Abstract
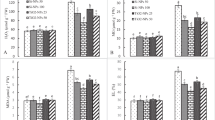
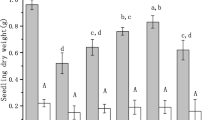
Arsenic (As) pollution in cultivated soils poses a significant risk to the sustainable growth of agriculture and jeopardizes food security. However, the mechanisms underlying how zinc (Zn) regulates the toxic effects induced by As in plants remain poorly understood. Hence, this study aimed to explore the potential of ZnO as an effective and environmentally friendly amendment to alleviate As toxicity in rice, thereby addressing the significant risk posed by As pollution in cultivated soils. Through a hydroponic experiment, the study assessed the mitigating effects of different ZnO dosages (Zn5, 5 mg L-1; Zn15, 15 mg L-1; Zn30, 30 mg L-1) on rice seedlings exposed to varying levels of As stress (As0, 0 µM L-1; As25, 25 µM L-1). The findings of the study demonstrate significant improvements in plant height and biomass (shoot and root), with a notable increase of 16–40% observed in the Zn15 treatment, and an even more substantial enhancement of 29–53% observed in the Zn30 treatment under As stress, compared to respective control treatment. Furthermore, in the Zn30 treatment, the shoot and root As contents substantially reduced by 47% and 63%, respectively, relative to the control treatment. The elevated Zn contents in shoots and roots enhanced antioxidant enzyme activities (POD, SOD, and CAT), and decreased MDA contents (13-25%) and H2O2 contents (11-27%), indicating the mitigation of oxidative stress. Moreover, the expression of antioxidant-related genes, OsSOD-Cu/Zn, OsCATA, OsCATB, and OsAPX1 was reduced when rice seedlings were exposed to As stress and significantly enhanced after Zn addition. Overall, the research suggests that ZnO application could effectively mitigate As uptake and toxicity in rice plants cultivated in As-contaminated soils, offering potential solutions for sustainable agriculture and food security.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Abbas G, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Khan MI, Amjad M, Hussain M, Natasha (2018) Arsenic uptake, toxicity, detoxification, and speciation in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(1):59
Adil MF, Sehar S, Han Z, Wa Lwalaba JL, Jilani G, Zeng F, Shamsi IH (2020) Zinc alleviates cadmium toxicity by modulating photosynthesis, ROS homeostasis, and cation flux kinetics in rice. Environ Pollut 265:114979
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ahmad P, Alyemeni MN, Al-Huqail AA, Alqahtani MA, Wijaya L, Ashraf M, Bajguz A (2020) Zinc oxide nanoparticles application alleviates arsenic (As) toxicity in soybean plants by restricting the uptake of As and modulating key biochemical attributes, antioxidant enzymes, ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. Plants 9:825
Ahmed T, Noman M, Rizwan M, Ali S, Ijaz U, Nazir MM, Alhaithloul HAS, Alghanem SM, Abdulmajeed AM, Bin L (2021) Green molybdenum nanoparticles-mediated bio-stimulation of Bacillus sp. strain ZH16 improved the wheat growth by managing in planta nutrients supply, ionic homeostasis and arsenic accumulation. J Hazard Mater 423:127024
Ahmed T, Noman M, Rizwan M, Ali S, Shahid MS, Li B (2023) Recent progress on the heavy metals ameliorating potential of engineered nanomaterials in rice paddy: a comprehensive outlook on global food safety with nanotoxicitiy issues. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 63(16):2672–2686
Ahmed T, Guo J, Noman M, Lv L, Manzoor N, Qi X, Li B (2024) Metagenomic and biochemical analyses reveal the potential of silicon to alleviate arsenic toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Pollut 345:123537
Akhtar N, Khan S, Rehman SU, Rha ES, Jamil M (2022) Combined effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles and bacteria on osmolytes and antioxidative parameters of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant grown in heavy metal-contaminated water. Adsorpt Sci Technol 2022:4148765
Alengebawy A, Abdelkhalek ST, Qureshi SR, Wang MQ (2021) Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 9(3):42
Ali MA, Fahad S, Haider I, Ahmed N, Ahmad S, Hussain S, Arshad M (2019a) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in plants exposed to metal/metalloid toxicity. Reactive oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur species in plants: production, metabolism, signal. Def Mech 353–370
