Abstract
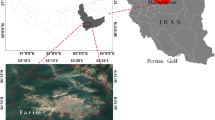
Rapid urbanisation has led to significant environmental and climatic changes worldwide, especially in urban heat islands where increased land surface temperature (LST) poses a major challenge to sustainable urban living. In the city of Abha in southwestern Saudi Arabia, a region experiencing rapid urban growth, the impact of such expansion on LST and the resulting microclimatic changes are still poorly understood. This study aims to explore the dynamics of urban sprawl and its direct impact on LST to provide important insights for urban planning and climate change mitigation strategies. Using the random forest (RF) algorithm optimised for land use and land cover (LULC) mapping, LULC models were derived that had an overall accuracy of 87.70%, 86.27% and 93.53% for 1990, 2000 and 2020, respectively. The mono-window algorithm facilitated the derivation of LST, while Markovian transition matrices and spatial linear regression models assessed LULC dynamics and LST trends. Notably, built-up areas grew from 69.40 km2 in 1990 to 338.74 km2 in 2020, while LST in urban areas showed a pronounced warming trend, with temperatures increasing from an average of 43.71 °C in 1990 to 50.46 °C in 2020. Six landscape fragmentation indices were then calculated for urban areas over three decades. The results show that the Largest Patch Index (LPI) increases from 22.78 in 1990 to 65.24 in 2020, and the number of patches (NP) escalates from 2,531 in 1990 to an impressive 10,710 in 2020. Further regression analyses highlighted the morphological changes in the cities and attributed almost 97% of the LST variability to these urban patch dynamics. In addition, water bodies showed a cooling trend with a temperature decrease from 33.76 °C in 2000 to 29.69 °C in 2020, suggesting an anthropogenic influence. The conclusion emphasises the urgent need for sustainable urban planning to counteract the warming trends associated with urban sprawl and promote climate resilience.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abulibdeh A (2021) Analysis of urban heat island characteristics and mitigation strategies for eight arid and semi-arid gulf region cities. Environ Earth Sci 80:1–26
Abulfatih HA (1984) Elevationally restricted floral elements of the Asir Mountains, Saudi Arabia. J arid environ 7(1):35–41
AlDousari AE, Kafy AA, Saha M, Fattah MA, Almulhim AI, Al Rakib A, ... Rahman MM (2022) Modelling the impacts of land use/land cover changing pattern on urban thermal characteristics in Kuwait. Sustain Cities Soc 86:04107
Almeida CRD, Teodoro AC, Gonçalves A (2021) Study of the urban heat island (UHI) using remote sensing data/techniques: a systematic review. Environments 8(10):105
Alqurashi AF, Kumar L (2019) An assessment of the impact of urbanization and land use changes in the fast-growing cities of Saudi Arabia. Geocarto Inte 34(1):78–97
Alqurashi AF, Kumar L, Sinha P (2016) Urban land cover change modelling using time-series satellite images: A case study of urban growth in five cities of Saudi Arabia. Remote Sens 8(10):838
An NN, Nhut HS, Phuong TA et al (2022) Groundwater simulation in Dak Lak province based on MODFLOW model and climate change scenarios. Front Eng Built Environ 2:55–67
Aryal J, Sitaula C, Frery AC (2023) Land use and land cover (LULC) performance modeling using machine learning algorithms: a case study of the city of Melbourne, Australia. Sci Rep 13(1):13510
Atef I, Ahmed W, Abdel-Maguid RH (2023) Modelling of land use land cover changes using machine learning and GIS techniques: a case study in El-Fayoum Governorate, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 195(6):637
Azabdaftari A, Sunar F (2022) District-based urban expansion monitoring using multitemporal satellite data: application in two mega cities. Environ Monit Assess 194(5):335
Bartesaghi-Koc C, Osmond P, Peters A (2022) Innovative use of spatial regression models to predict the effects of green infrastructure on land surface temperatures. Energy Build 254:111564
Bindajam AA, Mallick J, Hang HT (2023) Assessing landscape fragmentation due to urbanization in English Bazar Municipality, Malda, India, using landscape metrics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(26):68716–68731
Bindajam AA, Mallick J, AlQadhi S, Singh CK, Hang HT (2020) Impacts of vegetation and topography on land surface temperature variability over the semi-arid mountain cities of Saudi Arabia. Atmos 11(7):762
Chakraborti S, Banerjee A, Sannigrahi S, Pramanik S, Maiti A, Jha S (2019) Assessing the dynamic relationship among land use pattern and land surface temperature: a spatial regression approach. Asian Geogr 36(2):93–116
