Abstract
Background
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is characterized by a high frequency of KRAS mutations and frequent deregulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and other EGFR family members such as HER2/ErbB2. The EGFR inhibitor erlotinib is approved for treatment of pancreatic cancer, but has shown modest activity in most patients.
Objective
Here we investigated the activity of afatinib, a second-generation irreversible pan-EGFR family kinase inhibitor, alone or in combination with ionizing radiation, toward pancreatic cancer cells.
Methods
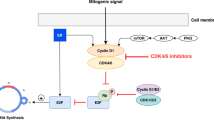
The influence of afatinib on cell proliferation, cell cycle distribution, clonogenic survival, nuclear fragmentation, ploidy, and centrosome amplification following irradiation was determined. Expression and phosphorylation of HER receptors, Akt, DNA-PKcs, and ERK1/2 was characterized by Western blot analysis.
Results
Afatinib was growth-inhibitory for all three cell lines but cytotoxic only toward BxPC3 (KRAS wt) and Capan-2 (KRAS mut) cells, both of which express high levels of EGFR, HER2, and HER3 receptors. Afatinib increased the radiosensitivity of BxPC3 and Capan-2 cells, prevented the radio-induced phosphorylation of Akt, and induced mitotic catastrophe following irradiation. In comparison, Panc-1 cells (KRAS mut) expressing low levels of EGFR family receptors were resistant to afatinib-induced radiosensitization.
Limitations
These results must be confirmed in vivo.
Conclusions
Afatinib showed cytotoxic and radiosensitizing effects toward a subset of pancreatic cancer cells which was closely correlated with expression of EGFR, HER2, and HER3 receptors, but not with KRAS status.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA (2005) Cancer principles and practice of oncology, 7th edn. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia
Burris HA 3rd, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR et al (1997) Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 15:2403–13
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S et al (2007) Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada clinical trials group. J Clin Oncol 25:1960–6. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.07.9525
Huguet F, Girard N, Guerche CS, Hennequin C, Mornex F, Azria D (2009) Chemoradiotherapy in the management of locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma: a qualitative systematic review. J Clin Oncol 27:2269–77
Ciardiello F, Tortora G (2008) EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med 358:1160–74
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–37
Zhang L, Yuan SZ (2002) Expression of c-erbB-2 oncogene protein, epidermal growth factor receptor, and TGF-beta1 in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 1:620–3
Tobita K, Kijima H, Dowaki S, Kashiwagi H, Ohtani Y, Oida Y et al (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in human pancreatic cancer: Significance for liver metastasis. Int J Mol Med 11:305–9
Xiong HQ (2004) Molecular targeting therapy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 54(Suppl 1):S69–77
Immervoll H, Hoem D, Kugarajh K, Steine SJ, Molven A (2006) Molecular analysis of the EGFR-RAS-RAF pathway in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas: lack of mutations in the BRAF and EGFR genes. Virchows Arch 448:788–96
Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Davis DW, Portera CA, Tsan R, McConkey DJ et al (2000) Epidermal growth factor receptor blockade with C225 plus gemcitabine results in regression of human pancreatic carcinoma growing orthotopically in nude mice by antiangiogenic mechanisms. Clin Cancer Res 6:1936–48
Harari PM, Huang SM (2001) Head and neck cancer as a clinical model for molecular targeting of therapy: combining EGFR blockade with radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49:427–33
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB et al (2006) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354:567–78
Giocanti N, Hennequin C, Rouillard D, Defrance R, Favaudon V (2004) Additive interaction of gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) and ionising radiation in human tumour cells in vitro. Br J Cancer 91:2026–33
Larbouret C, Robert B, Navarro-Teulon I, Thezenas S, Ladjemi MZ, Morisseau S et al (2007) In vivo therapeutic synergism of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor and anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies against pancreatic carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 13:3356–62
Gupta AK, Bakanauskas VJ, Cerniglia GJ, Cheng Y, Bernhard EJ, Muschel RJ et al (2001) The Ras radiation resistance pathway. Cancer Res 61:4278–82
Lievre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V, Landi B, Emile JF et al (2006) KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 66:3992–5
Lee J, Jang KT, Ki CS, Lim T, Park YS, Lim HY et al (2007) Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase mutations, EGFR gene amplifications, and KRAS mutations on survival of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 109:1561–9
Grana TM, Rusyn EV, Zhou H, Sartor CI, Cox AD (2002) Ras mediates radioresistance through both phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and Raf-dependent but mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase-independent signaling pathways. Cancer Res 62:4142–50
