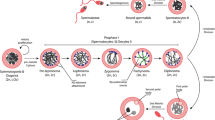
Abstract
Functional telomeres protect chromosome ends and play important roles in stem cell maintenance and differentiation. Short telomeres negatively impact germ cell development and can contribute to age-associated infertility. Moreover, telomere syndrome resulting from mutations of telomerase or telomere-associated genes exhibits short telomeres and reduced fertility. It remains elusive whether and how telomere lengths affect germ cell specification. We report that functional telomere is required for the coordinated germ cell and somatic cell fate decisions. Using telomerase gene Terc deficient mice as a model, we show that short telomeres restrain germ cell specification of epiblast cells but promote differentiation towards somatic lineage. Short telomeres increase chromatin accessibility to elevate TGFβ and MAPK/ERK signaling for somatic cell differentiation. Notably, elevated Fst expression in TGFβ pathway represses the BMP4-pSmad signaling pathway, thus reducing germ cell formation. Re-elongation of telomeres by targeted knock-in of Terc restores normal chromatin accessibility to suppress TGFβ and MAPK signaling, thereby facilitating germ cell formation. Taken together, our data reveal that functional telomeres are required for germ cell specification by repressing TGFβ and MAPK signaling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aramaki, S., Hayashi, K., Kurimoto, K., Ohta, H., Yabuta, Y., Iwanari, H., Mochizuki, Y., Hamakubo, T., Kato, Y., Shirahige, K., et al. (2013). A mesodermal factor, T, specifies mouse germ cell fate by directly activating germline determinants. Dev Cell 27, 516–529.
Aydos, S.E., Elhan, A.H., and Tükün, A. (2005). Is telomere length one of the determinants of reproductive life span? Arch Gynecol Obstet 272, 113–116.
Barbosa, R., Acevedo, L.A., and Marmorstein, R. (2021). The MEK/ERK network as a therapeutic target in human cancer. Mol Cancer Res 19, 361–374.
Blasco, M.A., Lee, H.W., Hande, M.P., Samper, E., Lansdorp, P.M., DePinho, R.A., and Greider, C.W. (1997). Telomere shortening and tumor formation by mouse cells lacking telomerase RNA. Cell 91, 25–34.
Bosman, E.A., Lawson, K.A., Debruyn, J., Beek, L., Francis, A., Schoonjans, L., Huylebroeck, D., and Zwijsen, A. (2006). Smad5 determines murine amnion fate through the control of bone morphogenetic protein expression and signalling levels. Development 133, 3399–3409.
Buenrostro, J.D., Giresi, P.G., Zaba, L.C., Chang, H.Y., and Greenleaf, W.J. (2013). Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA-binding proteins and nucleosome position. Nat Methods 10, 1213–1218.
Cawthon, R.M. (2002). Telomere measurement by quantitative PCR. Nucl Acids Res 30, 47e–47.
Coucouvanis, E., and Martin, G.R. (1999). BMP signaling plays a role in visceral endoderm differentiation and cavitation in the early mouse embryo. Development 126, 535–546.
Criqui, M., Qamra, A., Chu, T.W., Sharma, M., Tsao, J., Henry, D.A., Barsyte-Lovejoy, D., Arrowsmith, C.H., Winegarden, N., Lupien, M., et al. (2020). Telomere dysfunction cooperates with epigenetic alterations to impair murine embryonic stem cell fate commitment. eLife 9, e47333.
Dai, K., Xu, H., Ouyang, N., Li, Y., Yuan, P., Wang, L., Zhao, X., and Wang, W. (2019). Correlation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase single nucleotide polymorphisms with in vitro fertilisation outcomes. J Assist Reprod Genet 36, 517–527.
Darmishonnejad, Z., Zarei-Kheirabadi, F., Tavalaee, M., Zarei-Kheirabadi, M., Zohrabi, D., and Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. (2020). Relationship between sperm telomere length and sperm quality in infertile men. Andrologia 52, e13546.
