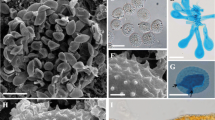
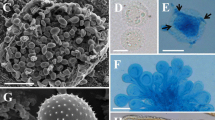
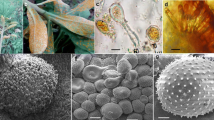
Abstract
Through the morphological and molecular examinations of Melampsora species on willows, we clarified the taxonomic identity of the rust specimens on Salix bakko, S. hultenii and S. leucopithecia from Japan and described the following rust fungus as a new species, Melampsora salicis-bakko. This rust fungus resembled M. caprearum in morphology of teliospores, but it differed from M. caprearum mainly in the density of spines on the urediniospores. Molecular phylogenetic analyses using the rDNA ITS region (complete ITS1, 5.8S rRNA gene and ITS2) revealed that M. salicis-bakko was monophyletic, and that this rust fungus was distinct from other Melampsora species, including M. caprearum.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azbukina ZM (1974) Rust fungi of the Soviet Far East (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow, pp 120–140
Bagyanarayana G (2005) The species of Melampsora on Salix (Salicaceae). In: Pei MH, McCracken AR (eds) Rust diseases of willow and poplar. CABI, Wallingford, pp 20–50
Braun U (1982) Die Rostpilze (Uredinales) der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik (in German). Feddes Repert Beih 93:213–334
Bubner B, Wunder S, Zaspel I, Zander M, Gloger J, Fehrenz S, Ulrichs C (2014) Melampsora rust species on biomass willows in central and north-eastern Germany. Fungal Biol 118:910–923. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2014.08.002
Chatasiri S, Ono Y (2008) Phylogeny and taxonomy of the Asian grapevine leaf rust fungus, Phakopsora euvitis, and its allies (Uredinales). Mycoscience 49:66–74. doi:10.1007/s10267-007-0390-4
Damadi SM,Pei MH,Smith JA, AbbasiM (2011) A new species ofMelampsorarust onSalix elbursensisfrom Iran. For Path 41:392–397
Farr DF, Rossman AY (2015) Fungal databases, systematic mycology and microbiology laboratory, ARS, USDA. Retrieved 24 Nov 2015, from http://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/
Feau N, Vialle A, Allaire M, Tanguay P, Joly DL, Frey P, Callan BE, Hamelin RC (2009) Fungal pathogen (mis-) identifications: a case study with DNA barcodes on Melampsora rusts of aspen and white poplar. Mycol Res 113:713–724. doi:10.1007/s13225-011-0129-6
Gardes M, Bruns TD (1993) ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol Ecol 2:113–118. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.1993.tb00005.x
González-García S, Mola-Yudego B, Dimitriou I, Aronsson P, Murphy R (2012) Environmental assessment of energy production based on long term commercial willow plantations in Sweden. Sci Total Environ 421:210–219. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.01.041
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hiratsuka N (1927). Studies on the Melampsoraceae of Japan. J Fac Agric Hokkaido Imp Univ Sapporo 21:1–41
Hiratsuka N, Kaneko S (1982) A taxonomic revision of Melampsora on willows in Japan. Rept Tottori Mycol Inst 20:1–32
Hiratsuka N, Sato S, Katsuya K, Kakishima M, Hiratsuka Y, Kaneko S, Ono Y, Sato T, Harada Y (1992) The rust flora of Japan. Tsukuba Shuppankai, Tsukuba
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754
Hylander N, Jørstad I, Nannfeldt JA (1953) Enumerato Uredinearum Scandinavicarum. Oper Bot 1:1–102
Ito S (1938) Mycological flora of Japan, II (in Japanese). Yokendo, Tokyo
Kenaley SC, Smart LB, Hudler GW (2014) Genetic evidence for three discrete taxa of Melampsora (Pucciniales) affecting willows (Salix spp.) in New York State. Fungal Biol 118:704–720. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2014.05.001
Klebahn H (1914) Uredineae (in German). Kryptogamenflora der Mark Brandenburg Va. Borntraeger, Leipzig, pp 69–903
Kobayashi T (2007) Index of fungi inhabiting woody plants in Japan. host, distribution and literature. Zenkoku-Noson-Kyoiku Kyokai, Tokyo
Kuprevich VF, Tranzschel VG (1957) Rust fungi. 1. Family Melampsoraceae. In: Savich VP (ed) Cryptogamic plants of the USSR, vol 4. Botanicheskogo Instituta, Komarova, pp 423–464
Kuzovkina Y, Quigley M (2005) Willows beyond wetlands: uses of Salix L. species for environmental projects. Water Air Soil Pollut 162:183–204. doi:10.1007/s11270-005-6272-5
Lee SK, Kakishima M (1999) Surface structures of peridial cells of Gymnosporangium and Roestelia (Uredinales). Mycoscience 40:121–131. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2014.05.001
Liang YM (2006) Taxonomic evaluation of morphologically similar species of Pucciniastrum in Japan based on comparative analyses of molecular phylogeny and morphology. Doctoral dissertation, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan
Liro JI (1908) Uredineae fennicae Finlands rostsvampar (in Swedish). Finska Litteratursällskapets Tryckeri, Helsingfors
Liu WX (2005) A taxonomic study of Melampsora species on Salicaceae plants in Inner Mongolia (in Chinese). Master thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Huhhot
