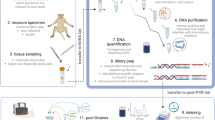
Abstract
Purpose
Viruses are the largest genetic repository and most diverse host-associated replicating organisms in a wide range of ecosystems in the entire biosphere. Although playing crucial roles in numerous processes such as nutrient cycles, viral shunt, and population control within marine ecosystems, viral communities continue to be the least explored biological entities, particularly in extreme marine habitats. Therefore, details about the viral diversity and their metabolic potential from Arctic sediments has great importance.
Methods
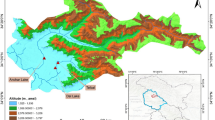
Sediment samples were collected from two Arctic fjords, Kongsfjorden and Krossfjorden, in Svalbard. Viral nucleic acids were extracted from both fjord sediments after a pre-processing step. Illumina Novaseq based shotgun sequencing was performed and bioinformatic analysis was done to explore viral communities and their functional potential.
Results
An array of DNA and RNA viruses especially bacteriophages along with viruses infecting algae, plants, molluscs, shrimps, fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, humans, and other mammals were detected from both fjords. The double-stranded DNA viruses were the most abundant (Siphoviridae, Podoviridae, Myoviridae, and Phycodnaviridae), followed by single-stranded DNA (Inoviridae) and RNA (Retroviridae and Betaflexiviridae) viruses from both metavirome. Functional analysis explored genes encoding virus structures, enzymes for phage replication, integration and excision and proteins related to phage regulation of gene expression.
Conclusions
Fjord metavirome analysis revealed the occurrence of virus groups endemic to Arctic freshwater and marine habitats along with an extra pool of unclassified or unassigned virus reads. Viruses infecting a variety of bacterial groups, and other higher trophic levels in fjord environments were explored. Functional annotation revealed the abundance of phage-related structural genes and metabolic genes. Comparative analysis revealed the abundance of dsDNA viruses from Caudovirales (Myoviridae, Podoviridae and Siphoviridae) in all the analysed Arctic samples in different proportions. The present study enhances our understanding of viral diversity and their metabolic potential in Arctic fjord sediments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre de Cárcer D, López-Bueno A, Pearce DA, Alcamí A (2015) Biodiversity and distribution of polar freshwater DNA viruses. Sci Adv 1(5). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1400127
Anesio AM, Mindl B, Laybourn-Parry J, Hodson AJ, Sattler B (2007) Viral dynamics in cryoconite holes on a high Arctic glacier (Svalbard). J Geophys Res-Biogeo 112:G04S31. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JG000350
Angly FE, Felts B, Breitbart M, Salamon P, Edwards RA et al (2006) The marine viromes of four oceanic regions. PLoS Biol 4(11). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040368
Angly FE, Willner D, Prieto-Davó A, Edwards RA, Schmieder R et al (2009) The GAAS metagenomic tool and its estimations of viral and microbial average genome size in four major biomes. PLoS Comput Biol 5(12). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000593
Aylward FO, Boeuf D, Mende DR, Wood-Charlson EM, Vislova A, Eppley JM, Romano AE, DeLong EF (2017) Diel cycling and long-term persistence of viruses in the ocean’s euphotic zone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114(43):11446–11451. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1714821114
Ballinger MJ, Bruenn JA, Hay J, Czechowski D, Taylor DJ (2014) Discovery and evolution of bunyavirids in Arctic phantom midges and ancient bunyavirid-like sequences in insect genomes. J Virol 88(16):8783–8794. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00531-14
Bellas CM, Anesio AM, Barker G (2015) Analysis of virus genomes from glacial environments reveals novel virus groups with unusual host interactions. Front Microbiol 6:656. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00656
Bellas CM, Anesio AM (2013) High diversity and potential origins of T4-type bacteriophages on the surface of Arctic glaciers. Extremophiles 17(5):861–870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0569-x
Bench SR, Hanson TE, Williamson KE, Ghosh D, Radosovich M, Wang K, Wommack KE (2007) Metagenomic characterization of Chesapeake Bay virioplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(23):7629–7641. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00938-07
