Abstract
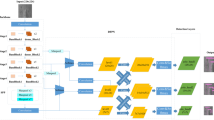
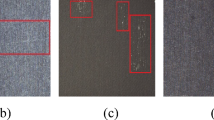
In this paper, we propose a lightweight and fast detection framework called Mixed YOLOv4-LITE series based on You Only Look Once (YOLOv4) for industrial defect detection. To reduce the size of the model and achieve a better balance between accuracy and speed, MobileNet series (MobileNetv1, MobileNetv2, MobileNetv3) and depthwise separable convolutions are employed in the modified network architecture to replace the backbone network CSPdarknet53 and traditional convolution in the neck and head of YOLOv4, respectively. Additionally, we combine the Mosic data enhancement method to enrich the dataset. To accelerate the convergence of the network, transfer learning is used in the training stage, in which pseudo-convergence is precluded as much as possible by adjusting the learning rate of the cosine annealing scheduler. Finally, we evaluate the proposed methods on both public defect datasets, NEU-DET and PCB-DET, with different types and scales. On NEU-DET, Mixed YOLOv4-LITEv1 achieved an improvement of 214% in detection speed while maintaining accuracy, detecting at a rate of 88 FPS on a single GPU. Meanwhile, Mixed YOLOv4-LITEv1 realizes an outstanding maximum improvement of 200% in detection speed while only losing a mean average precision (mAP) value of 1.77% on PCB-DET. Furthermore, the sizes of our proposed series models are only about one-fifth of the original YOLOv4 model. The extensive test results indicate that our work can provide an efficient scheme with low deployment cost for surface defect detection at different scales in multiple scenarios, meeting the needs of practical industrial applications.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Subramanyam, V., Kumar, J., Singh, S.N.: Temporal synchronization framework of machine-vision cameras for high-speed steel surface inspection systems. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 19, 445–461 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-022-01198-z
Borselli, A., Colla, V., Vannucci, M.: Surface defects classification in steel products: a comparison between different artificial intelligence-based approaches. In: Artificial intelligence and applications/718: modelling, identification, and control. ACTAPRESS, Innsbruck, Austria (2011)
Anter, A.M., Hassenian, A.E., Oliva, D.: An improved fast fuzzy c-means using crow search optimization algorithm for crop identification in agricultural. Expert Syst. Appl. 118, 340–354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.10.009
Luo, J., Yang, Z., Li, S., Wu, Y.: FPCB surface defect detection: a decoupled two-stage object detection framework. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2021.3092510
Kang, Z., Yuan, C., Yang, Q.: The fabric defect detection technology based on wavelet transform and neural network convergence. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on information and automation (ICIA). pp. 597–601. IEEE, Yinchuan, China (2013)
Anter, A.M., Abd Elaziz, M., Zhang, Z.: Real-time epileptic seizure recognition using bayesian genetic whale optimizer and adaptive machine learning. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 127, 426–434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.09.032
Mandriota, C., Nitti, M., Ancona, N., Stella, E., Distante, A.: Filter-based feature selection for rail defect detection. Mach. Vis. Appl. 15, 179–185 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-004-0148-3
Song, K., Yan, Y.: A noise robust method based on completed local binary patterns for hot-rolled steel strip surface defects. Appl. Surf. Sci. 285, 858–864 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.09.002
Basha, S.H., Anter, A.M., Hassanien, A.E., Abdalla, A.: Hybrid intelligent model for classifying chest X-ray images of COVID-19 patients using genetic algorithm and neutrosophic logic. Soft Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06103-7
Anter, A.M., Huang, G., Li, L., Zhang, L., Liang, Z., Zhang, Z.: A new type of fuzzy-rule-based system with chaotic swarm intelligence for multiclassification of pain perception from fMRI. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28, 1096–1109 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2979150
Yu, N., Xu, Q., Wang, H., Lin, J.: Wafer bin map inspection based on DenseNet. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 2436–2450 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4778-7
Feng, C., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Wang, S., Wang, H.: Efficient real-time defect detection for spillway tunnel using deep learning. J Real-Time Image Proc. 18, 2377–2387 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-021-01130-x
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 580–587 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.81
Girshick, R.: Fast R-CNN. In: IEEE international conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1440–1448 (2015)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 1137–1149 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