Fainsod, A., Deißler, K., Yelin, R., Marom, K., Epstein, M., Pillemer, G., Steinbeisser, H., and Blum, M. (1997). The dorsalizing and neural inducing gene follistatin is an antagonist of BMP-4. Mech Dev 63, 39–50.
Fujiwara, T., Dunn, N.R., and Hogan, B.L.M. (2001). Bone morphogenetic protein 4 in the extraembryonic mesoderm is required for allantois development and the localization and survival of primordial germ cells in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 13739–13744.
Grabole, N., Tischler, J., Hackett, J.A., Kim, S., Tang, F., Leitch, H.G., Magnúsdóttir, E., and Surani, M.A. (2013). Prdm14 promotes germline fate and naive pluripotency by repressing FGF signalling and DNA methylation. EMBO Rep 14, 629–637.
Guo, Q., Kumar, T.R., Woodruff, T., Hadsell, L.A., DeMayo, F.J., and Matzuk, M.M. (1998). Overexpression of mouse follistatin causes reproductive defects in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol 12, 96–106.
Hackett, J.A., Zylicz, J.J., and Surani, M.A. (2012). Parallel mechanisms of epigenetic reprogramming in the germline. Trends Genet 28, 164–174.
Hajkova, P., Ancelin, K., Waldmann, T., Lacoste, N., Lange, U.C., Cesari, F., Lee, C., Almouzni, G., Schneider, R., and Surani, M.A. (2008). Chromatin dynamics during epigenetic reprogramming in the mouse germ line. Nature 452, 877–881.
Hayashi, K., Kobayashi, T., Umino, T., Goitsuka, R., Matsui, Y., and Kitamura, D. (2002). SMAD1 signaling is critical for initial commitment of germ cell lineage from mouse epiblast. Mech Dev 118, 99–109.
Hayashi, K., Ogushi, S., Kurimoto, K., Shimamoto, S., Ohta, H., and Saitou, M. (2012). Offspring from oocytes derived from in vitro primordial germ cell-like cells in mice. Science 338, 971–975.
Hayashi, K., Ohta, H., Kurimoto, K., Aramaki, S., and Saitou, M. (2011). Reconstitution of the mouse germ cell specification pathway in culture by pluripotent stem cells. Cell 146, 519–532.
Herrera, E., Samper, E., Martín-Caballero, J., Flores, J.M., Lee, H.W., and Blasco, M.A. (1999). Disease states associated with telomerase deficiency appear earlier in mice with short telomeres. EMBO J 18, 2950–2960.
Hochberg, Y., and Benjamini, Y. (1990). More powerful procedures for multiple significance testing. Statist Med 9, 811–818.
Horbelt, D., Denkis, A., and Knaus, P. (2012). A portrait of transforming growth factor β superfamily signalling: background matters. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44, 469–474.
Huang, J., Wang, F., Okuka, M., Liu, N., Ji, G., Ye, X., Zuo, B., Li, M., Liang, P., Ge, W.W., et al. (2011). Association of telomere length with authentic pluripotency of ES/iPS cells. Cell Res 21, 779–792.
Jia, S., Ren, Z., Li, X., Zheng, Y., and Meng, A. (2008). smad2 and smad3 are required for mesendoderm induction by transforming growth factor-β/nodal signals in zebrafish. J Biol Chem 283, 2418–2426.
Kalmbach, K.H., Antunes, D.M.F., Kohlrausch, F., and Keefe, D.L. (2015). Telomeres and female reproductive aging. Semin Reprod Med 33, 389–395.
Keefe, D.L., and Liu, L. (2009). Telomeres and reproductive aging. Reprod Fertil Dev 21, 10–14.
