Abstract
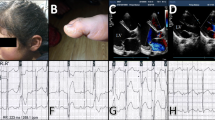
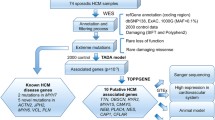
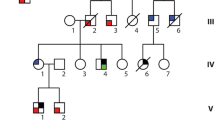
To reveal genetic risks of early-onset sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) patients in the Chinese Han population, we enlisted 363 DCM cases and 414 healthy controls. Whole-exome sequencing and phenotypic characterization were conducted. In total, we identified 26 loss-of-function (LOF) candidates and 66 pathogenic variants from 33 genes, most of which were novel. The deleterious variants can account for 25.07% (91/363) of all patients. Furthermore, rare missense variants in 21 genes were found to be significantly associated with DCM in burden tests. Other than rare variants, twelve common SNPs were significantly associated with an increased risk of DCM in allele-based genetic model association analysis. Of note, in the cumulative risk model, high-risk subjects had a 3.113-fold higher risk of developing DCM than low-risk subjects. Also, DCM in the high-risk group had a younger age of onset than that in the low-risk group. In terms of cardiac function, the mean left ventricular ejection fraction of patients with the deleterious variants was lower than those without (27.73%±10.02% vs. 30.61%±10.85%, P=0.026). To conclude, we mapped a comprehensive atlas of genetic risks in Chinese patients with DCM that might lead to new insights into the mechanisms and risk stratification for DCM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bozkurt, B., Colvin, M., Cook, J., Cooper, L.T., Deswal, A., Fonarow, G. C., Francis, G.S., Lenihan, D., Lewis, E.F., McNamara, D.M., et al. (2016). Current diagnostic and treatment strategies for specific dilated cardiomyopathies: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 134, e579–e646.
Brofferio, A., Sachdev, V., Hannoush, H., Marshall, J.D., Naggert, J.K., Sidenko, S., Noreuil, A., Sirajuddin, A., Bryant, J., Han, J.C., et al. (2017). Characteristics of cardiomyopathy in Alström syndrome: Prospective single-center data on 38 patients. Mol Genets Metab 121, 336–343.
Domínguez, F., Cuenca, S., Bilińska, Z., Toro, R., Villard, E., Barriales-Villa, R., Ochoa, J.P., Asselbergs, F., Sammani, A., Franaszczyk, M., et al. (2018). Dilated cardiomyopathy due to BLC2-associated athanogene 3 (BAG3) mutations. J Am Coll Cardiol 72, 2471–2481.
Elliott, P., Andersson, B., Arbustini, E., Bilinska, Z., Cecchi, F., Charron, P., Dubourg, O., Kühl, U., Maisch, B., McKenna, W.J., et al. (2008). Classification of the cardiomyopathies: a position statement from the European Society Of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J 29, 270–276.
Elming, M.B., Thøgersen, A.M., Videbæk, L., Bruun, N.E., Eiskjær, H., Haarbo, J., Egstrup, K., Gustafsson, F., Hastrup Svendsen, J., Høfsten, D.E., et al. (2019). Duration of heart failure and effect of defibrillator implantation in patients with nonischemic systolic heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 12, e006022.
Esslinger, U., Garnier, S., Korniat, A., Proust, C., Kararigas, G., Muller-Nurasyid, M., Empana, J.P., Morley, M.P., Perret, C., Stark, K., et al. (2017). Exome-wide association study reveals novel susceptibility genes to sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy. PLoS ONE 12, e0172995.
Gigli, M., Merlo, M., Graw, S.L., Barbati, G., Rowland, T.J., Slavov, D.B., Stolfo, D., Haywood, M.E., Dal Ferro, M., Altinier, A., et al. (2019). Genetic risk of arrhythmic phenotypes in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 74, 1480–1490.
Gulati, A., Jabbour, A., Ismail, T.F., Guha, K., Khwaja, J., Raza, S., Morarji, K., Brown, T.D.H., Ismail, N.A., Dweck, M.R., et al. (2013). Association of fibrosis with mortality and sudden cardiac death in patients with nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. JAMA 309, 896–908.
Haas, J., Frese, K.S., Peil, B., Kloos, W., Keller, A., Nietsch, R., Feng, Z., Müller, S., Kayvanpour, E., Vogel, B., et al. (2015). Atlas of the clinical genetics of human dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 36, 1123–1135.
