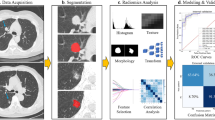
Abstract
Purpose
Lung cancer has significant genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity, leading to poor prognosis. Radiomic features have emerged as promising predictors of the tumor phenotype. However, the role of underlying information surrounding the cancer remains unclear.
Materials and methods
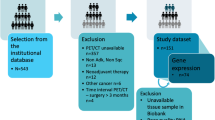
We conducted a retrospective study of 508 patients with NSCLC from three institutions. Radiomics models were built using features from six tumor regions and seven classifiers to predict three prognostically significant tumor phenotypes. The models were evaluated and interpreted by the mean area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) under nested cross-validation and Shapley values. The best-performing predictive models corresponding to six tumor regions and three tumor phenotypes were identified for further comparative analysis. In addition, we designed five experiments with different voxel spacing to assess the sensitivity of the experimental results to the spatial resolution of the voxels.
Results
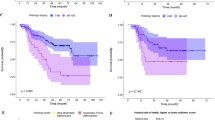
Our results demonstrated that models based on 2D, 3D, and peritumoral region features yielded mean AUCs and 95% confidence intervals of 0.759 and [0.747–0.771] for lymphovascular invasion, 0.889 and [0.882–0.896] for pleural invasion, and 0.839 and [0.829–0.849] for T-staging in the testing cohort, which was significantly higher than all other models. Similar results were obtained for the model combining the three regional features at five voxel spacings.
Conclusion
Our study revealed the predictive role of the developed methods with multi-regional features for the preoperative assessment of prognostic factors in NSCLC. The analysis of different voxel spacing and model interpretability strengthens the experimental findings and contributes to understanding the biological significance of the radiological phenotype.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- PI:
-
Pleural invasion
- LVI:
-
Lymphovascular invasion
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- ROI:
-
Regions of interest
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- FAHGMU:
-
First Affiliated Hospital of Gannon Medical University
- GLCM:
-
Gray level co-occurrence matrix
- GLRLM:
-
Gray level run length matrix
- GLSZM:
-
Gray level size zone matrix
- NGTDM:
-
Neighboring gray level difference matrix
- GLDM:
-
Gray level dependence matrix
- CC:
-
Correlation coefficient
- mRMR:
-
Multivariate minimum medundancy maximum relevance
- LASSO:
-
Embedded least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- kNN:
-
K-nearest neighbors
- RF:
-
Random forests
- NB:
-
Naive Bayes classifier
- LR:
-
Logistic regression
- MLP:
-
Multilayer perceptron
- LDA:
-
Linear discriminant analysis
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- SHAP:
-
Shapley additive explanation.
References
Miller KD, Ortiz AP, Pinheiro PS, Bandi P, Minihan A, Fuchs HE et al (2021) Cancer statistics for the US Hispanic/Latino population, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. ISSN: 0007–9235. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21695
Li J, Qiu Z, Zhang C, Chen S, Wang M, Meng Q, Lu H, Wei L, Lv H, Zhong W, Zhang X (2023) ITHscore: comprehensive quantification of intra-tumor heterogeneity in NSCLC by multi-scale radiomic features. Eur Radiol 33(2):893–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-09055-0
Chen Q, Shao J, Xue T, Peng H, Li M, Duan S, Feng F (2023) Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics nomograms for the preoperative prediction of lymphovascular invasion and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Radiol 33(2):947–958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-09109-3
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A et al (2021) Non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2021 featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 19(3):254–266. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2021.0013
Zhang XP, Zhang YC, Zhang GJ, Qiu XT, Tan WJ, Yin XX et al (2022) Prospective clinical research of radiomics and deep learning in oncology: a translational review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103823
Novellis P, Cominesi SR, Rossetti F, Mondoni M, Gregorc V, Veronesi G (2021) Lung cancer screening: who pays? who receives? The European perspectives. Transl Lung Cancer Res 10(5):2395–2406. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-677
Ghosh S, Mehta AC, Abuquyyas S, Raju S, Farver C (2020) Primary lung neoplasms presenting as multiple synchronous lung nodules. Eur Respir Rev. https://doi.org/10.1183/16000617.0142-2019
Zwanenburg A, Vallieres M, Abdalah MA, Aerts HJWL, Andrearczyk V, Apte A et al (2020) The image biomarker standardization initiative: standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping. Radiology 295(2):328–338. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020191145
Tomaszewski MR, Gillies RJ (2021) The biological meaning of radiomic features. Radiology 299(2):E256–E256. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021219005
Lohmann P, Galldiks N, Kocher M, Heinzel A, Filss CP, Stegmayr C et al (2021) Radiomics in neuro-oncology: basics, workflow, and applications. Methods 188:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.06.003