He, Y., Song, K., Meng, Q., Yan, Y.: An end-to-end steel surface defect detection approach via fusing multiple hierarchical features. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69, 1493–1504 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2019.2915404
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). pp. 779–788. IEEE, Las Vegas, NV, USA (2016)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: YOLO9000: better, faster, stronger. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). pp. 6517–6525. IEEE, Honolulu, HI (2017)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: YOLOv3: an incremental improvement. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1804.02767 (2018)
Bochkovskiy, A., Wang, C.-Y., Liao, H.-Y.M.: Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv preprint. arXiv: 2004.10934 (2020)
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S., Fu, C.Y., Berg, A.C.: Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: European -conference on computer vision, pp. 21–37. Springer (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
Tu, Y., Ling, Z., Guo, S., Wen, H.: An accurate and real-time surface defects detection method for sawn lumber. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 70, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2020.3024431
Ding, F., Zhuang, Z., Liu, Y., Jiang, D., Yan, X., Wang, Z.: Detecting defects on solid wood panels based on an improved SSD algorithm. Sensors. 20, 5315 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185315
Guo, F., Qian, Y., Shi, Y.: Real-time railroad track components inspection based on the improved YOLOv4 framework. Autom. Constr. 125, 1035 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103596
Wang, C.-Y., Mark Liao, H.-Y., Wu, Y.-H., Chen, P.-Y., Hsieh, J.-W., Yeh, I.-H.: CSPNet: a new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops (CVPRW). pp. 1571–1580. IEEE, Seattle, WA, USA (2020)
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., Zitnick, C.L.: Microsoft COCO: common objects in context. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2014, pp. 740–755. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2014)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37, 1904–1916 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
Liu, S., Qin, H., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In: IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, pp. 8759–8768 (2018)
Lei, J., Gao, X., Song, J., et al.: A review of deep network model compression. J. Softw. 29(2), 251–266 (2018)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep Residual learning for -image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). pp. 770–778. IEEE, Las Vega-s, NV, USA (2016)
Li, X., Wang, Z., Geng, S., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Liu, L., Li, D.: Yolov3-Pruning(transfer): real-time object detection algorithm based on transfer learning. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 19, 839–852 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-022-01227-x
Luo, J.-H., Wu, J., Lin, W.: ThiNet: a filter level pruning method for deep neural network compression. In: 2017 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). pp. 5068–5076. I-EEE, Venice (2017)
Howard, A.G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., Adam, H.: MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1704.04861 (2017)
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., Chen, L.C.: Mobilenetv2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 4510–4520 (2018)
Howard, A., Sandler, M., Chen, B., Wang, W., Chen, L.-C., Tan, M., Chu, G., Vasudevan, V., Zhu, Y., Pang, R., Adam, H., Le, Q.: Searching for MobileNetV3. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International conference on computer vision (ICCV). pp. 1314–1324. IEEE, S-eoul, Korea (South) (2019)
Chollet, F.: Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and -pattern recognition (CVPR). pp. 1800–1807. IEEE, Honolulu, HI (2017)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Albanie, S., Sun, G., Wu, E.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42, 2011–2023 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372
Everingham, M., Eslami, S.M.A., Van Gool, L., Williams, C.K.I., Winn, J., Zisserman, A.: The pascal visual object classes challenge: a retrospective. Int J Comput Vis. 111, 98–136 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-014-0733-5
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 52006095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and GC wrote the main manuscript text and Cengdi Xiao prepared figures 1-14. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This paper does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects and all authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Cui, G. & Xiao, C. A real-time and efficient surface defect detection method based on YOLOv4. J Real-Time Image Proc 20, 77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-023-01333-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-023-01333-4