Chen H, Zhao Y, Fu X, Tang M, Guo M, Zhang S, ... Wu G (2022) Impacts of regional land-use patterns on ecosystem services in the typical agro-pastoral ecotone of Northern China. Ecosyst Health Sustain 8(1):2110521
Chughtai AH, Abbasi H, Karas IR (2021) A review on change detection method and accuracy assessment for land use land cover. Remote Sens Appl: Society and Environment 22:100482
Corumluoglu O (2023) Evaluation of the urban ecosystem and local climate changes caused by urbanization in İzmir in terms of long-term UHI formation with the SSI method. Resilience 7(1):11–58. https://doi.org/10.32569/resilience.1172781
Derdouri A, Wang R, Murayama Y, Osaragi T (2021) Understanding the links between LULC changes and SUHI in cities: insights from two-decadal studies (2001–2020). Remote Sens 13(18):3654
Dewa DD, Buchori I, Sejati AW, Liu Y (2022) Shannon entropy-based urban spatial fragmentation to ensure sustainable development of the urban coastal city: a case study of Semarang, Indonesia. Remote Sens Appl: Society and Environment 28:100839
Elfarkh J, Ezzahar J, Er-Raki S, Simonneaux V, Ait Hssaine B, Rachidi S, ... Jarlan L (2020) Multi-scale evaluation of the TSEB model over a complex agricultural landscape in Morocco. Remote Sens 12(7):1181
Ermida SL, Soares P, Mantas V, Göttsche FM, Trigo IF (2020) Google earth engine open-source code for land surface temperature estimation from the landsat series. Remote Sens 12(9):1471
Farid N, Moazzam MFU, Ahmad SR, Coluzzi R, Lanfredi M (2022) Monitoring the impact of rapid urbanization on land surface temperature and assessment of surface urban heat island using landsat in megacity (Lahore) of Pakistan. Front Remote Sens 3:897397
Furlan R, Marthya KL, Ellath LA, Esmat M, Al-Matwi R (2022) An urban regeneration-placemaking strategy for the Qatar National Museum and Souq Waqif’s transit-oriented development in Doha, State of Qatar. J Urban Regen Renewal 16(2):182–206
Garg V, Anand A (2022) Impact of city expansion on hydrological regime of Rispana Watershed, Dehradun, India. Geojournal 87(Suppl 4):973–997
Gerace A, Kleynhans T, Eon R, Montanaro M (2020) Towards an operational, split window-derived surface temperature product for the thermal infrared sensors onboard Landsat 8 and 9. Remote Sens 12(2):224
Ghosh S, Kumar D, Kumari R (2022) Assessing spatiotemporal dynamics of land surface temperature and satellite-derived indices for new town development and suburbanization planning. Urban Governance 2(1):144–156
Gohain KJ, Goswami A, Mohammad P, Kumar S (2023) Modelling relationship between land use land cover changes, land surface temperature and urban heat island in Indore city of central India. Theoret Appl Climatol 151(3–4):1981–2000
Guha S, Govil H (2022) Annual assessment on the relationship between land surface temperature and six remote sensing indices using Landsat data from 1988 to 2019. Geocarto Int 37(15):4292–4311
Gunawardena KR, Wells MJ, Kershaw T (2017) Utilising green and bluespace to mitigate urban heat island intensity. Sci Total Environ 584:1040–1055
Guo G, Wu Z, Xiao R, Chen Y, Liu X, Zhang X (2015) Impacts of urban biophysical composition on land surface temperature in urban heat island clusters. Landsc Urban Plan 135:1–10
He BJ, Wang W, Sharifi A, Liu X (2023) Progress, knowledge gap and future directions of urban heat mitigation and adaptation research through a bibliometric review of history and evolution. Energy Build 112976
Hou J, Du Y (2020) Spatial simulation of rainstorm waterlogging based on a water accumulation diffusion algorithm. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 11(1):71–87
Hu Q, Zhang Z, Niu L (2022) Identification and evolution of territorial space from the perspective of composite functions. Habitat Int 128:102662
Ignatieva M, Stewart GH, Meurk C (2011) Planning and design of ecological networks in urban areas. Landscape Ecol Eng 7:17–25
Imran HM, Hossain A, Islam AS, Rahman A, Bhuiyan MAE, Paul S, Alam A (2021) Impact of land cover changes on land surface temperature and human thermal comfort in Dhaka city of Bangladesh. Earth Syst Environ 5:667–693
Jamali A (2020) Land use land cover mapping using advanced machine learning classifiers: a case study of Shiraz city, Iran. Earth Sci Inform 13(4):1015–1030
Kabir S, Pahlevan N, O’Shea RE, Barnes BB (2023) Leveraging Landsat-8/-9 underfly observations to evaluate consistency in reflectance products over aquatic environments. Remote Sens Environ 296:113755
Kaiser, E. A., Rolim, S. B. A., Grondona, A. E. B., Hackmann, C. L., de Marsillac Linn, R., Käfer, P. S., ... & Diaz, L. R. (2022). Spatiotemporal Influences of LULC changes on land surface temperature in rapid urbanization area by using Landsat-TM and TIRS images. Atmosphere, 13(3), 460.