Ali S, Rizwan M, Noureen S, Anwar S, Ali B, Naveed M, Ahmad P (2019b) Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:11288–11299
Azam M, Bhatti HN, Khan A, Zafar L, Iqbal M (2022) Zinc oxide nano-fertilizer application (foliar and soil) effect on the growth, photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant system of maize cultivar. Biocatal Agricul Biotech 42:102343
Banerjee S, Mondal S, Islam J, Sarkar R, Saha B, Sen A (2024) Rhizospheric nano-remediation salvages arsenic genotoxicity: zinc-oxide nanoparticles articulate better oxidative stress management, reduce arsenic uptake, and increase yield in Pisum sativum (L.). Sci Total Environ 913:169493
Bashir A, Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rehman MZU, Qayyum MF (2020) Effect of composted organic amendments and zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth and cadmium accumulation by wheat; a life cycle study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:23926–23936
Bennett AC, Knauer J, Bennett LT, Haverd V, Arndt SK (2024) Variable influence of photosynthetic thermal acclimation on future carbon uptake in Australian wooded ecosystems under climate change. Glob Chang Biol 30(1):e17021
Beniwal R, Yadav R, Ramakrishna W (2023) Multifarious effects of arsenic on plants and strategies for mitigation. Agriculture 13(2):401
Bhat JA, Faizan M, Bhat MA, Huang F, Yu D, Ahmad A, Ahmad P (2022) Defense interplay of the zinc-oxide nanoparticles and melatonin in alleviating the arsenic stress in soybean (Glycine max L.). Chemosphere 288:132471
Bidi H, Fallah H, Niknejad Y, Barari Tari D (2021) Iron oxide nanoparticles alleviate arsenic phytotoxicity in rice by improving iron uptake, oxidative stress tolerance and diminishing arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiol Biochem 163:348–357
Choudhury S, Moulick D, Mazumder MK, Pattnaik BK, Ghosh D, Vemireddy LR, Hossain A (2022) An in vitro and in silico perspective study of seed priming with zinc on the phytotoxicity and accumulation pattern of arsenic in rice seedlings. Antioxidants 11(8):1500
Das DK, Sur P, Das K (2008) Mobilisation of arsenic in soils and in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants affected by organic matter and zinc application in irrigation water contaminated with arsenic. Plant Soil Environ 54(1):30
Das I, Sanyal SK, Ghosh K, Das DK (2016) Arsenic mitigation in soil-plant system through zinc application in West Bengal soils. Bioremed J 20:24–37
Dhaliwal SS, Sharma V, Shukla AK, Verma V, Behera SK, Singh P, Hossain A (2021) Comparative efficiency of mineral, chelated and nano forms of zinc and iron for improvement of zinc and iron in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) through biofortification. Agronomy 11:2436
Dimkpa CO, Andrews J, Sanabria J, Bindraban PS, Singh U, Elmer WH, White JC (2020) Interactive effects of drought, organic fertilizer, and zinc oxide nanoscale and bulk particles on wheat performance and grain nutrient accumulation. Sci Tot Environ 722:137808
Elbasan F, Arikan B, Ozfidan-Konakci C, Tofan A, Yildiztugay E (2024) Hesperidin and chlorogenic acid mitigate arsenic-induced oxidative stress via redox regulation, photosystems-related gene expression, and antioxidant efficiency in the chloroplasts of Zea mays. Plant Physiol Biochem 108445
Elshamly AM, Iqbal R, Ali B, Ahmed I, Akram MI, Ali S, Ditta A, Fatih ÇIĞ, Elshikh MS, Mustafa AEZM, Hamed MH (2024) Zinc and amino acids improve the growth, physiological, and biochemical attributes of corn under different irrigation levels. Rhizosphere 29:100820
Fahad S, Rehman A, Shahzad B, Tanveer M, Saud S, Kamran M, ur Rahman MH (2019) Rice responses and tolerance to metal/metalloid toxicity. In: Advances in rice research for abiotic stress tolerance, Woodhead publishing, pp 299–312
Faizan M, Sehar S, Rajput VD, Faraz A, Afzal S, Minkina T, Faisal M (2021) Modulation of cellular redox status and antioxidant defense system after synergistic application of zinc oxide nanoparticles and salicylic acid in rice (Oryza sativa) plant under arsenic stress. Plants 10(11):2254
Farooq MA, Gill RA, Islam F, Ali B, Liu H, Xu J, He S, Zhou W (2016) Methyl jasmonate regulates antioxidant defense and suppresses arsenic uptake in Brassica napus. L Front Plant Sci 7:468