Berube PM, Biller SJ, Hackl T, Hogle SL, Satinsky BM, Becker JW et al (2018) Single cell genomes of Prochlorococcus, Synechococcus, and sympatric microbes from diverse marine environments. Sci Data 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.154
Breitbart M, Miyake JH, Rohwer F (2004) Global distribution of nearly identical phage-encoded DNA sequences. FEMS Microbiol Lett 236(2):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2004.05.042
Breitbart M, Salamon P, Andresen B, Mahaffy JM, Segall AM, Mead D, Azam F, Rohwer F (2002) Genomic analysis of uncultured marine viral communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(22):14250–14255. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.202488399
Brum JR, Sullivan MB (2015) Rising to the challenge: accelerated pace of discovery transforms marine virology. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3404
Cai L, Jørgensen BB, Suttle CA, He M, Cragg BA, Jiao N, Zhang R (2019) Active and diverse viruses persist in the deep sub-seafloor sediments over thousands of years. ISME J 13(7):1857–1864. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0397-9
Cai L, Zhang R, He Y, Feng X, Jiao N (2016) Metagenomic Analysis of virioplankton of the subtropical Jiulong river estuary. China Viruses 8(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8020035
Carreira C, Larsen M, Glud RN, Brussaard C, Middelboe M (2013) Heterogeneous distribution of prokaryotes and viruses at the microscale in a tidal sediment. Aquat Biol 69(3):183–192. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame01639
Chen F, Suttle CA (1995) Amplification of DNA polymerase gene fragments from viruses infecting microalgae. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(4):1274–1278. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.4.1274-1278.1995
Convey P, Gibson JA, Hillenbrand CD, Hodgson DA, Pugh PJ, Smellie JL, Stevens MI (2008) Antarctic terrestrial life–challenging the history of the frozen continent? Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 83(2):103–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2008.00034.x
Corinaldesi C, Tangherlini M, Dell’Anno A (2017) From virus isolation to metagenome generation for investigating viral diversity in deep-sea sediments. Sci Rep 7:8355. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08783-4
Culley A (2018) New insight into the RNA aquatic virosphere via viromics. Virus Res 244:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2017.11.008
Culley AI, Mueller JA, Belcaid M, Wood-Charlson EM, Poisson G, Steward GF (2014) The characterization of RNA viruses in tropical seawater using targeted PCR and metagenomics. MBio 5(3):e01210–e01214. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01210-14
Danovaro R, Dell’Anno A, Corinaldesi C, Magagnini M, Noble R, Tamburini C, Weinbauer M (2008) Major viral impact on the functioning of benthic deep-sea ecosystems. Nature 454(7208):1084–1087. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07268
Dávila-Ramos S, Castelán-Sánchez HG, Martínez-Ávila L, Sánchez-Carbente MDR, Peralta R, Hernández-Mendoza A, Dobson ADW, Gonzalez RA, Pastor N, Batista-García RA (2019) A Review on viral metagenomics in extreme environments. Front Microbiol 10:2403. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02403
Dinsdale EA, Edwards RA, Hall D, Angly F, Breitbart M et al (2008) Functional metagenomic profiling of nine biomes. Nature 452(7187):629–632. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06810
Dudley JP, Hoberg EP, Jenkins EJ, Parkinson AJ (2015) Climate change in the North American Arctic: A One Health perspective. EcoHealth 12(4):713–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-015-1036-1
Dwivedi B, Xue B, Lundin D, Edwards RA, Breitbart M (2013) A bioinformatic analysis of ribonucleotide reductase genes in phage genomes and metagenomes. BMC Evol Biol 13:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-13-33
Edwards RA, Rohwer F (2005) Viral Metagenomics Nature Rev Microbiol 3:504–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1163
Endo H, Blanc-Mathieu R, Li Y, Salazar G, Henry N, Labadie K, de Vargas C, Sullivan MB, Bowler C, Wincker P, Karp-Boss L, Sunagawa S, Ogata H (2020) Biogeography of marine giant viruses reveals their interplay with eukaryotes and ecological functions. Nat Ecol Evol 4:1639–1649. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-020-01288-w
