Abstract
This study investigates the production of solketal (2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolane-4-methanol) from glycerol via ketalization reaction using M-ZSM-5 catalysts (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn). The wet impregnation method ensured precise metal loading and versatility in catalyst preparation. We present a novel approach by employing a suite of characterization techniques, including X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), to elucidate the catalyst’s structure, bonding, surface area, thermal stability, and morphology, ultimately linking these properties to their performance. Solketal synthesis was optimized in a reactor, with parameters like temperature, glycerol:acetone molar ratio, catalyst amount, reaction time, and stirring speed. Optimal conditions were identified as 60 °C, 1:4, 0.2 g, 60 min, and 1200 rpm, respectively. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS) analysis confirmed successful solketal formation. Among M-ZSM-5 catalysts tested, Cu-ZSM-5 emerged the most efficient, achieving an impressive 99% glycerol conversion and 96% solketal selectivity. Notably, Cu-ZSM-5 catalyst displayed exceptional reusability, regaining its initial activity through calcination, thus minimizing waste generation. This research unveils Cu-ZSM-5 as a highly efficient catalyst and promotes sustainability by utilizing a renewable glycerol feedstock to produce valuable solketal with applications in fuel additives, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. This work paves the way for developing environmentally friendly processes for waste valorization and producing valuable bio-based chemicals.
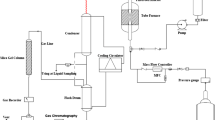
Graphical abstract


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated is available within the published version of the manuscript.
References
Abo BO, Gao M, Wang Y (2019) Production of butanol from biomass: recent advances and future prospects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20164–20182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05437-y
Aghbashlo M, Hosseinpour S, Tabatabaei M (2019) Multi-objective exergoeconomic and exergoenvironmental optimization of continuous synthesis of solketal through glycerol ketalization with acetone in the presence of ethanol as co-solvent. Renew Energy 130:735–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.06.103
Ahmad Farid MA, Hassan MA, Roslan AM (2021) Improving the decolorization of glycerol by adsorption using activated carbon derived from oil palm biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:27976–27987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12585-7
Akinnawo CA, Mosia L, Alimi OA (2021) Eco-friendly synthesis of valuable fuel bio-additives from glycerol. Catal Commun 152:106287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2021.106287
Al-Dughaither AS, de Lasa H (2014) HZSM-5 zeolites with different SiO2/Al2O3 ratios. Characterization and NH3 desorption kinetics. Ind & Eng Chem Res 53:15303–15316. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4039532
Ali I, Hassan A, Shabaan S, El-Nasser K (2017) Synthesis and characterization of composite catalysts Cr/ZSM-5 and their effects toward photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol. Arab J Chem 10:S2106–S2114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.042
Ammaji S, Rao GS, Chary KVR (2018) Acetalization of glycerol with acetone over various metal-modified SBA-15 catalysts. Appl Petrochemical Res 8:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13203-018-0197-6
Babu S, Subha P, Swapna B (2024) Valorizing biomass waste glycerol to fuel additive at room temperature using a nanostructured WO3/Nb2O5 catalyst. Catal Commun 186:106827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2023.106827
Barzallo D, Lazo R, Medina C (2023) Synthesis and application of ZSM-5 catalyst supported with zinc and/or nickel in the conversion of pyrolytic gases from recycled polypropylene and polystyrene mixtures under hydrogen atmosphere. Polymers 15:3329–3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163329
Catuzo GL, Santilli CV, Martins L (2021) Hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of ZSM-5 zeolites on the two-phase ketalization of glycerol with acetone. Catal Today 381:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.07.008
Chotchuang A, Kunsuk P, Phanpitakkul A (2022) Production of glycerol carbonate from glycerol over modified sodium-aluminate-doped calcium oxide catalysts. Catal Today 388–389:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.06.007