Tan WJ, Liu P, Li XS, Xu SX, Chen YF, Yang JZ (2022) Segmentation of lung airways based on deep learning methods. Iet Image Process 16(5):1444–1456. https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.12423
Ibrahim A, Primakov S, Beuque M, Woodruff HC, Halilaj I, Wu G et al (2021) Radiomics for precision medicine: current challenges, future prospects, and the proposal of a new framework. Methods 188:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.05.022
Conti A, Duggento A, Indovina I, Guerrisi M, Toschi N (2021) Radiomics in breast cancer classification and prediction. Semin Cancer Biol 72:238–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.04.002
Meng LW, Dong D, Chen X, Fang MJ, Wang RP, Li J et al (2021) 2d and 3d CT radiomic features performance comparison in characterization of gastric cancer: a multi-center study. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 25(3):755–763. https://doi.org/10.1109/Jbhi.2020.3002805
Papp L, Spielvogel CP, Grubmuller B, Grahovac M, Krajnc D, Ecsedi B et al (2021) Supervised machine learning enables non-invasive lesion characterization in primary prostate cancer with [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48(6):1795–1805
Mirniaharikandehei S, Heidari M, Danala G, Lakshmivarahan S, Zheng B (2021) Applying a random projection algorithm to optimize machine learning model for predicting peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer patients using ct images. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 200:105937
Nazari M, Shiri I, Zaidi H (2021) Radiomics-based machine learning model to predict risk of death within 5-years in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Comput Biol Med 129:159
Chong HH, Yang L, Sheng RF, Yu YL, Wu DJ, Rao SX et al (2021) Multi-scale and multi-parametric radiomics of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in patients with solitary hepatocellular carcinoma \(<\)/= 5 cm. Eur Radiol 31(7):4824–4838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07601-2
Staal FCR, van der Reijd DJ, Taghavi M, Lambregts DMJ, Beets-Tan RGH, Maas M (2021) Radiomics for the prediction of treatment outcome and survival in patients with colorectal cancer: a systematic review. Clin Colorectal Cancer 20(1):52–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clcc.2020.11.001
Khodabakhshi Z, Mostafaei S, Arabi H, Oveisi M, Shiri I, Zaidi H (2021) Non-small cell lung carcinoma histopathological subtype phenotyping using high-dimensional multinomial multiclass CT radiomics signature. Comput Biol Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104752
Cong MD, Feng H, Ren JL, Xu Q, Cong LN, Hou ZZ et al (2020) Development of a predictive radiomics model for lymph node metastases in pre-surgical CT-based stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 139:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.11.003
Dercle L, Fronheiser M, Lu L, Du SY, Hayes W, Leung DK et al (2020) Identification of non-small cell lung cancer sensitive to systemic cancer therapies using radiomics. Clin Cancer Res 26(9):2151–2162. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-19-2942
Zhang TN, Xu ZH, Liu GX, Jiang BB, de Bock GH, Groen HJM et al (2021) Simultaneous identification of egfr, kras, erbb2, and tp53 mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer by machine learning-derived three-dimensional radiomics. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081814
Liu C, Gong J, Yu H, Liu Q, Wang S, Wang J (2021) A CT-based radiomics approach to predict nivolumab response in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 16(3):S638–S638
Yang Y, Yang JC, Shen L, Chen JJ, Xia LL, Ni BB et al (2021) A multi-omics-based serial deep learning approach to predict clinical outcomes of single-agent anti-pd-1/pd-l1 immunotherapy in advanced stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Am J Transl Res 13(2):743
Kothari G, Korte J, Lehrer EJ, Zaorsky NG, Lazarakis S, Kron T et al (2021) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prognostic value of radiomics based models in non-small cell lung cancer treated with curative radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 155:188–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.10.023
Zhang XP, Zhang YC, Zhang GJ, Qiu XT, Tan WJ, Yin XX et al (2022) Deep learning with radiomics for disease diagnosis and treatment: challenges and potential. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.773840
Fiz F, Masci C, Costa G, Sollini M, Chiti A, Ieva F et al (2022) PET/CT-based radiomics of mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma improves prediction of pathology data and survival. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-05765-1
Hu YH, Xie CY, Yang H, Ho JWK, Wen J, Han LJ et al (2020) Assessment of intratumoral and peritumoral computed tomography radiomics for predicting pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. JAMA Netw Open. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.15927
Bakr S, Gevaert O, Echegaray S, Ayers K, Zhou M, Shafiq M et al (2018) A radiogenomic dataset of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Data. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.202