Filee J, Tetart F, Suttle CA, Krisch HM (2005) Marine T4-type bacteriophages, a ubiquitous component of the dark matter of the biosphere. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(35):12471–12476. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0503404102
Gao C, Xia J, Zhou X, Liang Y, Jiang Y, Wang M, Shao H, Shi X, Guo C, He H, Wang H, He J, Hu D, Wang X, Zhao J, Zhang YZ, Sung YY, Mok WJ, Wong LL, McMinn A, Suttle CA, Wang M (2021) Viral characteristics of the warm Atlantic and cold Arctic water masses in the Nordic Seas. Appl Environ Microbiol 87(22). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01160-21
Gass JD Jr, Dusek RJ, Hall JS, Hallgrimsson GT, Halldórsson HP et al (2023) Global dissemination of Influenza A virus is driven by wild bird migration through arctic and subarctic zones. Mol Ecol 32(1):198–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.16738
Gass JD Jr, Kellogg HK, Hill NJ, Puryear WB, Nutter FB, Runstadler JA (2022) Epidemiology and ecology of Influenza A viruses among wildlife in the Arctic. Viruses 14(7):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14071531
Gudbergsdóttir SR, Menzel P, Krogh A, Young M, Peng X (2016) Novel viral genomes identified from six metagenomes reveal wide distribution of archaeal viruses and high viral diversity in terrestrial hot springs. Environ Microbiol 18(3):863–874. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13079
Guidi L, Chaffron S, Bittner L, Eveillard D, Larhlimi A, Roux S et al (2016) Plankton networks driving carbon export in the oligotrophic ocean. Nature 532:465–470. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16942
Huson DH, Beier S, Flade I, Górska A, El-Hadidi M, Mitra S, Ruscheweyh HJ, Tappu R (2016) MEGAN Community Edition - interactive exploration and analysis of large-scale microbiome sequencing data. PLoS Comput Biol 12(6):e1004957. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004957
Jaiani E, Kusradze I, Kokashvili T, Geliashvili N, Janelidze N et al (2020) Microbial diversity and phage-host interactions in the Georgian coastal area of the Black Sea revealed by whole genome metagenomic sequencing. Mar Drugs 18(11):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18110558
Jin M, Guo X, Zhang R, Qu W, Gao B, Zeng R (2019) Diversities and potential biogeochemical impacts of mangrove soil viruses. Microbiome 7(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0675-9
John SG, Mendez CB, Deng L, Poulos B, Kauffman AK, Kern S, Brum J, Polz MF, Boyle EA, Sullivan MB (2011) A simple and efficient method for concentration of ocean viruses by chemical flocculation. Environ Microbiol Rep 3(2):195–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00208.x
Kabeer FA, Jabir T, Krishnan KP, Abdulla MH (2019) Metagenomic data of fungal community in Kongsfjorden, Arctic using Illumina next generation sequencing. Data Brief 22:195–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.12.026
Kachiprath B, Puthumana J, Gopi J, Solomon S, Krishnan KP, Philip R (2018) Amplicon sequencing based profiling of bacterial diversity from Krossfjorden, Arctic. Data Brief 21:2522–2525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.11.101
Kachiprath B, Solomon S, Gopi J, Jayachandran PR, Thajudeen J, Sarasan M, Mohan AS, Puthumana J, Chaithanya ER, Philip R (2024) Exploring bacterial diversity in Arctic fjord sediments: a 16S rRNA–based metabarcoding portrait. Braz J Microbiol 55:499–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-023-01217-6
Labonté JM, Suttle CA (2013) Previously unknown and highly divergent ssDNA viruses populate the oceans. ISME J 7(11):2169–2177. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.110
Lang AS, Rise ML, Culley AI, Steward GF (2009) RNA viruses in the sea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33(2):295–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00132.x
Lauro FM, DeMaere MZ, Yau S, Brown MV, Ng C, Wilkins D, Raftery MJ, Gibson JA, Andrews-Pfannkoch C, Lewis M, Hoffman JM, Thomas T, Cavicchioli R (2011) An integrative study of a meromictic lake ecosystem in Antarctica. ISME J 5(5):879–895. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.185
Lee MM, Jaspers VLB, Gabrielsen GW, Jenssen BM, Ciesielski TM, Mortensen ÅK, Lundgren SS, Waugh CA (2020) Evidence of avian influenza virus in seabirds breeding on a Norwegian high-Arctic Archipelago. BMC Vet Res 16(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-020-2265-2
Liang Y, Wang L, Wang Z, Zhao J, Yang Q, Wang M, Yang K, Zhang L, Jiao N, Zhang Y (2019) Metagenomic analysis of the diversity of DNA viruses in the surface and deep sea of the south China Sea. Front Microbiol 10:1951. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01951