Kim M, Kim D, Kim G (2022) Examining the relationship between land use/land cover (LULC) and land surface temperature (LST) using explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) models: a case study of Seoul, South Korea. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(23):15926
Kotrosits M (2013) Affect, violence, and belonging in early Christianity. PhD. Diss., Union Theol Seminary
Krivoguz D, Chernyi SG, Zinchenko E, Silkin A, Zinchenko A (2023) Using Landsat-5 for accurate historical LULC classification: a comparison of machine learning models. Data 8(9):138
Lal P, Dubey AK, Kumar A, Kumar P, Dwivedi CS (2022) Measuring the control of landscape modifications on surface temperature in India. Geocarto Int 37(27):15736–15753
Li W, Bai Y, Chen Q, He K, Ji X, Han C (2014) Discrepant impacts of land use and land cover on urban heat islands: a case study of Shanghai, China. Ecol Ind 47:171–178
Li Z, Wang F, Kang T, Wang C, Chen X, Miao Z, ... Zhang H (2022) Exploring differentiated impacts of socioeconomic factors and urban forms on city-level CO2 emissions in China: spatial heterogeneity and varying importance levels. Sustain Cities Soc 84:104028
Li ZL, Wu H, Duan SB, Zhao W, Ren H, Liu X, ... Zhou C (2023) Satellite remote sensing of global land surface temperature: definition, methods, products, and applications. Rev Geophys 61(1):e2022RG000777
Lin J, Qiu S, Tan X, Zhuang Y (2023) Measuring the relationship between morphological spatial pattern of green space and urban heat island using machine learning methods. Build Environ 228:109910
Loukika KN, Keesara VR, Sridhar V (2021) Analysis of land use and land cover using machine learning algorithms on google earth engine for Munneru River Basin, India. Sustainability 13(24):13758
Mahmood R, Pielke Sr RA, Hubbard KG, Niyogi D, Dirmeyer PA, McAlpine C, ... Fall S (2014) Land cover changes and their biogeophysical effects on climate. Int J Climatol 34(4):929–953
Malanson GP, Alftine KJ (2023) Ecological impacts of climate change. In Biological and Environmental Hazards, Risks, and Disasters (pp. 449–479). Elsevier
Mallick J, Kant Y, Bharath BD (2008) Estimation of land surface temperature over Delhi using Landsat-7 ETM+. J Ind Geophys Union 12(3):131–140
Mendes CB, Prevedello JA (2020) Does habitat fragmentation affect landscape-level temperatures? A global analysis. Landscape Ecol 35:1743–1756
Moazzam MFU, Doh YH, Lee BG (2022) Impact of urbanization on land surface temperature and surface urban heat Island using optical remote sensing data: a case study of Jeju Island, Republic of Korea. Build Environ 222:109368
Mohamed A, Worku H, Lika T (2020) Urban and regional planning approaches for sustainable governance: The case of Addis Ababa and the surrounding area changing landscape. City Environ Interact 8:100050
Moisa MB, Dejene IN, Gemeda DO (2022) Integration of geospatial technologies with multiple regression model for urban land use land cover change analysis and its impact on land surface temperature in Jimma City, southwestern Ethiopia. Appl Geomatics 14(4):653–667
Mokarram M, Taripanah F, Pham TM (2023) Investigating the effect of surface urban heat island on the trend of temperature changes. Adv Space Res 72(8):3150–3169
Mukherjee F, Singh D (2020) Assessing land use–land cover change and its impact on land surface temperature using LANDSAT data: a comparison of two urban areas in India. Earth Syst Environ 4:385–407
Naikoo MW, Rihan M, Ishtiaque M (2020) Analyses of land use land cover (LULC) change and built-up expansion in the suburb of a metropolitan city: spatio-temporal analysis of Delhi NCR using landsat datasets. J Urban Manag 9(3):347–359
Naikoo MW, Islam ARMT, Mallick J, Rahman A (2022a) Land use/land cover change and its impact on surface urban heat island and urban thermal comfort in a metropolitan city. Urban Climate 41:101052
Naikoo MW, Rihan M, Shahfahad Peer AH, Talukdar S, Mallick J, ... Rahman A (2022b) Analysis of peri-urban land use/land cover change and its drivers using geospatial techniques and geographically weighted regression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–19