Han, F., and Pan, W. (2010). A data-adaptive sum test for disease association with multiple common or rare variants. Hum Hered 70, 42–54.
Hasselberg, N.E., Haland, T.F., Saberniak, J., Brekke, P.H., Berge, K.E., Leren, T.P., Edvardsen, T., and Haugaa, K.H. (2018). Lamin A/C cardiomyopathy: young onset, high penetrance, and frequent need for heart transplantation. Eur Heart J 39, 853–860.
Hearn, T. (2019). ALMS1 and Alström syndrome: a recessive form of metabolic, neurosensory and cardiac deficits. J Mol Med 97, 1–17.
Herman, D.S., Lam, L., Taylor, M.R.G., Wang, L., Teekakirikul, P., Christodoulou, D., Conner, L., DePalma, S.R., McDonough, B., Sparks, E., et al. (2012). Truncations of titin causing dilated cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 366, 619–628.
Hershberger, R.E., Hedges, D.J., and Morales, A. (2013). Dilated cardiomyopathy: the complexity of a diverse genetic architecture. Nat Rev Cardiol 10, 531–547.
Hobbs, F.D.R., Roalfe, A.K., Davis, R.C., Davies, M.K., and Hare, R. (2007). Prognosis of all-cause heart failure and borderline left ventricular systolic dysfunction: 5 year mortality follow-up of the Echocardiographic Heart of England Screening Study (ECHOES). Eur Heart J 28, 1128–1134.
Horvat, C., Johnson, R., Lam, L., Munro, J., Mazzarotto, F., Roberts, A.M., Herman, D.S., Parfenov, M., Haghighi, A., McDonough, B., et al. (2019). A gene-centric strategy for identifying disease-causing rare variants in dilated cardiomyopathy. Genet Med 21, 133–143.
Madsen, B.E., and Browning, S.R. (2009). A groupwise association test for rare mutations using a weighted sum statistic. PLoS Genet 5, e1000384.
Mazzarotto, F., Tayal, U., Buchan, R.J., Midwinter, W., Wilk, A., Whiffin, N., Govind, R., Mazaika, E., de Marvao, A., Dawes, T.J.W., et al. (2020). Reevaluating the genetic contribution of monogenic dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 141, 387–398.
McNally, E.M., and Mestroni, L. (2017). Dilated cardiomyopathy: genetic determinants and mechanisms. Circ Res 121, 731–748.
Meder, B., Rühle, F., Weis, T., Homuth, G., Keller, A., Franke, J., Peil, B., Lorenzo Bermejo, J., Frese, K., Huge, A., et al. (2014). A genome-wide association study identifies 6p21 as novel risk locus for dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 35, 1069–1077.
Ortiz-Genga, M.F., Cuenca, S., Dal Ferro, M., Zorio, E., Salgado-Aranda, R., Climent, V., Padrón-Barthe, L., Duro-Aguado, I., Jiménez-Jáimez, J., Hidalgo-Olivares, V.M., et al. (2016). Truncating FLNC mutations are associated with high-risk dilated and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies. J Am Coll Cardiol 68, 2440–2451.
Pirruccello, J.P., Bick, A., Wang, M., Chaffin, M., Friedman, S., Yao, J., Guo, X., Venkatesh, B.A., Taylor, K.D., Post, W.S., et al. (2020). Analysis of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in 36,000 individuals yields genetic insights into dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Commun 11, 2254.
Pua, C.J., Bhalshankar, J., Miao, K., Walsh, R., John, S., Lim, S.Q., Chow, K., Buchan, R., Soh, B.Y., Lio, P.M., et al. (2016). Development of a comprehensive sequencing assay for inherited cardiac condition genes. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 9, 3–11.
Pugh, T.J., Kelly, M.A., Gowrisankar, S., Hynes, E., Seidman, M.A., Baxter, S.M., Bowser, M., Harrison, B., Aaron, D., Mahanta, L.M., et al. (2014). The landscape of genetic variation in dilated cardiomyopathy as surveyed by clinical DNA sequencing. Genet Med 16, 601–608.
Purcell, S., Neale, B., Todd-Brown, K., Thomas, L., Ferreira, M.A.R., Bender, D., Maller, J., Sklar, P., de Bakker, P.I.W., Daly, M.J., et al. (2007). PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81, 559–575.
