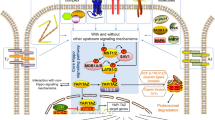
Abstract
Canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays a central role in development, homeostasis, as well as tumorigenesis. The regulation of the pathway involves various and complicated mechanisms, including the extracellular, intracellular and endonuclear regulation. As the key component of the pathway, the Lef1/Tcfs-β-catenin complex is also the key target of regulation in the nucleus. In the current review, we are going to summarize the regulators in the nucleus which can modify the transcriptional activity of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohn AD, Moon RT (2005) Wnt and calcium signaling: beta-catenin-independent pathways. Cell Calcium 38:439–446
Chinnadurai G (2002) CtBP, an unconventional transcriptional corepressor in development and oncogenesis. Mol Cell 9:213–224
Kim W, Kim M, Jho EH (2013) Wnt/beta-catenin signalling: from plasma membrane to nucleus. Biochem J 450:9–21
de Sousa EM, Vermeulen L, Richel D et al (2011) Targeting Wnt signaling in colon cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res 17:647–653
Peifer M, Polakis P (2000) Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogenesis—a look outside the nucleus. Science 287:1606–1609
Vacik T, Lemke G (2011) Dominant-negative isoforms of Tcf/Lef proteins in development and disease. Cell Cycle 10:4199–4200
Mao CD, Byers SW (2011) Cell-context dependent TCF/LEF expression and function: alternative tales of repression, de-repression and activation potentials. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 21:207–236
Waterman ML (2004) Lymphoid enhancer factor/T cell factor expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 23:41–52
Stamos JL, Weis WI (2013) The beta-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:a007898
Sokol SY (2011) Wnt signaling through T-cell factor phosphorylation. Cell Res 21:1002–1012
Fiedler M, Sanchez-Barrena MJ, Nekrasov M et al (2008) Decoding of methylated histone H3 tail by the Pygo–BCL9 Wnt signaling complex. Mol Cell 30:507–518
Cantu C, Valenta T, Hausmann G et al (2013) The Pygo2–H3K4me2/3 interaction is dispensable for mouse development and Wnt signaling-dependent transcription. Development 140:2377–2386
Waltzer L, Bienz M (1998) Drosophila CBP represses the transcription factor TCF to antagonize Wingless signalling. Nature 395:521–525
Elfert S, Weise A, Bruser K et al (2013) Acetylation of human TCF4 (TCF7L2) proteins attenuates inhibition by the HBP1 repressor and induces a conformational change in the TCF4: DNA complex. PLoS One 8:e61867
Ota S, Ishitani S, Shimizu N et al (2012) NLK positively regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signalling by phosphorylating LEF1 in neural progenitor cells. EMBO J 31:1904–1915
Bauer A, Huber O, Kemler R (1998) Pontin52, an interaction partner of beta-catenin, binds to the TATA box binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14787–14792
Carlson ML, Wilson ET, Prescott SM (2003) Regulation of COX-2 transcription in a colon cancer cell line by Pontin52/TIP49a. Mol Cancer 2:42
Togi S, Ikeda O, Kamitani S et al (2011) Zipper-interacting protein kinase (ZIPK) modulates canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling through interaction with Nemo-like kinase and T-cell factor 4 (NLK/TCF4). J Biol Chem 286:19170–19177
Benchabane H, Xin N, Tian A et al (2011) Jerky/Earthbound facilitates cell-specific Wnt/Wingless signalling by modulating beta-catenin-TCF activity. EMBO J 30:1444–1458
Jennings BH, Ish-Horowicz D (2008) The Groucho/TLE/Grg family of transcriptional co-repressors. Genome Biol 9:205
Brantjes H, Roose J, van De WM et al (2001) All Tcf HMG box transcription factors interact with Groucho-related co-repressors. Nucleic Acids Res 29:1410–1419
Grigoletto A, Lestienne P, Rosenbaum J (2011) The multifaceted proteins Reptin and Pontin as major players in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1815:147–157
Bauer A, Chauvet S, Huber O et al (2000) Pontin52 and reptin52 function as antagonistic regulators of beta-catenin signalling activity. EMBO J 19:6121–6130
Gallant P (2007) Control of transcription by pontin and reptin. Trends Cell Biol 17:187–192
Hovanes K, Li TW, Munguia JE et al (2001) Beta-catenin-sensitive isoforms of lymphoid enhancer factor-1 are selectively expressed in colon cancer. Nat Genet 28:53–57
Ishitani T, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K (2003) Regulation of lymphoid enhancer factor 1/T-cell factor by mitogen-activated protein kinase-related Nemo-like kinase-dependent phosphorylation in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol 23:1379–1389
