Abstract
Objectives
Previously, Interferon-induced Protein with Tetratricopeptide Repeats 1 (IFIT1) has been shown to promote cancer development. Here, we aimed to explore the role of IFIT1 in the development and progression of pancreatic cancer, including the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
We explored IFIT1 expression in pancreatic cancer samples using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8), colony formation, scratch wound-healing and Transwell assays were performed to assess the proliferation, migration and invasion abilities of pancreatic cancer cells. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and Western blotting were performed to assess the regulatory effect of IFIT1 on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Results
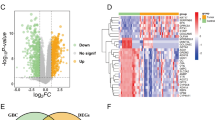
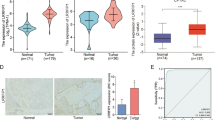
We found that upregulation of IFIT1 expression is common in pancreatic cancer and is negatively associated with overall patient survival. Knockdown of IFIT1 expression led to decreased proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. We also found that IFIT1 could regulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and that a Wnt/β-catenin agonist could reverse this effect. In addition, we found that IFIT1 can promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of pancreatic cancer cells.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that IFIT1 increases pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. In addition, we found that EMT could be regulated by IFIT1. IFIT1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Abbreviations
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- CCK8:
-
Implementation Outcomes Framework
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
- FBS:
-
Fetal Bovine Serum
- GEO:
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- GSEA:
-
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
- GTEx:
-
Genotype-Tissue Expression
- HR:
-
Hazard Ratio
- IFIT1:
-
Interferon-induced Protein with Tetratricopeptide Repeats 1
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- KD:
-
Knockdown
- KM:
-
Kaplan-Meier
- OE:
-
Overexpression
- OS:
-
Overall Survival
- OSCC:
-
Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse Transcription-polymerase Chain Reaction
- TRP:
-
Tetratricopeptide Repeat
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
References
T. Kamisawa, L.D. Wood, T. Itoi, K. Takaori, Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 388, 73–85 (2016)
C. Neuzillet, A. Tijeras-Raballand, P. Bourget, J. Cros, A. Couvelard, A. Sauvanet et al., State of the art and future directions of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 155, 80–104 (2015)
S. Gillen, T. Schuster, C. Meyer Zum, H. Büschenfelde, J. Friess, Kleeff, Preoperative/neoadjuvant therapy in pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of response and resection percentages. PLoS Med. 7, e1000267 (2010)
V.P. Groot, N. Rezaee, W. Wu, J.L. Cameron, E.K. Fishman, R.H. Hruban et al., Patterns, timing, and predictors of recurrence following pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 267, 936–945 (2018)
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer Stat. 2017 CA Cancer J. Clin. 67, 7–30 (2017)
J. He, N. Ahuja, M.A. Makary, J.L. Cameron, F.E. Eckhauser, M.A. Choti et al., 2564 resected periampullary adenocarcinomas at a single institution: trends over three decades. HPB (Oxford). 16, 83–90 (2014)
D. Hanahan, R.A. Weinberg, Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144, 646–674 (2011)
H. Acloque, M.S. Adams, K. Fishwick, M. Bronner-Fraser, M.A. Nieto, Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: the importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 1438–1449 (2009)
R. Kalluri, R.A. Weinberg, The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 1420–1428 (2009)
S. Wang, S. Huang, Y.L. Sun, Epithelial-Mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer: a review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2646148 (2017)
N. Gaianigo, D. Melisi, C. Carbone, EMT and treatment resistance in pancreatic Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 9, (2017)
A.D. Rhim, E.T. Mirek, N.M. Aiello, A. Maitra, J.M. Bailey, F. Mcallister et al., EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic tumor formation. Cell. 148, 349– 61 (2012)
D.M. Gonzalez, D. Medici, Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Signal. 7, re8 (2014)
J.M. Lee, S. Dedhar, R. Kalluri, E.W. Thompson, The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J. Cell. Biol. 172, 973–981 (2006)
M. Nakamoto, M. Hisaoka, Clinicopathological implications of Wingless/int1 (WNT) signaling pathway in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Uoeh. 38, 1–8 (2016)
W.H. Lien, E. Fuchs, Wnt some lose some: transcriptional governance of stem cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Genes Dev. 28, 1517–1532 (2014)
V.S. Li, S.S. Ng, P.J. Boersema, T.Y. Low, W.R. Karthaus, J.P. Gerlach et al., Wnt signaling through inhibition of β-catenin degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell. 149, 1245–1256 (2012)
L.C. Platanias, Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 375–386 (2005)
R.C. Fleith, H.V. Mears, X.Y. Leong, T.J. Sanford, E. Emmott, S.C. Graham et al., IFIT3 and IFIT2/3 promote IFIT1-mediated translation inhibition by enhancing binding to non-self RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, 5269–5285 (2018)
