Abstract
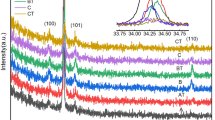
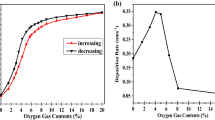
With the purpose of investigating the origin of ferromagnetism (FM), Mn-doped ZnO thin films had been fabricated by radio frequency (rf) magnetron sputtering and subsequent anneal process. The characterization of the Mn-doped ZnO thin films was conducted by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID). With increasing the anneal temperature from 300°C to 700°C for 3 min, the influence on magnetism of the Mn-doped ZnO thin films is slight. While extending the anneal time from 3 to 50 min at 300°C, the influence on magnetism is obvious and the Mn-doped ZnO thin films with 30 min clearly demonstrate FM. Compared with the effect of oxygen vacancy and substitutional Mn2+ on the ferromagnetic behavior, OV plays the main role in inducing FM of the Mn-doped ZnO thin films with good crystal structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando K. Materials science: Seeking room-temperature ferromagnetic semiconductors. Science, 2006, 312: 1883–1885
Chen B, Yu Q X, Gao Q Q, et al. Structural reconstruction and defects transition in mediating room temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO film. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102: 132405
Garcia M A, Merino J M, Fernández Pinel E, et al. Magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Nano Lett, 2007, 7: 1489–1494
Dietl T, Ohno H, Matsukura F, et al. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science, 2000, 287: 1019–1022
Wang Q, Sun Q, Chen G, et al. Vacancy-induced magnetism in ZnO thin films and nanowires. Phys Rev B, 2008, 77: 205411
Lee J K, Nastasi M, Hamby D W, et al. Optical observation of donor-bound excitons in hydrogen-implanted ZnO. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 171102
Tuomisto F, Ranki V, Saarinen K, et al. Evidence of the Zn vacancy acting as the dominant acceptor in n-type ZnO. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 91: 205502
Cui Y, Shi S, Chen L, et al. Hydrogen-doping induced reduction in the phase transition temperature of VO2: A first-principles study. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2015, 17: 20998–21004
Shi S, Gao J, Liu Y, et al. Multi-scale computation methods: Their applications in lithium-ion battery research and development. Chin Phys B, 2016, 25: 018212
Qi B, Ólafsson S, Gíslason H P. Vacancy defect-induced d0 ferromagnetism in undoped ZnO nanostructures: Controversial origin and challenges. Prog Mater Sci, 2017, 90: 45–74
Rainey K, Chess J, Eixenberger J, et al. Defect induced ferromagnetism in undoped ZnO nanoparticles. J Appl Phys, 2014, 115: 17D727
Snure M, Kumar D, Tiwari A. Ferromagnetism in Ni-doped ZnO films: Extrinsic or intrinsic? Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94: 012510
Ahmed Khan Z, Ghosh S. Robust room temperature ferromagnetism in Cu doped ZnO thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 99: 042504
Ilyas U, Rawat R S, Wang Y, et al. Alteration of Mn exchange coupling by oxygen interstitials in ZnO:Mn thin films. Appl Surf Sci, 2012, 258: 6373–6378
Sasikala Devi A A, Roqan I S. Analysis on the energetics, magnetism and electronic properties in a 45° ZnO grain boundary doped with Gd. RSC Adv, 2018, 8: 13850–13856
Sharma P, Gupta A, Rao K V, et al. Ferromagnetism above room temperature in bulk and transparent thin films of Mn-doped ZnO. Nat Mater, 2003, 2: 673–677
Djerdj I, Jaglicić Z, Arcon D, et al. Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Minireview. Nanoscale, 2010, 2: 1096–1104
Gao W, Li Z. ZnO thin films produced by magnetron sputtering. Ceramics Int, 2004, 30: 1155–1159
Kim C, Kim S, Lee C. Effects of rf power and substrate temperature during rf magnetron sputtering on crystal quality of zno thin films. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2005, 44: 8501–8503
Yan H, Wang J, Zhong X, et al. Spatial distribution of manganese and room temperature ferromagnetism in manganese-doped ZnO nanorods. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 19: 142502
Ando K, Saito H, Jin Z, et al. Magneto-optical properties of ZnO-based diluted magnetic semiconductors. J Appl Phys, 2001, 89: 7284–7286
Chattopadhyay S, Neogi S K, Sarkar A, et al. Defects induced ferromagnetism in Mn doped ZnO. J Magn Magn Mater, 2011, 323: 363–368
Chen S, Carraro G, Barreca D, et al. Aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition of Ga-doped ZnO films for energy efficient glazing: Effects of doping concentration on the film growth behaviour and optoelectronic properties. J Mater Chem A, 2015, 3: 13039–13049
Bekermann D, Gasparotto A, Barreca D, et al. Highly oriented ZnO nanorod arrays by a novel plasma chemical vapor deposition process. Cryst Growth Des, 2010, 10: 2011–2018
Sahai A, Goswami N. Probing the dominance of interstitial oxygen defects in ZnO nanoparticles through structural and optical characterizations. Ceramics Int, 2014, 40: 14569–14578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, S., Nasu, N., Zhang, Y. et al. Oxygen vacancy and Mn2+ induced ferromagnetism in Mn-doped ZnO thin films. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62, 1755–1759 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-018-9463-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-018-9463-6