Abstract
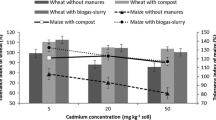
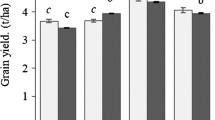
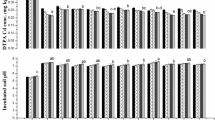
Cadmium (Cd) availability in arable soils is a serious issue while little is known about the role of co-composted organic amendments and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) foliar spray on biomass and Cd accumulation in wheat grains. The current study investigated the soil application of organic amendment (composted biochar and farmyard manure) at a level of 0, 1, and 2% w/w and foliar spray of ZnO-NPs (0, 100, and 200 mg/L) on biomass, yield, and Cd in wheat grains cultivated in an aged Cd-contaminated agricultural soil. The results indicated that organic amendment increased the biomass, chlorophyll concentrations, yield, and activities of peroxidase and superoxide dismutase of wheat while decreased the electrolyte leakage and Cd concentrations in different parts of wheat such as shoots, roots, husks, and grains. This effect of organic amendment was further enhanced by the foliar spray of ZnO-NPs in a dose-additive manner. Cadmium concentration in grains was below threshold level (0.2 mg/kg DW) for cereals in combined application of 200 mg/L ZnO-NPs and 1% organic amendment as well as in higher treatment (2%) of organic amendment and NPs. Thus, combined use of organic materials and NPs might be a suitable way of reducing Cd and probably other toxic trace element concentrations in wheat and other cereals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Mahmood A, Rehman MZ, Ibrahim M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF (2018) Biochar application increased the growth and yield and reduced cadmium in drought stressed wheat grown in an aged contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:825–833
Agegnehu G, Bass AM, Nelson PN, Muirhead B, Wright G, Bird MI (2015) Biochar and biochar-compost as soil amendments: effects on peanut yield soil properties and greenhouse gas emissions in tropical North Queensland, Australia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 213:72–85
Agegnehu G, Srivastava AK, Bird MI (2017) The role of biochar and biochar-compost in improving soil quality and crop performance: a review. Appl Soil Ecol 119:156–170
Ali B, Gill RA, Yang S, Gill MB, Farooq MA, Liu D, Daud MK, Ali S, Zhou W (2015) Regulation of cadmium-induced proteomic and metabolic changes by 5-aminolevulinic acid in leaves of Brassica napus L. PLoS One 10:1–23
Ali S, Rizwan M, Qayyum MF, Ok YS, Ibrahim M, Riaz M, Arif MS, Hafeez F, Al-Wabel MI, Shahzad AN (2017) Biochar soil amendment on alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:12700–12712
Ali S, Rizwan M, Noureen S, Anwar S, Ali B, Naveed M, Abd Allah EF, Alqarawi AA, Ahmad P (2019) Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:11288–11299
Almaroai YA, Usman AR, Ahmad M, Moon DH, Cho JS, Joo YK, Jeon C, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Effects of biochar, cow bone, and eggshell on Pb availability to maize in contaminated soil irrigated with saline water. Environ Earth Sci 71:1289–1296
Bashir A, Rizwan M, ur Rehman MZ, Zubair M, Riaz M, Qayyum MF, Alharby HF, Bamagoos AA, Ali S (2020) Application of co-composted farm manure and biochar increased the wheat growth and decreased cadmium accumulation in plants under different water regimes. Chemosphere 246:1–10
Bayçu G, Gevrek-Kürüm N, Moustaka J, Csatári I, Rognes SE, Moustakas M (2017) Cadmium-zinc accumulation and photosystem II responses of Noccaea caerulescens to Cd and Zn exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2840–2850
Beccaloni E, Vanni F, Beccaloni M, Carere M (2013) Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, lead and zinc in homegrown vegetables and fruits: estimated intake by population in an industrialized area of Sardinia, Italy. Microchem J 107:190–195
Bian R, Li L, Bao D, Zheng J, Zhang X, Zheng J, Liu X, Cheng K, Pan G (2016) Cd immobilization in a contaminated rice paddy by inorganic stabilizers of calcium hydroxide and silicon slag and by organic stabilizer of biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:10028–10036
Buss W, Kammann C, Koyro HW (2012) Biochar reduces copper toxicity in Chenopodium quinoa Willd. in a sandy soil. J Environ Qual 41:1157–1165