Namgyal T, Thakur DA, Rishi DS, Mohanty MP (2023) Are open-source hydrodynamic models efficient in quantifying flood risks over mountainous terrains? An exhaustive analysis over the Hindu-Kush-Himalayan region. Sci Total Environ 897:165357
Nath B, Ni-Meister W, Choudhury R (2021) Impact of urbanization on land use and land cover change in Guwahati city, India and its implication on declining groundwater level. Groundw Sustain Dev 12:100500
Ouma Y, Nkwae B, Moalafhi D, Odirile P, Parida B, Anderson G, Qi J (2022) Comparison of machine learning classifiers for multitemporal and multisensor mapping of urban LULC features. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci 43:681–689
Pande CB, Moharir KN, Varade AM, Abdo HG, Mulla S, Yaseen ZM (2023) Intertwined impacts of urbanization and land cover change on urban climate and agriculture in Aurangabad city (MS), India using Google Earth Engine platform. J Clean Prod 422:138541
Phelps NA, Nichols D (2022) Can growth be planned? The case of melbourne’s urban periphery. J Plan Educ Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456X221121248
Rahaman ZA, Kafy AA, Saha M, Rahim AA, Almulhim AI, Rahaman SN, ... Al Rakib A (2022) Assessing the impacts of vegetation cover loss on surface temperature, urban heat island and carbon emission in Penang city, Malaysia. Build Environ 222:109335
Rihan M, Bindajam AA, Talukdar S, Naikoo MW, Mallick J, Rahman A (2023) Forest fire susceptibility mapping with sensitivity and uncertainty analysis using machine learning and deep learning algorithms. Adv Space Res 72(2):426–443
Roy S, Pandit S, Eva EA, Bagmar MSH, Papia M, Banik L, ... Razi MA (2020) Examining the nexus between land surface temperature and urban growth in Chattogram Metropolitan Area of Bangladesh using long term Landsat series data. Urban Clim 32:100593
Saleem MS, Ahmad SR, Javed MA (2020) Impact assessment of urban development patterns on land surface temperature by using remote sensing techniques: a case study of Lahore, Faisalabad and Multan district. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(32):39865–39878
Salvati L, Zambon I, Chelli FM, Serra P (2018) Do spatial patterns of urbanization and land consumption reflect different socioeconomic contexts in Europe? Sci Total Environ 625:722–730
Sarkar SK, Talukdar S, Rahman A et al (2021) Groundwater potentiality mapping using ensemble machine learning algorithms for sustainable groundwater management. Front Eng Built Environ 2:43–54
Sekertekin A, Bonafoni S (2020) Land surface temperature retrieval from Landsat 5, 7, and 8 over rural areas: assessment of different retrieval algorithms and emissivity models and toolbox implementation. Remote Sens 12(2):294
Seyam MMH, Haque MR, Rahman MM (2023) Identifying the land use land cover (LULC) changes using remote sensing and GIS approach: a case study at Bhaluka in Mymensingh, Bangladesh. Case Stud Chem Environ Eng 7:100293
Shahfahad, Talukdar S, Rihan M, Hang HT, Bhaskaran S, Rahman A (2021) Modelling urban heat island (UHI) and thermal field variation and their relationship with land use indices over Delhi and Mumbai metro cities. Environ Dev Sustain 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01587-7
Shahfahad Bindajam AA, Naikoo MW, Horo JP, Mallick J, Rihan M, ... Rahman A (2023a) Response of soil moisture and vegetation conditions in seasonal variation of land surface temperature and surface urban heat island intensity in sub-tropical semi-arid cities. Theor Appl Climatol 1–29
Shahfahad Bindajam AA, Naikoo MW, Talukdar S, Asif Mallick J, Rahman A (2023b) Analysing diurnal temperature range and extreme temperature events over Delhi and Mumbai mega cities. Natural Hazards 1–29
Shen C, Hou H, Zheng Y, Murayama Y, Wang R, Hu T (2022) Prediction of the future urban heat island intensity and distribution based on landscape composition and configuration: a case study in Hangzhou. Sustain Cities Soc 83:103992