V.K. Pidugu, M.M. Wu, A.H. Yen, H.B. Pidugu, K.W. Chang, C.J. Liu et al., IFIT1 and IFIT3 promote oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and contribute to the anti-tumor effect of gefitinib via enhancing p-EGFR recycling. Oncogene. 38, 3232–3247 (2019)
G. Liu, J. Sun, Z.F. Yang, C. Zhou, P.Y. Zhou, R.Y. Guan et al., Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived CXCL11 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and tumor metastasis through the circUBAP2/miR-4756/IFIT1/3 axis. Cell. Death Dis. 12, 260 (2021)
R.L. Siegel, K.D. Miller, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 69, 7–34 (2019)
S.H. Lin, G.S. Raju, C. Huff, Y. Ye, J. Gu, J.S. Chen et al., The somatic mutation landscape of premalignant colorectal adenoma, Gut 67, 1299– 305 (2018)
N. Marschner, S. Zacharias, F. Lordick, S. Hegewisch-Becker, U. Martens, A. Welt et al., Association of Disease Progression with Health-Related quality of life among adults with breast, lung, pancreatic, and Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open. 3, e200643 (2020)
D. Creytens, NKX2.2 immunohistochemistry in the distinction of ewing sarcoma from cytomorphologic mimics: diagnostic utility and pitfalls-comment on Russell-Goldman et al. Cancer Cytopathol. 127, 202 (2019)
B.Q. Li, Z.Y. Liang, S. Seery, Q.F. Liu, L. You, T.P. Zhang et al., WT1 associated protein promotes metastasis and chemo-resistance to gemcitabine by stabilizing Fak mRNA in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 451, 48–57 (2019)
K. Willert, R. Nusse, Beta-catenin: a key mediator of wnt signaling. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8, 95–102 (1998)
S. Yang, Y. Liu, M.Y. Li, C.S.H. Ng, S.L. Yang, S. Wang et al., FOXP3 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer. 16, 124 (2017)
C.C. Liu, D.L. Cai, F. Sun, Z.H. Wu, B. Yue, S.L. Zhao et al., FERMT1 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote colon cancer metastasis via modulation of β-catenin transcriptional activity. Oncogene. 36, 1779–1792 (2017)
V. Fensterl, G.C. Sen, Interferon-induced ifit proteins: their role in viral pathogenesis. J. Virol. 89, 2462–2468 (2015)
R.K. Allan, T. Ratajczak, Versatile TPR domains accommodate different modes of target protein recognition and function. Cell. Stress Chaperones. 16, 353–367 (2011)
V. Fensterl, G.C. Sen, The ISG56/IFIT1 gene family. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 31, 71–78 (2011)
H.H. Danish, S. Goyal, N.K. Taunk, H. Wu, M.S. Moran, B.G. Haffty, Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 (IFIT1) as a prognostic marker for local control in T1-2 N0 breast cancer treated with breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy (BCS + RT). Breast J. 19, 231–239 (2013)
Y. Zhao, A. Altendorf-Hofmann, I. Pozios, P. Camaj, T. Däberitz, X. Wang et al., Elevated interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3 (IFIT3) is a poor prognostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 143, 1061–1068 (2017)
Y. Zhang, Y. Kong, S. Liu, L. Zeng, L. Wan, Z. Zhang, Curcumin induces apoptosis in human leukemic cell lines through an IFIT2-dependent pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 18, 43–50 (2017)
Y. Yang, Y. Zhou, J. Hou, C. Bai, Z. Li, J. Fan et al., Hepatic IFIT3 predicts interferon-α therapeutic response in patients of hepatocellular carcinoma, Hepatology 66, 152– 66 (2017)
M.A. Nieto, R.Y. Huang, R.A. Jackson, J.P. Thiery, EMT: 2016, Cell 166, 21–45 (2016)
H. Hugo, M.L. Ackland, T. Blick, M.G. Lawrence, J.A. Clements, E.D. Williams et al., Epithelial–mesenchymal and mesenchymal–epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 213, 374–383 (2007)
S. Valastyan, R.A. Weinberg, Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms, Cell 147, 275– 92 (2011)
A. Puisieux, T. Brabletz, J. Caramel, Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat. Cell. Biol. 16, 488–494 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81773215) and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (No. 2019XK320002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.T.H. and Z.B.B. contributed to the research design, preparation of the manuscript and collection of the data. Q.C., W.Y.Y., LZR, Y.X.Y. and Z.X.T. designed the research and revised the manuscript. W.W.B. supervised the research. All the authors contributed to the article and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Supplementary Material 1: Fig.1
mRNA expression of IFIT1 in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Transient transduction of IFIT1 knockdown and overexpression constructs was performed, and the mRNA expression of β-catenin was examined. (A) mRNA expression of IFIT1 in 6 PC cell lines. (B) The efficiency of IFIT1 KD in Aspc-1 and Bxpc-3 cells was confirmed by qPCR. (C) The efficiency of IFIT1 overexpression in Aspc-1 and Panc-1 cells was confirmed by qPCR. (D, E) The mRNA expression of β-catenin in transiently transduced cells.
Supplementary Material 2: Table 1
Correlation between IFIT1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics of pancreatic cancer patients in TCGA datasets.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, TH., Zhao, BB., Qin, C. et al. IFIT1 modulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell Oncol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-024-00925-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-024-00925-x