Lin X, Zhang L, Liu Y, Li Y (2017) Bacterial and archaeal community structure of pan-Arctic Ocean sediments revealed by pyrosequencing. Acta Oceanol Sin 36:146–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1030-2
López-Bueno A, Tamames J, Velázquez D, Moya A, Quesada A, Alcamí A (2009) High diversity of the viral community from an Antarctic lake. Science 326(5954):858–861. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1179287
Maat DS, Prins MA, Brussaard CPD (2019) Sediments from Arctic tide-water glaciers remove coastal marine viruses and delay host infection. Viruses 11(2):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020123
Maniloff J, Ackermann HW (1998) Taxonomy of bacterial viruses: establishment of tailed virus genera and the order Caudovirales. Arch Virol 143(10):2051–2063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050442
Mei ML, Danovaro R (2004) Virus production and life strategies in aquatic sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 49(2):459–470. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2004.49.2.0459
Meyer F, Paarmann D, D’Souza M, Olson R, Glass EM et al (2008) The metagenomics RAST server - a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinformatics 9:386. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-386
Miranda JA, Culley AI, Schvarcz CR, Steward GF (2016) RNA viruses as major contributors to Antarctic virioplankton. Environ Microbiol 18(11):3714–3727. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13291
Moon K, Kim S, Kang I, Cho JC (2020) Viral metagenomes of Lake Soyang, the largest freshwater lake in South Korea. Sci Data 7(1):349. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-00695-9
Ortmann AC, Suttle CA (2005) High abundances of viruses in a deep-sea hydrothermal vent system indicates viral mediated microbial mortality. Deep-Sea Res I Oceanogr Res Pap 52(8):1515–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2005.04.002
Overbeek R, Begley T, Butler RM, Choudhuri JV, Chuang HY, Cohoon M, de Crécy-Lagard V, Diaz N, Disz T, Edwards R, Fonstein M et al (2005) The subsystems approach to genome annotation and its use in the project to annotate 1000 genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 33(17):5691–5702. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki866
Pearce DA, Newsham KK, Thorne MA, Calvo-Bado L, Krsek M, Laskaris P, Hodson A, Wellington EM (2012) Metagenomic analysis of a southern maritime Antarctic soil. Front Microbiol 3:403. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00403
Perez-Mon C, Frey B, Frossard A (2020) Functional and structural responses of Arctic and alpine soil prokaryotic and fungal communities under freeze-thaw cycles of different frequencies. Front Microbiol 11:982. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00982
Plyusnin I, Kant R, Jääskeläinen AJ, Sironen T, Holm L, Vapalahti O, Smura T (2020) Novel NGS pipeline for virus discovery from a wide spectrum of hosts and sample types. Virus Evol 6(2):veaa091. https://doi.org/10.1093/ve/veaa091
Polischuk V, Budzanivska I, Shevchenko T, Oliynik S (2007) Evidence for plant viruses in the region of Argentina Islands. Antarctica FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59(2):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00242.x
Potapov SA, Tikhonova IV, Krasnopeev AY, Kabilov MR, Tupikin AE, Chebunina NS, Zhuchenko NA, Belykh OI (2019) Metagenomic analysis of virioplankton from the pelagic zone of Lake Baikal. Viruses 11(11):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11110991
Rassner SM, Anesio AM, Girdwood SE, Hell K, Gokul JK, Whitworth DE, Edwards A (2016) Can the bacterial community of a High Arctic glacier surface escape viral control? Front Microbiol 7:956. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00956
Rohwer F, Edwards R (2002) The Phage Proteomic Tree: a genome-based taxonomy for phage. J Bacteriol 184(16):4529–4535. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.16.4529-4535.2002
Rosario K, Breitbart M (2011) Exploring the viral world through metagenomics. Curr Opin Virol 1:289–297
Roux S, Adriaenssens EM, Dutilh BE, Koonin EV et al (2019) Minimum Information about an Uncultivated Virus Genome (MIUViG). Nat Biotechnol 37(1):29–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4306
Roux S, Brum JR, Dutilh BE, Sunagawa S, Duhaime MB, Loy A et al (2016a) Ecogenomics and potential biogeochemical impacts of globally abundant ocean viruses. Nature 537(7622):689–693. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19366