Shetty S (2019) Analysis of machine learning classifiers for LULC classification on Google Earth Engine (Master’s thesis, University of Twente)
Singh RK, Singh P, Drews M, Kumar P, Singh H, Gupta AK, ... Kumar M (2021) A machine learning-based classification of LANDSAT images to map land use and land cover of India. Remote Sens Appl: Society and Environment 24:100624
Srikanth K, Swain D (2022) Urbanization and land surface temperature changes over Hyderabad, a semi-arid mega city in India. Remote Sens Appl: Society and Environment 28:100858
Srivastava A, Bharadwaj S, Dubey R, Sharma VB, Biswas S (2022) Mapping vegetation and measuring the performance of machine learning algorithm in LULC classification in the large area using Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 datasets of Dehradun as a test case. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci 43:529–535
Su H, Han G, Li L, Qin H (2021) The impact of macro-scale urban form on land surface temperature: an empirical study based on climate zone, urban size and industrial structure in China. Sustain Cities Soc 74:103217
Sumanta DAS (2022) A review of urban heat island formation over changing climate and its impacts on urban land use and environments and adaptation measures. Int J Environ Geoinform 9(1):64–73
Talukdar S, Singha P, Mahato S, Pal S, Liou YA, Rahman A (2020) Land-use land-cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observations—a review. Remote Sens 12(7):1135
Talukdar S, Eibek KU, Akhter S, Ziaul SK, Islam ARMT, Mallick J (2021) Modeling fragmentation probability of land-use and land-cover using the bagging, random forest and random subspace in the Teesta River Basin, Bangladesh. Ecol Indic 126:107612
Tan J, Yu D, Li Q, Tan X, Zhou W (2020) Spatial relationship between land-use/land-cover change and land surface temperature in the Dongting Lake area, China. Sci Rep 10(1):9245
Tang H, Yan X, Liu T, Zheng J (2023) Spatio-temporal evolution of urban expansion along suburban railway lines in megacities based on multi-source data: a case study of Beijing, China. Remote Sens 15(19):4684
Thakur S, Maity D, Mondal I, Basumatary G, Ghosh PB, Das P, De TK (2021) Assessment of changes in land use, land cover, and land surface temperature in the mangrove forest of Sundarbans, northeast coast of India. Environ Dev Sustain 23:1917–1943
Tian Y, Tsendbazar NE, van Leeuwen E, Fensholt R, Herold M (2022) A global analysis of multifaceted urbanization patterns using Earth Observation data from 1975 to 2015. Landsc Urban Plan 219:104316
Tsagkatakis G, Aidini A, Fotiadou K, Giannopoulos M, Pentari A, Tsakalides P (2019) Survey of deep-learning approaches for remote sensing observation enhancement. Sensors 19(18):3929
Varade D, Singh H, Singh AP, Awasthi S (2023) Assessment of urban sprawls, amenities, and indifferences of LST and AOD in sub-urban area: a case study of Jammu. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(49):107179–107198
Wang F, Qin Z, Song C, Tu L, Karnieli A, Zhao S (2015) An improved mono-window algorithm for land surface temperature retrieval from Landsat 8 thermal infrared sensor data. Remote Sens 7(4):4268–4289
Wang Y, Wang D, Geng N, Wang Y, Yin Y, Jin Y (2019) Stacking-based ensemble learning of decision trees for interpretable prostate cancer detection. Appl Soft Comput 77:188–204
Wang R, Hou H, Murayama Y, Derdouri A (2020) Spatiotemporal analysis of land use/cover patterns and their relationship with land surface temperature in Nanjing, China. Remote Sens 12(3):440
Wang J, Bretz M, Dewan MAA, Delavar MA (2022) Machine learning in modelling land-use and land cover-change (LULCC): current status, challenges and prospects. Sci Total Environ 822:153559
Wu W, Zhi C, Gao Y, Chen C, Chen Z, Su H, ... Tian B (2022) Increasing fragmentation and squeezing of coastal wetlands: status, drivers, and sustainable protection from the perspective of remote sensing. Sci Total Environ 811:152339
Wulder MA, Coops NC, Roy DP, White JC, Hermosilla T (2018) Land cover 2.0. Int J Remote Sens 39(12):4254–4284