Gajić G, Djurdjević L, Kostić O, Jarić S, Stevanović B, Mitrović M, Pavlović P (2020) Phytoremediation potential, photosynthetic and antioxidant response to arsenic-induced stress of Dactylis glomerata L. sown on fly ash deposits. Plants 9(5):657
Ganguly P, Mandal J, Paramsivam M, Patra S (Eds.) (2024) Environmental contaminants: impact, assessment, and remediation. CRC Press
Geng A, Wang X, Wu L, Wang F, Wu Z, Yang H, Liu X (2018) Silicon improves growth and alleviates oxidative stress in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) by strengthening antioxidant defense and enhancing protein metabolism under arsanilic acid exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:266–273
Genty B, Briantais JM, Baker NR (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 990(1):87–92
Ghorbani A, Tafteh M, Roudbari N, Pishkar L, Zhang W, Wu C (2021) Piriformospora indica augments arsenic tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) by immobilizing arsenic in roots and improving iron translocation to shoots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 209:111793
Ghosh S, Shaw AK, Azahar I, Adhikari S, Jana S, Roy S, Hossain Z (2016) Arsenate (AsV) stress response in maize (Zea mays L.). Environ Exp Bot 130:53–67
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases: I. occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gong B, He E, Qiu H, Van Gestel CA, Romero-Freire A, Zhao L, Xu X, Cao X (2020) Interactions of arsenic, copper, and zinc in soil-plant system: partition, uptake and phytotoxicity. Sci Total Environ 745:140926
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan MHMB, Zulfiqar F, Raza A, Mohsin SM, Mahmud JA, Fotopoulos V (2020) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 9:681
He X, Richmond ME, Williams DV, Zheng W, Wu F (2019) Exogenous glycinebetaine reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in two tobacco genotypes differing in cadmium tolerance. Int J Mol Sci 20(7):1612
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Zia urRehman M, Javed MR, Imran M, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Jalil S, Alghanem SM, Al-Huqail AA, Nazir MM, Zulfiqar F, Ahmed T, Jin X (2023) Zinc oxide nanoparticles mitigated the arsenic induced oxidative stress through modulation of physio-biochemical aspects and nutritional ions homeostasis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chemosphere 338:139566
Karmakar S, Prakash P, Chattopadhyay A, Dutta D (2021) Zinc sulphate and vermicompost mitigate phytotoxic effects of arsenic by altering arsenic uptake, biochemical and antioxidant enzyme activities in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Russian. J Plant Physiol 68:S72–S81
Khan Z, Thounaojam TC, Upadhyaya H (2022) Arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa) and its amelioration approaches. Plant Stress 4:100076
Khatri K, Rathore MS (2022) Salt and osmotic stress-induced changes in physio-chemical responses, PSII photochemistry and chlorophyll a fluorescence in peanut. Plant Stress 3:100063
Kumar A, Basu S, Rishu AK, Kumar G (2022a) Revisiting the mechanisms of arsenic uptake, transport and detoxification in plants. Environ Exp Botany 194:104730
Kumar A, Yadav PK, Singh A (2022b) An overview on emerging and innovative technologies for regulating arsenic toxicity in plants arsenic in plants. Conseq Remediat Techniq 367–394
Lata S, Samadder SR (2016) Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: a review. J Environ Manag 166:387–406
Li J, Sun Y, Jiang X, Chen B, Zhang X (2018) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate arsenic toxicity to Medicago sativa by influencing arsenic speciation and partitioning. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 157:235–243
Liu J, Dhungana B, Cobb GP (2018) Environmental behavior, potential phytotoxicity, and accumulation of copper oxide nanoparticles and arsenic in rice plants. Environ Toxicol Chem 37:11–20
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Loukola-Ruskeeniemi K, Müller I, Reichel S, Jones C, Battaglia-Brunet F, Elert M, Valkama H (2022) Risk management for arsenic in agricultural soil–water systems: lessons learned from case studies in Europe. J Hazard Mater 424:127677
Lu Y, Wang Q, Li J, Xiong J, Zhou L, He S, Liu H (2019) Effects of exogenous sulfur on alleviating cadmium stress in tartary buckwheat. Sci Rep 9:7397