Kimura, T., Kaga, Y., Ohta, H., Odamoto, M., Sekita, Y., Li, K., Yamano, N., Fujikawa, K., Isotani, A., Sasaki, N., et al. (2014). Induction of primordial germ cell-like cells from mouse embryonic stem cells by ERK signal inhibition. Stem Cells 32, 2668–2678.
Kurimoto, K., Yabuta, Y., Hayashi, K., Ohta, H., Kiyonari, H., Mitani, T., Moritoki, Y., Kohri, K., Kimura, H., Yamamoto, T., et al. (2015). Quantitative dynamics of chromatin remodeling during germ cell specification from mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 16, 517–532.
Lawson, K.A., Dunn, N.R., Roelen, B.A.J., Zeinstra, L.M., Davis, A.M., Wright, C.V.E., Korving, J.P.W.F.M., and Hogan, B.L.M. (1999). Bmp4 is required for the generation of primordial germ cells in the mouse embryo. Genes Dev 13, 424–436.
Lee, H.W., Blasco, M.A., Gottlieb, G.J., Horner II, J.W., Greider, C.W., and DePinho, R.A. (1998). Essential role of mouse telomerase in highly proliferative organs. Nature 392, 569–574.
Li, Z., Fei, T., Zhang, J., Zhu, G., Wang, L., Lu, D., Chi, X., Teng, Y., Hou, N., Yang, X., et al. (2012). BMP4 signaling acts via dual-specificity phosphatase 9 to control ERK activity in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 10, 171–182.
Liu, L., Bailey, S.M., Okuka, M., Muñoz, P., Li, C., Zhou, L., Wu, C., Czerwiec, E., Sandler, L., Seyfang, A., et al. (2007). Telomere lengthening early in development. Nat Cell Biol 9, 1436–1441.
Liu, L., Blasco, M.A., and Keefe, D.L. (2002). Requirement of functional telomeres for metaphase chromosome alignments and integrity of meiotic spindles. EMBO Rep 3, 230–234.
Liu, L., Franco, S., Spyropoulos, B., Moens, P.B., Blasco, M.A., and Keefe, D.L. (2004). Irregular telomeres impair meiotic synapsis and recombination in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 6496–6501.
Liu, N., Yin, Y., Wang, H., Zhou, Z., Sheng, X., Fu, H., Guo, R., Wang, H., Yang, J., Gong, P., et al. (2019). Telomere dysfunction impairs epidermal stem cell specification and differentiation by disrupting BMP/pSmad/P63 signaling. PLoS Genet 15, e1008368.
M’kacher, R., Colicchio, B., Marquet, V., Borie, C., Najar, W., Hempel, W. M., Heidingsfelder, L., Oudrhiri, N., Al Jawhari, M., Wilhelm-Murer, N., et al. (2021). Telomere aberrations, including telomere loss, doublets, and extreme shortening, are increased in patients with infertility. Fertil Steril 115, 164–173.
Magnúsdóttir, E., Dietmann, S., Murakami, K., Günesdogan, U., Tang, F., Bao, S., Diamanti, E., Lao, K., Gottgens, B., and Azim Surani, M. (2013). A tripartite transcription factor network regulates primordial germ cell specification in mice. Nat Cell Biol 15, 905–915.
Magnúsdóttir, E., and Surani, M.A. (2014). How to make a primordial germ cell. Development 141, 245–252.
Mangaonkar, A.A., and Patnaik, M.M. (2018). Short telomere syndromes in clinical practice: bridging bench and bedside. Mayo Clinic Proc 93, 904–916.
Mansour, A.A.F., Gafni, O., Weinberger, L., Zviran, A., Ayyash, M., Rais, Y., Krupalnik, V., Zerbib, M., Amann-Zalcenstein, D., Maza, I., et al. (2012). The H3K27 demethylase Utx regulates somatic and germ cell epigenetic reprogramming. Nature 488, 409–413.
Martínez, P., and Blasco, M.A. (2011). Telomeric and extra-telomeric roles for telomerase and the telomere-binding proteins. Nat Rev Cancer 11, 161–176.