Roberts, A.M., Ware, J.S., Herman, D.S., Schafer, S., Baksi, J., Bick, A.G., Buchan, R.J., Walsh, R., John, S., Wilkinson, S., et al. (2015). Integrated allelic, transcriptional, and phenomic dissection of the cardiac effects of titin truncations in health and disease. Sci Transl Med 7, 270ra6.
Roncarati, R., Viviani Anselmi, C., Krawitz, P., Lattanzi, G., von Kodolitsch, Y., Perrot, A., di Pasquale, E., Papa, L., Portararo, P., Columbaro, M., et al. (2013). Doubly heterozygous LMNA and TTN mutations revealed by exome sequencing in a severe form of dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Hum Genet 21, 1105–1111.
Shenje, L.T., Andersen, P., Halushka, M.K., Lui, C., Fernandez, L., Collin, G.B., Amat-Alarcon, N., Meschino, W., Cutz, E., Chang, K., et al. (2014). Mutations in Alström protein impair terminal differentiation of cardiomyocytes. Nat Commun 5, 3416.
Szklarczyk, D., Gable, A.L., Lyon, D., Junge, A., Wyder, S., Huerta-Cepas, J., Simonovic, M., Doncheva, N.T., Morris, J.H., Bork, P., et al. (2019). STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 47, D607–D613.
Tobita, T., Nomura, S., Fujita, T., Morita, H., Asano, Y., Onoue, K., Ito, M., Imai, Y., Suzuki, A., Ko, T., et al. (2018). Genetic basis of cardiomyopathy and the genotypes involved in prognosis and left ventricular reverse remodeling. Sci Rep 8, 1998.
Vasilescu, C., Ojala, T.H., Brilhante, V., Ojanen, S., Hinterding, H.M., Palin, E., Alastalo, T.P., Koskenvuo, J., Hiippala, A., Jokinen, E., et al. (2018). Genetic basis of severe childhood-onset cardiomyopathies. J Am Coll Cardiol 72, 2324–2338.
Villard, E., Perret, C., Gary, F., Proust, C., Dilanian, G., Hengstenberg, C., Ruppert, V., Arbustini, E., Wichter, T., Germain, M., et al. (2011). A genome-wide association study identifies two loci associated with heart failure due to dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 32, 1065–1076.
Walsh, R., Thomson, K.L., Ware, J.S., Funke, B.H., Woodley, J., McGuire, K.J., Mazzarotto, F., Blair, E., Seller, A., Taylor, J.C., et al. (2017). Reassessment of Mendelian gene pathogenicity using 7,855 cardiomyopathy cases and 60,706 reference samples. Genet Med 19, 192–203.
Weintraub, R.G., Semsarian, C., and Macdonald, P. (2017). Dilated cardiomyopathy. Lancet 390, 400–414.
Writing Committee, M., Yancy, C.W., Jessup, M., Bozkurt, B., Butler, J., Casey Jr, D.E., Drazner, M.H., Fonarow, G.C., Geraci, S.A., Horwich, T., et al. (2013). 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure. Circulation 128, e240–e327.
Zawistowski, M., Gopalakrishnan, S., Ding, J., Li, Y., Grimm, S., and Zöllner, S. (2010). Extending rare-variant testing strategies: analysis of noncoding sequence and imputed genotypes. Am J Hum Genet 87, 604–617.
Ziaeian, B., and Fonarow, G.C. (2016). Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 13, 368–378.
Zmyslowska, A., Borowiec, M., Antosik, K., Ploski, R., Ciechanowska, M., Iwaniszewska, B., Jakubiuk-Tomaszuk, A., Janczyk, W., Krawczynski, M., Salmonowicz, B., et al. (2016). Genetic evaluation of patients with Alström syndrome in the Polish population. Clin Genet 89, 448–453.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0909400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91439203, 81630010 and 91839302), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (2017SHZDZX01), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2015ZDTD044 and 2016JCTD117), the Graduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Funds of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (2018JYCXJJ004), and Tongji Hospital Clinical Research Flagship Program (2019CR207 and 2019YBKY019). We gratefully acknowledge all the participants and funding sources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Tongji Hospital affiliated with the Tongji Medical School of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Conference on Harmonization Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants before they were enrolled in the study.
Electronic Supplementary Material
11427_2020_1951_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Whole-exome sequencing reveals genetic risks of early-onset sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy in the Chinese Han population
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, L., Wu, D., Sun, Y. et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals genetic risks of early-onset sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy in the Chinese Han population. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 770–780 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1951-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1951-4