Roux S, Enault F, Ravet V, Colombet J, Bettarel Y et al (2016b) Analysis of metagenomic data reveals common features of halophilic viral communities across continents. Environ Microbiol 18(3):889–903. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13084
Sandaa RA, Storesund E, J, Olesin E, Lund Paulsen M, Larsen A, Bratbak G, Ray JL, (2018) Seasonality drives microbial community structure, shaping both eukaryotic and prokaryotic host-viral relationships in an Arctic marine ecosystem. Viruses 10(12):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10120715
Sander M, Schmieger H (2001) Method for host-independent detection of generalized transducing bacteriophages in natural habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(4):1490–1493. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.4.1490-1493.2001
Sanguino L, Franqueville L, Vogel TM, Larose C (2015) Linking environmental prokaryotic viruses and their host through CRISPRs. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91(5):fiv046. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiv046
Schlitzer R (2023) Ocean Data View. https://odv.awi.de. Accessed 30 Jun 2023
Segobola J, Adriaenssens E, Tsekoa T, Rashamuse K, Cowan D (2018) Exploring viral diversity in a unique south African soil habitat. Sci Rep 8(1):111. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18461-0
Solomon S, Kachiprath B, Jayanath G, Sajeevan TP, Singh ISB, Philip R (2016) High-quality metagenomic DNA from marine sediment samples for genomic studies through a preprocessing approach. 3 Biotech 6:160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0482-y
Steward GF, Culley AI, Mueller JA, Wood-Charlson EM, Belcaid M, Poisson G (2013) Are we missing half of the viruses in the ocean? ISME J 7(3):672–679. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2012.121
Sun S, Gao S, Kondabagil K, Xiang Y, Rossmann MG, Rao VB (2012) Structure and function of the small terminase component of the DNA packaging machine in T4-like bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(3):817–822. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1110224109
Suttle CA, Chan AM (1994) Dynamics and distribution of cyanophages and their effect on marine Synechococcus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:3167–3174. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.60.9.3167-3174.1994
Suttle CA (2007) Marine viruse–Major players in the global ecosystem. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(10):801–812. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1750
Suttle CA (2005) Viruses in the sea. Nature 437(7057):356–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04160
Tangherlini M, Dell’Anno A, Allen LZ, Riccioni G, Corinaldesi C (2016) Assessing viral taxonomic composition in benthic marine ecosystems: reliability and efficiency of different bioinformatic tools for viral metagenomic analyses. Nat Sci Rep 6(1):28428. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28428
Treonis AM, Wall DH, Virginia RA (1999) Invertebrate biodiversity in Antarctic dry valley soils and sediments. Ecosystems 2:482–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100219900096
Trubl G, Hyman P, Roux S, Abedon ST (2020) Coming-of-age characterization of soil viruses: a user’s guide to virus isolation, detection within metagenomes, and viromics. Soil Syst 4(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems4020023
Tryland M (2000) Zoonoses of Arctic marine mammals. Infect Dis Rev 2(2):55–64
Urayama SI, Takaki Y, Nishi S, Yoshida-Takashima Y, Deguchi S, Takai K, Nunoura T (2018) Unveiling the RNA virosphere associated with marine microorganisms. Mol Ecol Resour 18(6):1444–1455. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12936
Varin T, Lovejoy C, Jungblut AD, Vincent WF, Corbeil J (2010) Metagenomic profiling of Arctic microbial mat communities as nutrient scavenging and recycling systems. Limnol Oceanogr 55(5):1901–1911. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.5.1901
Waits A, Emelyanova A, Oksanen A, Abass K, Rautio A (2018) Human infectious diseases and the changing climate in the Arctic. Environ Int 121(1):703–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.09.042
Weinbauer MG (2004) Ecology of prokaryotic viruses. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28(2):127–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2003.08.001