Milne JM, Helfer S, Kirk C, Hollingsworth PM, Ennos RA (2012) Molecular evidence indicates that subarctic willow communities in Scotland support a diversity of host-associated Melampsora rust taxa. Fungal Biol 116:603–612. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2012.02.008
Pei MH (2005) A brief review of Melampsora rusts on Salix. In: Pei MH, McCracken AR (eds) Rust diseases of willow and poplar. CABI, Wallingford, pp 20–50
Pei MH, Bayon C, Ruiz C (2005) Phylogenetic relationships in some Melampsora rusts on Salicaceae assessed using rDNA sequence information. Mycol Res 109:401–409. doi:10.1017/S0953756205002479
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.817
Royle DJ, Hubbes M (1992) Diseases and pests in energy crop plantations. Biomass Bioenergy 2:45–54. doi:10.1016/0961-9534(92)90087-7
Samils B, Lagercrantz U, Gullberg U (2002) Genetic relationships among genetically distinct forms of Melampsora larici-epitea and related species based on AFLP data. For Pathol 32:379–386
SmithJ, BlanchetteR, NewcombeG (2004) Molecular and morphological characterization of thewillow rust fungus,Melampsora epitea, from arctic and temperate hosts in North America.Mycologia96:1330–1338
Spaulding P (1961) Foreign diseases of forest trees of the world. USDA Agric Handb 197:1–361
Sydow P, Sydow H (1915) Monographia Uredinearum. III: Melampsoraceae, Zaghouaniaceae, Coleosporiaceae. Borntraeger, Leipzig
Tai FL (1979) Sylloge fungorum sinicorum. Science Press, Beijing
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Thümen F (1879) Melampsora salicina, der Weidenrost. Eine monographische Studie. Mitt Forstlichen Versuchswesen Österreichs 2:25–46
Tian CM, Shang YZ, Zhuang JY, Wang Q, Kakishima M (2004) Morphological and molecular phylogenetic analysis of Melampsora species on poplars in China. Mycoscience 45:55–66. doi:10.1007/S10267-003-0150-Z
Verwijst T (2001) Willows: an underestimated resource for environment and society. For Chron 77:281–285. doi:10.5558/tfc77281-2
Virtudazo EV, Nakamura H, Kakishima M (2001) Phylogenetic analysis of sugarcane rusts based on sequences of ITS, 5.8 S rDNA and D1/D2 regions of LSU rDNA. J Gen Plant Pathol 67:28–36. doi:10.1007/PL00012983
Wahyuno D, Kakishima M, Ono Y (2001) Morphological analyses of urediniospores and teliospores in seven Phragmidium species parasitic on ornamental roses. Mycoscience 42:519–533. doi:10.1007/BF02460950
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee SB, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic, New York, pp 315–322
Wilson M, Henderson DM (1966) The British rust fungi. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wright L (2006) Worldwide commercial development of bioenergy with a focus on energy crop-based projects. Biomass Bioenergy 30:706–714. doi:10.1016/j.biombioe.2005.08.008
Yamaoka Y, Shinyama Y, Obata K (2010) Species biology of a heteroecious rust, Melampsora chelidonii-pierotii in riparian vegetation. Trans Mycol Soc Jpn 51:35–47
Zhao P, Tian CM, Yao YJ, Wang Q, Yamaoka Y, Kakishima M (2013) New records of Melampsora species on willows in China. Mycotaxon 123:81–89. doi:10.5248/123.81
Zhao P, Tian CM, Yao YJ, Wang Q, Kakishima M, Yamaoka Y (2014) Melampsora salicis-sinicae (Melampsoraceae, Pucciniales), a new rust fungus found on willows in China. Mycoscience 55:390–399. doi:10.1016/j.myc.2013.12.005
Zhao P, Tian CM, Yao YJ, Wang Q, Yamaoka Y, Kakishima M (2015a) Two new species and one new record of Melampsora on willows from China. Mycol Prog 14:66. doi:10.1007/s11557-015-1091-6
Zhao P, Wang QH, Tian CM, Wang Q, Yamaoka Y, Kakishima M (2015b) A morphological and molecular survey of Japanese Melampsora species on willows reveals a new species and two new records. Mycol Prog 14:101. doi:10.1007/s11557-015-1121-4
Zhuang WY (2005) Fungi of northwestern China. Mycotaxon, Ithaca
Ziller WG (1974) The tree rusts of western Canada. Environment Canada, Forestry Service, Ottawa
Zwickl DJ (2006) Genetic algorithm approaches for the phylogenetic analysis of large biological sequence datasets under the maximum likelihood criterion. PhD thesis, University of Texas at Austin, Texas
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to Dr. Ming-Hao Pei (Rothamsted Research, Harpenden, Hertfordshire, UK), Dr. Zhi-Min Cao (Forestry College, Northwest A & F University, Yangling, China) and Dr. Tsuyoshi Hosoya (National Museum of Nature and Science, Tsukuba, Japan) for providing dried specimens for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest. All the experiments undertaken in this study comply with the current laws of Japan.
Additional information
Section Editor: Franz Oberwinkler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, P., Wang, QH., Tian, CM. et al. Melampsora salicis-bakko, a new species on willows in Japan evidenced by morphological and molecular phylogenetic analyses. Mycol Progress 15, 32 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-016-1175-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-016-1175-y