Miyauchi, H., Ohta, H., Nagaoka, S., Nakaki, F., Sasaki, K., Hayashi, K., Yabuta, Y., Nakamura, T., Yamamoto, T., and Saitou, M. (2017). Bone morphogenetic protein and retinoic acid synergistically specify female germ-cell fate in mice. EMBO J 36, 3100–3119.
Morgani, S.M., and Hadjantonakis, A.K. (2021). Quantitative analysis of signaling responses during mouse primordial germ cell specification. Biol Open 10.
Nakaki, F., Hayashi, K., Ohta, H., Kurimoto, K., Yabuta, Y., and Saitou, M. (2013). Induction of mouse germ-cell fate by transcription factors in vitro. Nature 501, 222–226.
Ohinata, Y., Ohta, H., Shigeta, M., Yamanaka, K., Wakayama, T., and Saitou, M. (2009). A signaling principle for the specification of the germ cell lineage in mice. Cell 137, 571–584.
Ohinata, Y., Payer, B., O’Carroll, D., Ancelin, K., Ono, Y., Sano, M., Barton, S.C., Obukhanych, T., Nussenzweig, M., Tarakhovsky, A., et al. (2005). Blimp1 is a critical determinant of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nature 436, 207–213.
Picelli, S., Björklund, A.K., Reinius, B., Sagasser, S., Winberg, G., and Sandberg, R. (2014a). Tn5 transposase and tagmentation procedures for massively scaled sequencing projects. Genome Res 24, 2033–2040.
Picelli, S., Faridani, O.R., Björklund, A.K., Winberg, G., Sagasser, S., and Sandberg, R. (2014b). Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat Protoc 9, 171–181.
Plath, K., Fang, J., Mlynarczyk-Evans, S.K., Cao, R., Worringer, K.A., Wang, H., de la Cruz, C.C., Otte, A.P., Panning, B., and Zhang, Y. (2003). Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in X inactivation. Science 300, 131–135.
Poon, S.S.S., Martens, U.M., Ward, R.K., and Lansdorp, P.M. (1999). Telomere length measurements using digital fluorescence microscopy. Cytometry 36, 267–278.
Reig-Viader, R., Garcia-Caldés, M., and Ruiz-Herrera, A. (2016). Telomere homeostasis in mammalian germ cells: a review. Chromosoma 125, 337–351.
Reik, W., and Surani, M.A. (2015). Germline and pluripotent stem cells. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7, a019422.
Robinson, L.R.G. Jr, Pimentel, R., Wang, F., Kramer, Y.G., Gonullu, D.C., Agarwal, S., Navarro, P.A., McCulloh, D., and Keefe, D.L. (2020). Impaired reproductive function and fertility preservation in a woman with a dyskeratosis congenita. J Assist Reprod Genet 37, 1221–1225.
Rudolph, K.L., Chang, S., Lee, H.W., Blasco, M., Gottlieb, G.J., Greider, C., and DePinho, R.A. (1999). Longevity, stress response, and cancer in aging telomerase-deficient mice. Cell 96, 701–712.
Saitou, M. (2009). Specification of the germ cell lineage in mice. Front Biosci 14, 1068–1087.
Saitou, M., and Miyauchi, H. (2016). Gametogenesis from pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 18, 721–735.
Savage, S.A., and Bertuch, A.A. (2010). The genetics and clinical manifestations of telomere biology disorders. Genet Med 12, 753–764.
Schoeftner, S., Blanco, R., Lopez de Silanes, I., Muñoz, P., Gómez-López, G., Flores, J.M., and Blasco, M.A. (2009). Telomere shortening relaxes X chromosome inactivation and forces global transcriptome alterations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 19393–19398.