Collard X, Li L, Lueangchaichaweng W (2014) Ga-MCM-41 nanoparticles: synthesis and application of versatile heterogeneous catalysts. Catal Today 235:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2014.02.055
Cruz-Navarro DS, Torres-Rodríguez M, Gutiérrez-Arzaluz M (2022) Comparative study of Cu/ZSM-5 catalysts synthesized by two ion-exchange methods. Crystals 12:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12040545
D’Angelo SC, Dall’Ara A, Mondelli C (2018) Techno-economic analysis of a glycerol biorefinery. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:16563–16572. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03770
Deplano G, Signorile M, Crocellà V (2022) Titration of Cu(I) sites in Cu-ZSM-5 by volumetric CO adsorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c03370
Deutsch J, Martin A, Lieske H (2007) Investigations on heterogeneously catalysed condensations of glycerol to cyclic acetals. J Catal 245:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2006.11.006
Dolsiririttigul N, Numpilai T, Wattanakit C (2023) Structure-activity relationships of Pt-WOx/Al2O3 prepared with different W contents and pretreatment conditions for glycerol conversion to 1,3-propanediol. Top Catal 66:205–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-022-01753-9
Frusteri F, Spadaro L, Beatrice C, Guido C (2007) Oxygenated additives production for diesel engine emission improvement. Chem Eng J 134:239–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.03.042
Gadamsetti S, Rajan NP, Rao GS, Chary KVR (2015) Acetalization of glycerol with acetone to bio fuel additives over supported molybdenum phosphate catalysts. J Mol Catal A Chem 410:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2015.09.006
Gui Z, Zahrtmann N, Saravanamurugan S (2016) Brønsted acid ionic liquids (BAILs) as efficient and recyclable catalysts in the conversion of glycerol to solketal at room temperature. ChemistrySelect 1:5869–5873. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201601600
Gujar JP, Modhera B (2023) A review on catalytic conversion of biodiesel derivative glycerol to bio-olefins. Mater Today Proc 72:2723–2730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.09.418
Guo Y, Delbari SA, Sabahi Namini A (2023) Recent developments in solid acid catalysts for biodiesel production. Mol Catal 547:113362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2023.113362
Hosseinpour M, Akizuki M, Yoko A (2020) Novel synthesis and characterization of Fe-ZSM-5 nanocrystals in hot compressed water for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 292:109708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109708
Ilgen O, Yerlikaya S, Akyurek FO (2016) Synthesis of solketal from glycerol and acetone over amberlyst-46 to produce an oxygenated fuel additive. Period Polytech Chem Eng 61(2):144–148. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPch.8895
Jiang Y, Zhou R, Ye B, Hou Z (2022) Acetalization of glycerol over sulfated UiO-66 under mild condition. J Ind Eng Chem 110:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2022.03.008
Khani Y, Kamyar N, Bahadoran F (2023) M-Al2O4 (M: Mg, Ni, and Co) as unique support for Ni active metal to form a catalyst for renewable biohydrogen and syngas production from glycerol reforming over a microchannel reactor. Fuel 332:126119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126119
Kosinov N, Wijpkema ASG, Uslamin E (2018) Confined carbon mediating dehydroaromatization of methane over Mo/ZSM-5. Angew Chemie Int Ed 57:1016–1020. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201711098
Krisyuningsih Krisnandi Y, Arifa Nurani D, Reza M (2021) Partial oxidation of methane to methanol on cobalt oxide-modified hierarchical ZSM-5. Biogas - Recent Adv Integr Approaches. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.86133
Lai S, Meng D, Zhan W (2015) The promotional role of Ce in Cu/ZSM-5 and in situ surface reaction for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. RSC Adv 5:90235–90244. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra12505g
Lee AF, Bennett JA, Manayil JC, Wilson K (2014) Heterogeneous catalysis for sustainable biodiesel production via esterification and transesterification. Chem Soc Rev 43:7887–7916. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00189c
Li KT, Li HH (2020) Glycerol conversion to lactic acid with unsupported copper salts and bulk cupric oxide in aqueous alkali media. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 191:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03237-6