Cakmak I, Kutman UB (2018) Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review. Eur J Soil Sci 69:172–180
Chaney RL (2015) How does contamination of rice soils with Cd and Zn cause high incidence of human Cd disease in subsistence rice farmers. Curr Pollut Rep 1:13–22
Dimkpa CO, Bindraban PS, Fugice J, Agyin-Birikorang S, Singh U, Hellums D (2017) Composite micronutrient nanoparticles and salts decrease drought stress in soybean. Agron Sustain Dev 37:5
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9
FAO (2014) ProdStat. Core production data base, Electronic resource under http://faostat.fao.org/. Accessed 30 June 2015
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
García-Gómez C, Obrador A, González D, Babín M, Fernández MD (2018) Comparative study of the phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles and Zn accumulation in nine crops grown in a calcareous soil and an acidic soil. Sci Total Environ 644:770–780
Haider G, Koyro HW, Azam F, Steffens D, Müller C, Kammann C (2015) Biochar but not humic acid product amendment affected maize yields via improving plant-soil moisture relations. Plant Soil 395:141–157
Hussain A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Rehman MZ, Javed MR, Imran M, Chatha SA, Nazir R (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the wheat physiological response and reduce the cadmium uptake by plants. Environ Pollut 242:1518–1526
Kammann CI, Schmidt HP, Messerschmidt N, Linsel S (2015) Plant growth improvement mediated by nitrate capture in co-composted biochar. Sci Rep 5:1–15
Karami N, Clemente R, Moreno-Jiménez E, Lepp NW, Beesley L (2011) Efficiency of green waste compost and biochar soil amendments for reducing lead and copper mobility and uptake to ryegrass. J Hazard Mater 191:41–48
Karer J, Wawra A, Zehetner F, Dunst G, Wagner M, Pavel PB, Puschenreiter M, Friesl-Hanl W, Soja G (2015) Effects of biochars and compost mixtures and inorganic additives on immobilisation of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:342
Khan A, Khan S, Alam M, Khan MA, Aamir M, Qamar Z, Rehman ZU, Perveen S (2016) Toxic metal interactions affect the bioaccumulation and dietary intake of macro-and micro-nutrients. Chemosphere 146:121–128
Khan ZS, Rizwan M, Hafeez M, Ali S, Javed MR, Adrees M (2019) The accumulation of cadmium in wheat (Triticum aestivum) as influenced by zinc oxide nanoparticles and soil moisture conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:19859–19870
Kolencik M, Ernst D, Komár M, Urík M, Šebesta M, Dobročka E, Černý I, Illa R, Kanike R, Qian Y, Feng H (2019) Effect of foliar spray application of zinc oxide nanoparticles on quantitative, nutritional, and physiological parameters of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) under field conditions. Nanomater 9:1–11
Krężel A, Maret W (2016) The biological inorganic chemistry of zinc ions. Arch Biochem Biophys 611:3–19
Li Y, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang L, Hou W, Yu N (2015) Effect of combined pollution of cd and B[a] P on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of wheat. Pol J Environ Stud 24:1–12
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods Enzymol, vol 148, pp 350–382
Liu R, Lal R (2015) Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci Total Environ 514:131–139
Naeem A, Ghafoor A, Farooq M (2015) Suppression of cadmium concentration in wheat grains by silicon is related to its application rate and cadmium accumulating abilities of cultivars. J Sci Food Agric 95:2467–2472
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Major J, Rondon M, Molina D, Riha SJ, Lehmann J (2012) Nutrient leaching in a Colombian savanna oxisol amended with biochar. J Environ Qual 41:1076–1086
Qayyum MF, Liaquat F, Rehman RA, Gul M, ul Hye MZ, Rizwan M, ur Rehaman MZ (2017) Effects of co-composting of farm manure and biochar on plant growth and carbon mineralization in an alkaline soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:26060–26068
Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Ali S, Fatima N, Yousaf B, Naeem A, Sabir M, Ahmad HR, Ok YS (2016) Contrasting effects of biochar, compost and farm manure on alleviation of nickel toxicity in maize (Zea mays L.) in relation to plant growth, photosynthesis and metal uptake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133:218–225