Xu C, Lin M, Fang Q, Chen J, Yue Q, Xia J (2023) Air temperature estimation over winter wheat fields by integrating machine learning and remote sensing techniques. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 122:103416
Yang Z, Huang Y, Duan Z, Tang J (2023) Capturing the spatiotemporal variations in the gross primary productivity in coastal wetlands by integrating eddy covariance, Landsat, and MODIS satellite data: a case study in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Ecol Indic 149:110154
Yang H, Xi C, Zhao X, Mao P, Wang Z, Shi Y, ... Li Z (2020) Measuring the urban land surface temperature variations under Zhengzhou city expansion using Landsat-like data. Remote Sens 12(5):801
Yao Y, Sun Z, Li L, Cheng T, Chen D, Zhou G, ... Guan Q (2023) CarbonVCA: A cadastral parcel-scale carbon emission forecasting framework for peak carbon emissions. Cities 138:104354
Yonaba R, Mounirou LA, Tazen F, Koïta M, Biaou AC, Zouré CO, ... Yacouba H (2023) Future climate or land use? Attribution of changes in surface runoff in a typical Sahelian landscape. Comptes Rendus. Géoscience 355(S1):1–28
Zhang S, Yang D, Yang Y, Piao S, Yang H, Lei H, Fu B (2018) Excessive afforestation and soil drying on China’s Loess Plateau. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 123(3):923–935
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Ding N (2022) Spatial effects of landscape patterns of urban patches with different vegetation fractions on urban thermal environment. Remote Sens 14(22):5684
Zhao ZQ, He BJ, Li LG, Wang HB, Darko A (2017) Profile and concentric zonal analysis of relationships between land use/land cover and land surface temperature: case study of Shenyang, China. Energy Build 155:282–295
Zhou W, Huang G, Cadenasso ML (2011) Does spatial configuration matter? Understanding the effects of land cover pattern on land surface temperature in urban landscapes. Landsc Urban Plan 102(1):54–63
Zhou W, Qian Y, Li X, Li W, Han L (2014) Relationships between land cover and the surface urban heat island: seasonal variability and effects of spatial and thematic resolution of land cover data on predicting land surface temperatures. Landscape Ecol 29:153–167
Zhou W, Wang J, Cadenasso ML (2017) Effects of the spatial configuration of trees on urban heat mitigation: a comparative study. Remote Sens Environ 195:1–12
Zhou Y, Chen T, Feng Z, Wu K (2022) Identifying the contradiction between the cultivated land fragmentation and the construction land expansion from the perspective of urban-rural differences. Eco Inform 71:101826
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through Research Group under grant number RGP2/349/44. The authors are also thankful to the undergraduate students of college of engineering, King Khalid University to assist in data collections.
Funding
Funding for this research was given under award numbers RGP2/349/44. by the Deanship of Scientific Research; King Khalid University, Ministry of Education, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Ahmed Ali A. Shohan, Hoang Thi Hang, Mohammed J. Alshayeb, Ahmed Ali Bindajam; data curation, Ahmed Ali A. Shohan, Hoang Thi Hang; formal analysis, Ahmed Ali A. Shohan, Hoang Thi Hang; funding acquisition, Mohammed J. Alshayeb; methodology, Ahmed Ali A. Shohan, Hoang Thi Hang; project administration, Mohammed J. Alshayeb, Ahmed Ali Bindajam; resources, Ahmed Ali A. Shohan, Hoang Thi Hang, Mohammed J. Alshayeb, Ahmed Ali Bindajam; software, Hoang Thi Hang; supervision, Mohammed J. Alshayeb, Ahmed Ali Bindajam; validation: Hoang Thi Hang; writing—original draft, Ahmed Ali A. Shohan, Hoang Thi Hang; writing—review and editing, Mohammed J. Alshayeb, Ahmed Ali Bindajam.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shohan, A.A.A., Hang, H.T., Alshayeb, M.J. et al. Spatiotemporal assessment of the nexus between urban sprawl and land surface temperature as microclimatic effect: implications for urban planning. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 29048–29070 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33091-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33091-6