Li X, Zheng L, Hou Z (2018a) Acetalization of glycerol with acetone over Co[II](Co[III]xAl2−x)O4 derived from layered double hydroxide. Fuel 233:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.096
Li Z, Miao Z, Wang X (2018b) One-pot synthesis of ZrMo-KIT-6 solid acid catalyst for solvent-free conversion of glycerol to solketal. Fuel 233:377–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.06.081
Li X, Jiang Y, Zhou R, Hou Z (2020) Acetalization of glycerol with acetone over appropriately-hydrophobic zirconium organophosphonates. Appl Clay Sci 189:105555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105555
Li J, Xiao G, Guo Z (2021) ZSM-5-supported V-Cu bimetallic oxide catalyst for remarkable catalytic oxidation of toluene in coal-fired flue gas. Chem Eng J 419:129675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129675
Ling R, Chen W, Hou J (2018) Preparation of modified MFI (ZSM-5 and silicalite-1) zeolites for potassium extraction from seawater. Particuology 36:190–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2017.04.003
Liu S, Musuku SR, Adhikari S, Fernando S (2009) Adsorption of glycerol from biodiesel washwaters. Environ Technol 30:505–510. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330902803019
Liu M, Yan W, Wu J (2020) Electronically coupled PtCo/MgAl hydrotalcite catalysts display tunable selectivity toward glyceric acid and lactic acid for glycerol conversion. Catal Letters 150:2590–2598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03149-4
Liu C, Kang R, Bin F (2022) Insights on copper, manganese, and nickel/ZSM-5 catalytic mechanisms for nitric oxides selective reduction with ammonia. Carbon Resour Convers 5:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crcon.2021.11.002
Mai CTQ, Ye Y, Rempel GL, Ng FTT (2023) A novel one-step synthesis of 1-propanol from hydrogenolysis of glycerol using a Ni-HSiW/Al2O3 catalyst – the impact of H2 pressure on catalyst performance. Catal Today 407:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2022.09.017
Maksimov AL, Nekhaev AI, Ramazanov DN (2011) Preparation of high-octane oxygenate fuel components from plant-derived polyols. Pet Chem 51:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965544111010117
Manjunathan P, Maradur SP, Halgeri AB, Shanbhag GV (2015a) Room temperature synthesis of solketal from acetalization of glycerol with acetone: effect of crystallite size and the role of acidity of beta zeolite. J Mol Catal A Chem 396:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2014.09.028
Mena-Cervantes VY, Hernández-Altamirano R, Tiscareño-Ferrer A (2020) Development of a green one-step neutralization process for valorization of crude glycerol obtained from biodiesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:28500–28509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07287-0
Mimura N, Muramatsu N, Hiyoshi N (2021) Continuous production of glyceric acid and lactic acid by catalytic oxidation of glycerol over an Au–Pt/Al2O3 bimetallic catalyst using a liquid-phase flow reactor. Catal Today 375:191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.03.029
Mohamed EF, Awad G, Zaitan H (2018) Transition metals-incorporated zeolites as environmental catalysts for indoor air ozone decomposition. Environ Technol (united Kingdom) 39:878–886. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1315457
Monteiro MR, Kugelmeier CL, Pinheiro RS (2018) Glycerol from biodiesel production: technological paths for sustainability. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 88:109–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.02.019
Mota CJA, Dodson JR, Pinto BP, Fernandes DR (2023) Sustainable acid catalyst from the hydrothermal carbonization of carrageenan: use in glycerol conversion to solketal. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 13:12009–12019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-02029-0
Nanda MR, Yuan Z, Qin W (2014a) Thermodynamic and kinetic studies of a catalytic process to convert glycerol into solketal as an oxygenated fuel additive. Fuel 117:470–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.09.066
Nanda MR, Yuan Z, Qin W (2014b) Catalytic conversion of glycerol to oxygenated fuel additive in a continuous flow reactor: process optimization. Fuel 128:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.02.068
Omar BM, Bita M, Louafi I, Djouadi A (2018) Esterification process catalyzed by ZSM-5 zeolite synthesized via modified hydrothermal method. MethodsX 5:277–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2018.03.004