Ma X, Sharifan H, Dou F, Sun W (2020) Simultaneous reduction of arsenic (As) and cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice by zinc oxide nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 384:123802
Maehly AC, Chance B (1954) The assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Biochem Anal 1:357–424
Mawia AM, Hui S, Zhou L, Li H, Tabassum J, Lai C, Tang S (2021) Inorganic arsenic toxicity and alleviation strategies in rice. J Hazard Mat 408:124751
Mazumder JA, Khan E, Perwez M, Gupta M, Kumar S, Raza K, Sardar M (2020) Exposure of biosynthesized nanoscale ZnO to Brassica juncea crop plant: morphological, biochemical and molecular aspects. Sci Rep 10:8531
Mishra S, Dwivedi S, Mallick S, Tripathi RD (2019) Redox homeostasis in plants under arsenic stress. In: Panda SK, Yamamoto YY (eds) Redox homeostasis in plants: from signalling to stress tolerance. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 179–198
Mishra S, Dwivedi S, Gupta A, Tiwari RK (2023) Evaluating the efficacy and feasibility of post harvest methods for arsenic removal from rice grain and reduction of arsenic induced cancer risk from rice-based diet. Sci Total Environ 874:162443
Morales M, Munné-Bosch S (2019) Malondialdehyde: facts and artifacts. Plant Physiol 180:1246–1250
Mousavi SR, Niknejad Y, Fallah H, Tari DB (2020) Methyl jasmonate alleviates arsenic toxicity in rice. Plant Cell Rep 39:1041–1060
Murphy T, Irvine K, Phan K, Lean D, Wilson K (2019) Environmental and health implications of the correlation between arsenic and zinc levels in rice from an arsenic-rich zone in Cambodia. J Health Pollut 9(22):190603
Nazir MM, Li Q, Noman M, Ulhassan Z, Ali S, Ahmed T, Zhang G (2022a) Calcium oxide nanoparticles have the role of alleviating arsenic toxicity of barley. Front Plant Sci 13:843795
Nazir MM, Noman M, Ahmed T, Ali S, Ulhassan Z, Zeng F, Zhang G (2022b) Exogenous calcium oxide nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity by reducing Cd uptake and enhancing antioxidative capacity in barley seedlings. J Hazard Mater 438:129498
Parashar R, Afzal S, Mishra M, Singh NK (2023) Improving biofortification success rates and productivity through zinc nanocomposites in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:44223–44233
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM, Rahman MA, Miah MAM (2007) Accumulation of arsenic in tissues of rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) and its distribution in fractions of rice grain. Chemosphere 69(6):942–948
Rizwan M, Ali S, Hussain A, Ali Q, Shakoor MB, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Asma M (2017) Effect of zinc-lysine on growth, yield and cadmium uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 187:35–42
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Waris AA (2019) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Romero-Puertas M, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Corpas F, Gomez MD, Del Rio L, Sandalio L (2004) Cadmium-induced subcellular accumulation of O2•− and H2O2 in pea leaves. Plant Cell Environ 27(9):1122–1134
Roy D, Sreekanth D, Pawar D, Mahawar H, Barman K (2021) Phytoremediation of arsenic contaminated water using aquatic, semi-aquatic and submerged weeds. In: Biodegradation technology of organic and inorganic pollutants. London: IntechOpen
Sattar A, Wang X, Ul-Allah S, Sher A, Ijaz M, Irfan M, Al-Hashimi A (2022) Foliar application of zinc improves morpho-physiological and antioxidant defense mechanisms, and agronomic grain biofortification of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under water stress. Saudi J Biol Sci 29(3):1699–1706
Sengupta S, Bhattacharyya K, Mandal J, Chattopadhyay AP (2022) Complexation, retention and release pattern of arsenic from humic/fulvic acid extracted from zinc and iron enriched vermicompost. J Environ Manag 318:115531
Sharma S, Anand G, Singh N, Kapoor R (2017) Arbuscular mycorrhiza augments arsenic tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by strengthening antioxidant defense system and thiol metabolism. Front Plant Sci 8:259098
Siddiqui F, Tandon PK, Srivastava S (2015) Arsenite and arsenate impact the oxidative status and antioxidant responses in Ocimum tenuiflorum L. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 21:453–458