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ibrahim M, Farid M, Adrees M, Bharwana SA, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Qayyum MF, Abbas F (2015) Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of drought and salt stress in plants: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:15416–15431
Rizwan M, Ali S, Qayyum MF, Ibrahim M, Rehman MZ, Abbas T, Ok YS (2016) Mechanisms of biochar-mediated alleviation of toxicity of trace elements in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:2230–2248
Rizwan M, Ali S, Rehman MZ, Maqbool A (2019a) A critical review on the effects of zinc at toxic levels of cadmium in plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:6279–6289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04174-6
Rizwan M, Ali S, ur Rehman MZ, Adrees M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF, Ali L, Hussain A, Chatha SA, Imran M (2019b) Alleviation of cadmium accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) by foliar spray of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biochar to contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 248:358–367
Saifullah JH, Naeem A, Rengel Z, Dahlawi S (2016) Timing of foliar Zn application plays a vital role in minimizing Cd accumulation in wheat. Environ Sci Pollut Res 223:16432–16439
Seneviratne M, Weerasundara L, Ok YS, Rinklebe J, Vithanage M (2017) Phytotoxicity attenuation in Vigna radiata under heavy metal stress at the presence of biochar and N fixing bacteria. J Environ Manag 186:293–300
Sohail MI, Rehman MZ, Rizwan M, Yousaf B, Ali S, Haq MA, Anayat A, Waris AA (2020) Efficiency of various silicon rich amendments on growth and cadmium accumulation in field grown cereals and health risk assessment. Chemosphere. 244:1–12
Sturikova H, Krystofova O, Huska D, Adam V (2018) Zinc, zinc nanoparticles and plants. J Hazard Mater 349:101–110
Taran N, Storozhenko V, Svietlova N, Batsmanova L, Shvartau V, Kovalenko M (2017) Effect of zinc and copper nanoparticles on drought resistance of wheat seedlings. Nanoscale Res Lett 12:60
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (2015) Silicon nanoparticles (SiNp) alleviate chromium (VI) phytotoxicity in Pisum sativum (L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 96:189–198
Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER, Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alleviate heavy metal-induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:59–69
Wang S, Wang F, Gao S (2015) Foliar application with nano-silicon alleviates Cd toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2837–2845
Wang H, Xu C, Luo ZC, Zhu HH, Wang S, Zhu QH, Huang DY, Zhang YZ, Xiong J, He YB (2018) Foliar application of Zn can reduce Cd concentrations in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29287–29294
Waqas M, Khan AL, Kang SM, Kim YH, Lee IJ (2014) Phytohormone-producing fungal endophytes and hardwood-derived biochar interact to ameliorate heavy metal stress in soybeans. Biol Fertil Soils 50:1155–1167
Waqas M, Li G, Khan S, Shamshad I, Reid BJ, Qamar Z, Chao C (2015) Application of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar to reduce polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and potentially toxic elements (PTE) accumulation in tomato. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:12114–12123
Zhang XZ (1992) The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT activities in biological system. Res Methodol Crop Physiol. Agriculture Press, Beijing, p 208-211
Acknowledgments
The financial support from Government College University, Faisalabad and Higher Education Commission (HEC) of Pakistan under HEC Project No. 5634/Punjab/NRPU/R&D/HEC/2016 is highly acknowledged. The results reported in the study are from PhD dissertation of the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, A., Rizwan, M., Ali, S. et al. Effect of composted organic amendments and zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth and cadmium accumulation by wheat; a life cycle study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 23926–23936 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08739-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08739-8