Seisenberger, S., Andrews, S., Krueger, F., Arand, J., Walter, J., Santos, F., Popp, C., Thienpont, B., Dean, W., and Reik, W. (2012). The dynamics of genome-wide DNA methylation reprogramming in mouse primordial germ cells. Mol Cell 48, 849–862.
Shaul, Y.D., and Seger, R. (2007). The MEK/ERK cascade: from signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Cell Res 1773, 1213–1226.
Sun, Y., Liu, W.Z., Liu, T., Feng, X., Yang, N., and Zhou, H.F. (2015). Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Receptors Signal Transduction 35, 600–604.
Tian, C., Liu, L., Ye, X., Fu, H., Sheng, X., Wang, L., Wang, H., Heng, D., and Liu, L. (2019). Functional oocytes derived from granulosa cells. Cell Rep 29, 4256–4267.e9.
Uysal, F., Kosebent, E.G., Toru, H.S., and Ozturk, S. (2021). Decreased expression of TERT and telomeric proteins as human ovaries age may cause telomere shortening. J Assist Reprod Genet 38, 429–441.
Vasilopoulos, E., Fragkiadaki, P., Kalliora, C., Fragou, D., Docea, A.O., Vakonaki, E., Tsoukalas, D., Calina, D., Buga, A.M., Georgiadis, G., et al. (2019). The association of female and male infertility with telomere length (Review). Int J Mol Med 44, 375–389.
Wang, P., Miao, Y., Li, X.H., Zhang, N., Wang, Q., Yue, W., Sun, S.C., Xiong, B., Qiao, J., and Li, M. (2021). Proteome landscape and spatial map of mouse primordial germ cells. Sci China Life Sci 64, 966–981.
Wen, L., Liu, Q., Xu, J., Liu, X., Shi, C., Yang, Z., Zhang, Y., Xu, H., Liu, J., Yang, H., et al. (2020). Recent advances in mammalian reproductive biology. Sci China Life Sci 63, 18–58.
Wu, J., Huang, B., Chen, H., Yin, Q., Liu, Y., Xiang, Y., Zhang, B., Liu, B., Wang, Q., Xia, W., et al. (2016). The landscape of accessible chromatin in mammalian preimplantation embryos. Nature 534, 652–657.
Wu, Q., Fukuda, K., Weinstein, M., Graff, J.M., and Saga, Y. (2015). SMAD2 and p38 signaling pathways act in concert to determine XY primordial germ cell fate in mice. Development 142, 575–586.
Ying, Y., Liu, X.M., Marble, A., Lawson, K.A., and Zhao, G.Q. (2000). Requirement of Bmp8b for the generation of primordial germ cells in the mouse. Mol Endocrinol 14, 1053–1063.
Zhang, J., Zhang, M., Acampora, D., Vojtek, M., Yuan, D., Simeone, A., and Chambers, I. (2018a). OTX2 restricts entry to the mouse germline. Nature 562, 595–599.
Zhang, M., Leitch, H.G., Tang, W.W.C., Festuccia, N., Hall-Ponsele, E., Nichols, J., Surani, M.A., Smith, A., and Chambers, I. (2018b). Esrrb complementation rescues development of nanog-null germ cells. Cell Rep 22, 332–339.
Zhang, Y., Feng, X.H., Wu, R.Y., and Derynck, R. (1996). Receptor-associated Mad homologues synergize as effectors of the TGF-β response. Nature 383, 168–172.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by China National Key R&D Program (2018YFA0107002, 2018YFC1003004) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32030033, 31430052). We thank Huasong Wang and Jie Li from Nankai University for assisting the experiments and discussion, and Haoze Vincent Yu from University of California San Diego for providing Tn5 enzyme and assisting the sample preparation of ATAC-seq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. For mice research, we confirmed with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 (as revised in 2008) concerning Animal Rights.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, C., Heng, D., Zhao, N. et al. Short telomeres impede germ cell specification by upregulating MAPK and TGFβ signaling. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 324–339 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2151-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2151-0