Singh AP, Dixit G, Mishra S, Dwivedi S, Tiwari M, Mallick S, Tripathi RD (2015) Salicylic acid modulates arsenic toxicity by reducing its root to shoot translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front Plant Sci 6:340
Srivastav A, Ganjewala D, Singhal RK, Rajput VD, Minkina T, Voloshina M, Shrivastava M (2021) Effect of ZnO nanoparticles on growth and biochemical responses of wheat and maize. Plants 10(12):2556
Srivastava S, Suprasanna P, Tripathi RD (2020) Safeguarding rice from arsenic contamination through the adoption of chemo-agronomic measures. In: Srivastava S (ed) Arsenic in drinking water and food. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 411–424
Sytar O, Kumar A, Latowski D, Kuczynska P, Strzałka K, Prasad MNV (2013) Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Acta Physiol Plant 35(4):985–999
Talukdar D (2013) Arsenic-induced changes in growth and antioxidant metabolism of fenugreek. Russ J Plant Physiol 60:652–660
Tanveer Y, Yasmin H, Nosheen A, Ali S, Ahmad A (2022) Ameliorative effects of plant growth promoting bacteria, zinc oxide nanoparticles and oxalic acid on Luffa acutangula grown on arsenic enriched soil. Environ Pollut 300:118889
Ulhassan Z, Bhat JA, Zhou W, Senan AM, Alam P, Ahmad P (2022) Attenuation mechanisms of arsenic induced toxicity and its accumulation in plants by engineered nanoparticles: a review. Environ Pollut 302:119038
Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER, Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alleviate heavy metal-induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:59–69
Wang X, Sun W, Ma X (2019) Differential impacts of copper oxide nanoparticles and copper(II) ions on the uptake and accumulation of arsenic in rice (Oryza sativa). Environ Pollut 252:967–973
Wu F, Fang Q, Yan S, Pan L, Tang X, Ye W (2020) Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.): germination, early growth, and arsenic uptake. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27(21):26974–26981
Yan S, Wu F, Zhou S, Yang J, Tang X, Ye W (2021) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviate the arsenic toxicity and decrease the accumulation of arsenic in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 21(1):1–11
Zeeshan M, Hu YX, Iqbal A, Salam A, Liu YX, Muhammad I, Zhou XB (2021) Amelioration of AsV toxicity by concurrent application of ZnO-NPs and Se-NPs is associated with differential regulation of photosynthetic indexes, antioxidant pool and osmolytes content in soybean seedling. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 225:112738
Zeeshan M, Hu YX, Afridi MS, Ahmad B, Ahmad S, Muhammad I, Zhou XB (2022) Interplay of ZnONPs and/or SeNPs induces arsenic tolerance in soybean by regulation of antioxidants pool, WRKY genes, and expression of arsenic transporters. Environ Exp Bot 195:104783
Zeng F, Chen S, Miao Y, Wu F, Zhang G (2008) Changes of organic acid exudation and rhizosphere pH in rice plants under chromium stress. Environ Pollut 155:284–289
Zhang S, Li Q, Nazir MM, Ali S, Ouyang Y, Ye S, Zeng F (2020) Calcium plays a double-edged role in modulating cadmium uptake and translocation in rice. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):8058
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Office of Zhejiang Province, China (project no. 2021C02063-6) and supported by the DOE Office of Science, Office of Biological and Environmental Research (BER), USA, grant nos. DE-SC0006634 and DE-SC0012379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sanaullah Jalil: conceptualization, investigation, and writing—original draft. Muhammad Mudassir Nazir and Mohamed A. Eweda: investigation, formal data analysis. Faisal Zulfiqar, Temoor Ahmed, Muhammad Noman, Muhammad A.U. Asad: validation and writing—review and editing. Kadambot H. M. Siddique: co-supervision, methodology, and investigation. Xiaoli Jin: supervision, conceptualization, project administration, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jalil, S., Nazir, M.M., Eweda, M.A. et al. Zinc oxide application alleviates arsenic-mediated oxidative stress via physio-biochemical mechanism in rice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 34200–34213 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33380-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33380-0