van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V et al (2017) Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res 77(21):E104–E107. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-0339
Korte JC, Cardenas C, Hardcastle N, Kron T, Wang JH, Bahig H et al (2021) Radiomics feature stability of open-source software evaluated on apparent diffusion coefficient maps in head and neck cancer. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96600-4
Fornacon-Wood I, Mistry H, Ackermann CJ, Blackhall F, McPartlin A, Faivre-Finn C et al (2020) Reliability and prognostic value of radiomic features are highly dependent on choice of feature extraction platform. Eur Radiol 30(11):6241–6250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-06957-9
Peng HC, Long FH, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information: criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–1238. https://doi.org/10.1109/Tpami.2005.159
Tibshirani R (2011) Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso: a retrospective. J R Stat Soc Ser B-Stat Methodol 73:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9868.2011.00771.x
Naseriparsa M, Al-Shammari A, Sheng M, Zhang Y, Zhou R (2020) RSMOTE: improving classification performance over imbalanced medical datasets. Health Inf Sci Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-020-00112-w
Wang TT, She YL, Yang Y, Liu XY, Chen SY, Zhong YF et al (2022) Radiomics for survival risk stratification of clinical and pathologic stage IA pure-solid non-small cell lung cancer. Radiology 302(2):425–434. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021210109
Zhu Ying, Yao Wang, Bing-Chen Xu, Lei Yi-Yan, Guo Qi-Kun, Liu Li-Zhi et al (2021) Predicting response to immunotherapy plus chemotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using non-invasive radiomic biomarkers. BMC Cancer 21(1):1167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08899-x
Xie XJ, Liu SY, Chen JY, Zhao Y, Jiang J, Wu L et al (2021) Development of unenhanced CT-based imaging signature for bap1 mutation status prediction in malignant pleural mesothelioma: consideration of 2d and 3d segmentation. Lung Cancer 157:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.04.023
Xu L, Yang PF, Yen EA, Wan YD, Jiang YK, Cao ZZ et al (2019) A multi-organ cancer study of the classification performance using 2d and 3d image features in radiomics analysis. Phys Med Biol. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/ab489f
Xie RW, Pan D, Zeng A, Xu XW, Wang TC, Ullah N et al (2023) Target area distillation and section attention segmentation network for accurate 3d medical image segmentation. Health Inf Sci Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-022-00200-z
Yang GJ, Nie P, Zhao LZ, Guo J, Xue W, Yan L et al (2020) 2d and 3d texture analysis to predict lymphovascular invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Eur J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109111
Ortiz-Ramon R, Larroza A, Arana E, Moratal D (2017) A radiomics evaluation of 2d and 3d mri texture features to classify brain metastases from lung cancer and melanoma. In: 2017 39th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC), pp 493–496, 2017. ISSN 1094-687x
Arefan D, Chai RM, Sun M, Zuley ML, Wu SD (2020) Machine learning prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer: 2d versus 3d radiomic features. Med Phys 47(12):6334–6342. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14538
Huang J, Chen YD, Zhang YY, Xie JN, Liang YQ, Yuan WZ et al (2021) Comparison of clinical-computed tomography model with 2d and 3d radiomics models to predict occult peritoneal metastases in advanced gastric cancer. Abdom Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03287-2
Liu Y, Zhang YW, Cheng RF, Liu SC, Qu FY, Yin XY et al (2019) Radiomics analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient in cervical cancer: a preliminary study on histological grade evaluation. J Magn Resonan Imaging 49(1):280–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26192
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Overseas Joint Training Program and the Innovative Research Grant Program (Grant No. 2022GDJC-D20) for Postgraduates of Guangzhou University, as well as by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61971118) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (Grant No. 2022A1515010102).
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ, HW, and YZ designed and wrote the study, and reviewed and edited the final manuscript. XZ, GZ, and XQ participated in data collection, tumor segmentation, statistical analysis, and clinical review of this work. YJ, WT, XY, HY, and LL contributed to the expert review of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no financial or non-financial competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The institutional review boards of the First Affiliated Hospital of Gannon Medical University approved this retrospective study and waived the requirement for informed consent (No. LLSC-2023149).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhang, G., Qiu, X. et al. Radiomics under 2D regions, 3D regions, and peritumoral regions reveal tumor heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter study. Radiol med 128, 1079–1092 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01676-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-023-01676-9