Li D, Ambrogio L, Shimamura T, Kubo S, Takahashi M, Chirieac LR et al (2008) BIBW2992, an irreversible EGFR/HER2 inhibitor highly effective in preclinical lung cancer models. Oncogene 27:4702–11
Solca F, Dahl G, Zoephel A, Bader G, Sanderson M, Klein C et al (2012) Target binding properties and cellular activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992), an irreversible ErbB family blocker. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 343:342–50
Piret B, Schoonbroodt S, Piette J (1999) The ATM protein is required for sustained activation of NF-kappaB following DNA damage. Oncogene 18:2261–71
Demarcq C, Bastian G, Remvikos Y (1992) BrdUrd/DNA flow cytometry analysis demonstrates cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-induced multiple cell-cycle modifications on human lung carcinoma cells. Cytometry 13:416–22
Normanno N, De Luca A, Bianco C, Strizzi L, Mancino M, Maiello MR et al (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene 366:2–16
Toulany M, Dittmann K, Baumann M, Rodemann HP (2005) Radiosensitization of Ras-mutated human tumor cells in vitro by the specific EGF receptor antagonist BIBX1382BS. Radiother Oncol 74:117–29
Toulany M, Kasten-Pisula U, Brammer I, Wang S, Chen J, Dittmann K et al (2006) Blockage of epidermal growth factor receptor-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT signaling increases radiosensitivity of K-RAS mutated human tumor cells in vitro by affecting DNA repair. Clin Cancer Res 12:4119–26
Kimple RJ, Vaseva AV, Cox AD, Baerman KM, Calvo BF, Tepper JE et al (2010) Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status. Clin Cancer Res 16:912–23
Ioannou N, Dalgleish AG, Seddon AM, Mackintosh D, Guertler U, Solca F et al (2011) Anti-tumour activity of afatinib, an irreversible ErbB family blocker, in human pancreatic tumour cells. Br J Cancer 105:1554–62
Poindessous V, Ouaret D, El Ouadrani K, Battistella A, Megalophonos VF, Kamsu-Kom N et al (2011) EGFR- and VEGF(R)-targeted small molecules show synergistic activity in colorectal cancer models refractory to combinations of monoclonal antibodies. Clin Cancer Res 17:6522–30
Buck E, Eyzaguirre A, Haley JD, Gibson NW, Cagnoni P, Iwata KK (2006) Inactivation of Akt by the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib is mediated by HER-3 in pancreatic and colorectal tumor cell lines and contributes to erlotinib sensitivity. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2051–9
Frolov A, Schuller K, Tzeng CW, Cannon EE, Ku BC, Howard JH et al (2007) ErbB3 expression and dimerization with EGFR influence pancreatic cancer cell sensitivity to erlotinib. Cancer Biol Ther 6:548–54
Toulany M, Minjgee M, Kehlbach R, Chen J, Baumann M, Rodemann HP. ErbB2 expression through heterodimerization with erbB1 is necessary for ionizing radiation- but not EGF-induced activation of Akt survival pathway. Radiother Oncol 2010.
Azuma K, Kawahara A, Sonoda K, Nakashima K, Tashiro K, Watari K et al (2014) FGFR1 activation is an escape mechanism in human lung cancer cells resistant to afatinib, a pan-EGFR family kinase inhibitor. Oncotarget 5:5908–19
Kim IA, Bae SS, Fernandes A, Wu J, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG et al (2005) Selective inhibition of Ras, phosphoinositide 3 kinase, and Akt isoforms increases the radiosensitivity of human carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 65:7902–10
Caron RW, Yacoub A, Mitchell C, Zhu X, Hong Y, Sasazuki T et al (2005) Radiation-stimulated ERK1/2 and JNK1/2 signaling can promote cell cycle progression in human colon cancer cells. Cell Cycle 4:456–64
Schutze C, Dorfler A, Eicheler W, Zips D, Hering S, Solca F et al (2007) Combination of EGFR/HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibition by BIBW 2992 and BIBW 2669 with irradiation in FaDu human squamous cell carcinoma. Strahlenther Onkol 183:256–64
Vitale I, Galluzzi L, Castedo M, Kroemer G (2011) Mitotic catastrophe: a mechanism for avoiding genomic instability. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:385–92
Calhoun ES, Kern SE (2008) Molecular genetics of pancreatic cancer. In: Lowy AM, Leach SD, Philip PA (eds) Pancreatic Cancer. Springer, New York, pp 27–39
Wang M, Kern AM, Hulskotter M, Greninger P, Singh A, Pan Y et al (2014) EGFR-Mediated Chromatin Condensation Protects KRAS-Mutant Cancer Cells against Ionizing Radiation. Cancer Res 74:2825–34
Hung LY, Tseng JT, Lee YC, Xia W, Wang YN, Wu ML et al (2008) Nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) interacts with signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) in activating Aurora-A gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 36:4337–51
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Valérie Fauquette (INSERM U837, Lille) for the generous gift of Capan-2 cells and Janet Hall (Institut Curie, Orsay) for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
F. Huguet, M. Fernet, N. Giocanti, V. Favaudon, and A.K. Larsen declare no conflict of interest.
F. Huguet was supported in part by the Nuovo-Soldati Research Foundation.
Additional information
Vincent Favaudon and Annette K. Larsen contributed equally to this work.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huguet, F., Fernet, M., Giocanti, N. et al. Afatinib, an Irreversible EGFR Family Inhibitor, Shows Activity Toward Pancreatic Cancer Cells, Alone and in Combination with Radiotherapy, Independent of KRAS Status. Targ Oncol 11, 371–381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-015-0403-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-015-0403-8