Williamson SJ, Rusch DB, Yooseph S, Halpern AL, Heidelberg KB, Glass JL, Pfannkoch CA, Fadrosh D, Miller CS, Sutton G, Frazier M, Venter JC (2008) The Sorcerer II global ocean sampling expedition: metagenomic characterization of viruses within aquatic microbial samples. PLoS ONE 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001456
Winter C, Garcia JA, Weinbauer MG, DuBow MS, Herndl GJ (2014) Comparison of deep-water viromes from the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 9(6). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100600
Wommack KE, Colwell RR (2000) Virioplankton: viruses in aquatic ecosystems. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(1):69–114. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.64.1.69-114.2000
Wommack KE, Nasko DJ, Chopyk J, Sakowski EG (2015) Counts and sequences, observations that continue to change our understanding of viruses in nature. J Microbiol 53(3):181–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-5068-6
Yang M, Xia Q, Du S, Zhang Z, Qin F, Zhao Y (2021) Genomic characterization and distribution pattern of a novel marine OM43 phage. Front Microbiol 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.651326
Yang Q, Gao C, Jiang Y, Wang M, Zhou X, Shao H, Gong Z, McMinn A (2019) Metagenomic characterization of the viral community of the South Scotia Ridge. Viruses 11(2):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020095
Yau S, Seth-Pasricha M (2019) Viruses of Polar Aquatic Environments Viruses 11(2):189. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020189
Yu ZC, Chen XL, Shen QT, Zhao DL, Tang BL et al (2015) Filamentous phages prevalent in Pseudoalteromonas spp. confer properties advantageous to host survival in Arctic sea ice. ISME J 9(4):871–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.185
Zablocki O, Adriaenssens EM, Cowan D (2015) Diversity and ecology of viruses in hyperarid desert soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(3):770–777. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02651-15
Zeigler Allen L, McCrow JP, Ininbergs K, Dupont CL, Badger JH, Hoffman JM, Ekman M, Allen AE, Bergman B, Venter JC (2017) The Baltic Sea Virome: Diversity and transcriptional activity of DNA and RNA Viruses. mSystems 2(1):e00125-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00125-16
Zhang T, Wang NF, Zhang YQ, Liu HY, Yu LY (2015) Diversity and distribution of fungal communities in the marine sediments of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard (High Arctic). Sci Rep 5:14524. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14524
Zhong Y, Chen F, Wilhelm SW, Poorvin L, Hodson RE (2002) Phylogenetic diversity of marine cyanophage isolates and natural virus communities as revealed by sequences of viral capsid assembly protein gene g20. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1576–1584. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.4.1576-1584.2002
Zimmerman AE, Howard-Varona C, Needham DM, John SG, Worden AZ, Sullivan MB, Waldbauer JR, Coleman ML (2020) Metabolic and biogeochemical consequences of viral infection in aquatic ecosystems. Nat Rev Microbiol 18(1):21–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0270-x
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Earth System Science Organization - National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (ESSO-NCPOR), Goa, for providing logistical assistance with sediment sampling. The authors express their gratitude to Macrogen Inc., Republic of Korea for performing shotgun sequencing of samples. BK is grateful to Mr. Ajithabh K. S. for his assistance in plotting the map with sampling location. Authors thankfully acknowledge Department of Marine Biology, Microbiology and Biochemistry and National Centre for Aquatic Animal Health (NCAAH), Cochin University of Science and Technology, for providing necessary facilities to perform the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JP and RP collected the sediment samples. BK carried out the experiment of the present work with support from MS and JG. The work was carried out under the supervision of RP. MS assisted the processing of sediment samples. BK wrote the manuscript. RP, JP, CER, JG, and MS reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this work.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Xia Liang
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kachiprath, B., Gopi, J., Sarasan, M. et al. Metavirome mining from fjord sediments of Svalbard Archipelago. J Soils Sediments (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03809-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-024-03809-7