fracture strength of ~ 1400 MPa and elongation of ~ 12 pct. Introducing an extra amount of Al into the IN718 alloy has also improved thermal stability, in which testing is conducted at 680 °C and held for 100 hours. Meanwhile, it is noted that by a new heat treatment approach, the Al-doped IN718 alloy achieves the best fracture strength at ~ 1600 MPa and elongation at ~ 10 pct. The implications of the study have been addressed.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. E. A. Loria: JOM, 1988, vol. 40, pp. 36-41.
2. R. F. Decker: JOM, 2006, vol. 58, pp. 32–36.
3. C.T. Sims, N.S. Stoloff, and W.C. Hagel: Superalloys II. Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1987, pp. 97-131.
4. R.C. Reed: The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications. Cambridge University Press, New York, 2008, pp. 33-99.
5. M. Sundararaman, P. Mukhopadhyay, and S. Banerjee: Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19, pp. 453-65.
J.P. Collier, A.O. Selius, and J.K. Tien: Superalloys,1988, pp. 43–52.
7. R. Martin and D. Evans: JOM, 2000, vol. 52, pp. 24-8.
8. R. Cozar and A. Pineau: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 47-59.
9. J.P. Collier, H.W. Song, J.K. Tien, and J.C. Phillips: Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19, pp. 1657–66.
10. S.H. Fu, J.X. Dong, M.C. Zhang, and X.S. Xie: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, vol. 499, pp. 215-20.
W. D. Cao and R. Kennedy: Superalloys, 2004, 2004, pp. 91-99.
12. I. Gibson, D.W. Rosen, and B. Stucker: Additive Manufacturing Technologies – Rapid Prototyping to Direct Digital Manufacturing. Springer, New York, 2010, pp. 32–55.
13. C.Y. Yap, C.K. Chua, Z.L. Dong, Z.H. Liu, D.Q. Zhang, L.E. Loh, and S.L. Sing: Appl. Phys. Rev., 2015, vol. 2, pp. 41-101.
14. K.N. Amato, S.M. Gaytan, L.E. Murr, E. Martinez, P.W. Shindo, J. Hernandez, S. Collins, and F. Medina: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 2229-39.
15. Q. Jia and D. Gu: J. Alloy Comp., 2014, vol. 585, pp. 713-21.
X. Wang, R.M. Ward, M.H. Jacobs, and M.D. Barratt: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 2981-89.
17. I. Gibson, D. Rosen, and B. Stucker: Additive Manufacturing Technologies.Springer, New York, 2010, pp 32–55.
18. B. Zhang, N.E. Fenineche, H. Liao, and C. Coddet: J. Magn. Mater., 2013, vol. 336, pp. 49-54.
19. B. Zhang, N.E. Fenineche, H. Liao, and C. Coddet: J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, vol. 29, pp. 757-60.
20. J.P. Kruth, L. Froyen, J. Van Vaerenbergh, P. Mercelis, M. Rombouts, and B. Lauwers: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, vol. 149, pp. 616-22.
21. Q. Jia and D. Gu: J. Mater. Res., 2014, vol. 29, pp. 1960-9.
22. X. Yao, S.K. Moon, B.Y. Lee and G. Bi: Int. J. Precision Eng. Manufact., 2017, vol. 18, pp. 1693-1701.
23. T. Trosch, J. Strößner, R. Völkl, and U. Glatzel: Mater. Lett., 2016, vol. 164, pp. 428-31.
24. M. Xia, D. Gu, G. Yu, D. Dai, H. Chen, and Q. Shi: Int. J. Mach. Tool Manufact., 2017, vol. 116, pp. 96-106.
M. J. Sohrabi, H. Mirzadeh, and M. Rafiei: Vacuum, 2018, vol. 154, pp. 235-43.
26. Y. Zhang, Z. Li, P. Nie, and Y. Wu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 708-16.
27. M.D. Sangid, T.A. Book, D. Naragani, J. Rotella, P. Ravi, A. Finch, P. Kenesei, J.S. Park, H. Sharma, J. Almer, and X. Xiao, Add. Manufact., 2018, vol. 22, pp. 479-96.
28. W.M. Tucho, P. Cuvillier, A.S. Kverneland, and V. Hansen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, vol. 689, pp. 220-32.
29. S.A. Khairallah, A.T. Anderson, A. Rubenchik, and W.E. King, Acta Mater., 2016, vol. 108, pp. 36-45.
30. E. Chlebus, K. Gruber, B. Kuźnicka, J. Kurzac, and T. Kurzynowski: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, vol. 639, pp. 647-55.
31. S. Raghavan, B. Zhang, P. Wang, C.N. Sun, M.L. Sharon, T. Li, and J. Wei: Mater. Manufact. Process., 2017, vol. 32, pp. 1588-95.
32. W.M. Tucho, P. Cuvillier, A.S. Kverneland, and V. Hansen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, vol. 689, pp. 220-32.
33. G.H. Cao, T.Y. Sun, C.H. Wang, X. Li, M. Liu, Z.X. Zhang, P.F. Hu, A.M. Russell, R. Schneider, D. Gerthsen, Z.J. Zhou, C.P. Li, and G.F. Chen: Mater. Character., 2018, vol. 136, pp. 398-406.
34. Y. H. Zhou, Z. H. Zhang, Y. P. Wang, G. Liu, S. Y. Zhou, Y. L. Li, J. Shen, and M. Yan: Add. Manufact., 2019, vol. 25, pp. 204-17.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission [ZDSYS201703031748354 and JCYJ20170817110358927] and the National Science Foundation of Guangdong Province [2016A030313756]. Dr M. Yan appreciates the support of the Humboldt Research Fellowship for Experienced Researchers. This work was also supported by the Pico Center at SUSTech with support from the Presidential fund and Development and Reform Commission of Shenzhen Municipality.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted January 8, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z.H., Zhou, Y.H., Zhou, S.Y. et al. Mechanically Blended Al: Simple but Effective Approach to Improving Mechanical Property and Thermal Stability of Selective Laser-Melted Inconel 718. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 3922–3936 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05299-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05299-6