Yamada M, Ohnishi J, Ohkawara B et al (2006) NARF, an nemo-like kinase (NLK)-associated ring finger protein regulates the ubiquitylation and degradation of T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF). J Biol Chem 281:20749–20760
Dai L, Aye TC, Liu XY et al (2012) TAK1, more than just innate immunity. IUBMB Life 64:825–834
Tago K, Nakamura T, Nishita M et al (2000) Inhibition of Wnt signaling by ICAT, a novel beta-catenin-interacting protein. Genes Dev 14:1741–1749
Takemaru K, Yamaguchi S, Lee YS et al (2003) Chibby, a nuclear beta-catenin-associated antagonist of the Wnt/Wingless pathway. Nature 422:905–909
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H et al (2010) p15RS attenuates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by disrupting β-catenin TCF4 Interaction. J Biol Chem 285:34621–34631
Park JI, Kim SW, Lyons JP et al (2005) Kaiso/p120-catenin and TCF/beta-catenin complexes coordinately regulate canonical Wnt gene targets. Dev Cell 8:843–854
Del Valle-Perez B, Casagolda D, Lugilde E et al (2011) Wnt controls the transcriptional activity of Kaiso through CK1epsilon-dependent phosphorylation of p120-catenin. J Cell Sci 124:2298–2309
Liu JA, Wu MH, Yan CH et al (2013) Phosphorylation of Sox9 is required for neural crest delamination and is regulated downstream of BMP and canonical Wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:2882–2887
Topol L, Chen W, Song H et al (2009) Sox9 inhibits Wnt signaling by promoting beta-catenin phosphorylation in the nucleus. J Biol Chem 284:3323–3333
Panza A, Pazienza V, Ripoli M et al (2013) Interplay between SOX9, beta-catenin and PPARgamma activation in colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:1853–1865
Brembeck FH, Wiese M, Zatula N et al (2011) BCL9-2 promotes early stages of intestinal tumor progression. Gastroenterology 141:1359–1370
Zhou SY, Xu ML, Wang SQ et al (2014) Overexpression of Pygopus-2 is required for canonical Wnt activation in human lung cancer. Oncol Lett 7:233–238
Li J, Sutter C, Parker DS et al (2007) CBP/p300 are bimodal regulators of Wnt signaling. EMBO J 26:2284–2294
Jessen S, Gu B, Dai X (2008) Pygopus and the Wnt signaling pathway: a diverse set of connections. Bioessays 30:448–456
Fang M, Li J, Blauwkamp T et al (2006) C-terminal-binding protein directly activates and represses Wnt transcriptional targets in Drosophila. EMBO J 25:2735–2745
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X (2009) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17:9–26
Arce L, Yokoyama NN, Waterman ML (2006) Diversity of LEF/TCF action in development and disease. Oncogene 25:7492–7504
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV et al (2004) WNT and beta-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet 5:691–701
Grossmann TN, Yeh JT, Bowman BR et al (2012) Inhibition of oncogenic Wnt signaling through direct targeting of beta-catenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:17942–17947
Paul S, Dey A (2008) Wnt signaling and cancer development: therapeutic implication. Neoplasma 55:165–176
Khan O, La Thangue NB (2012) HDAC inhibitors in cancer biology: emerging mechanisms and clinical applications. Immunol Cell Biol 90:85–94
Henderson WR Jr, Chi EY, Ye X et al (2010) Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin/CREB binding protein (CBP) signaling reverses pulmonary fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:14309–14314
Tian W, Han X, Yan M et al (2012) Structure-based discovery of a novel inhibitor targeting the beta-catenin/Tcf4 interaction. Biochemistry 51:724–731
Li X, Pu J, Jiang S et al (2013) Henryin, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid, inhibits Wnt signaling through interference with beta-catenin/TCF4 interaction in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One 8:e68525
Wei W, Chua MS, Grepper S et al (2010) Small molecule antagonists of Tcf4/beta-catenin complex inhibit the growth of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer 126:2426–2436
Lazarova DL, Chiaro C, Wong T et al (2013) CBP activity mediates effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor butyrate on WNT activity and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. J Cancer 4:481–490
Richon VM (2010) Targeting histone deacetylases: development of vorinostat for the treatment of cancer. Epigenomics 2:457–465
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81172034).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Han, W., Wang, H. Regulation of canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway in the nucleus. Chin. Sci. Bull. 59, 3530–3535 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0489-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0489-x