Oseke GG, Atta AY, Mukhtar B (2022) Synergistic effect of Zn with Ni on ZSM-5 as propane aromatization catalyst: effect of temperature and feed flowrate. J Porous Mater 29:1839–1852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-022-01294-2
Palacio R, López D, Hernández D (2019) Bimetallic Au-Cu nanoparticles supported on CeO2 as selective catalysts for glycerol conversion to lactic acid in aqueous basic medium. J Nanoparticle Res 21:148–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4594-2
Pariente S, Tanchoux N, Fajula F (2009) Etherification of glycerol with ethanol over solid acid catalysts. Green Chem 11:1256–1261. https://doi.org/10.1039/b905405g
Pavia D, Lampman G, Kriz G (2001) Introduction to spectroscopy, Chapter 2 infrared spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Thomson Learning, Singapore, pp 14–101
Peng X, Liu L, Shen B (2023) Insight into the catalytic oxidation of toluene over M/ZSM-5 (M = Cu, Mn, Fe, Ce, Ti) catalysts. J Fuel Chem Technol 51:841–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(22)60069-0
Raja BK, Mohindra N, Goswami U, Modhera B (2022) Conversion of glycerol to solketal using heterogeneous catalysts. J Inst Eng Ser E 103:145–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40034-020-00200-2
Rodrigues R, Gonçalves M, Mandelli D (2014) Solvent-free conversion of glycerol to solketal catalysed by activated carbons functionalised with acid groups. Catal Sci Technol 4:2293–2301. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cy00181h
Rossa V, Treichel H, Alexandre D, Aranda G (2017) Transformation of glycerol into solketal by beta and ferrierite acid. PERSPECTIVA 41:101–112
Rossa V, Pessanha YSP, Díaz GC (2016) Reaction kinetic study of solketal production from glycerol ketalization with acetone. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(2):479–488. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b03581
Santos-Vieira ICMS, Mendes RF, Paz FAA (2021) Solketal production via solvent-free acetalization of glycerol over triphosphonic-lanthanide coordination polymers. Catalysts 11:598
Shirani M, Ghaziaskar HS, Xu CC (2014) A new continuous-flow process for catalytic conversion of glycerol to oxygenated fuel additive: catalyst screening. Appl Energy 124:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.03.007
Sulistyo H, Huda EN, Utami TS (2020a) Solketal production by glycerol acetalization using amberlyst-15 catalyst. ASEAN J Chem Eng 20:67–76. https://doi.org/10.22146/ajche.52455
Sulistyo H, Perdana I, Pratiwi FT, Hartati I (2020b) Kinetics and thermodynamics studies of ketalization of glycerol and acetone in the presence of basolite F300 as catalyst. IOP Conference Series: Mater Sci Eng 742: Article No. - 012007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/742/1/012007
Talebian-Kiakalaieh A, Amin NAS, Najaafi N, Tarighi S (2018) A review on the catalytic acetalization of bio-renewable glycerol to fuel additives. Front Chem 6:68–80. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00573
Tamošiūnas A, Valatkevičius P, Gimžauskaitė D (2017) Energy recovery from waste glycerol by utilizing thermal water vapor plasma. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:10030–10040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8097-8
Tariq A, Ruiz Esquius J, Davies TE (2021) Combination of Cu/ZnO methanol synthesis catalysts and ZSM-5 zeolites to produce oxygenates from CO2 and H2. Top Catal 64:965–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-021-01447-8
Tatar DK, Jha JM (2023) Wet chemical synthesis and characterization of CuO nanoparticles and their application in pool boiling heat transfer. J Cryst Growth 617:127305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2023.127305
Urquieta-González EA, Martins L, Peguin RPS, Batista MS (2002) Identification of extra-framework species on Fe/ZSM-5 and Cu/ZSM-5 catalysts typical microporous molecular sieves with zeolitic structure. Mater Res 5:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-14392002000300017
Vannucci JA, Nichio NN, Pompeo F (2021) Solketal synthesis from ketalization of glycerol with acetone: a kinetic study over a sulfated zirconia catalyst. Catal Today 372:238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.10.005
Vasantha VT, Venkatesha NJ, Shamshuddin SZM (2018) Sulphated zirconia supported on cordierite honeycomb monolith for effective synthesis of solketal from acetalisation of glycerol with acetone. ChemistrySelect 3:602–608. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201702186
Veras STS, Rojas P, Florencio L (2020) 1,3-Propanediol production from glycerol in polyurethane foam containing anaerobic reactors: performance and biomass cultivation and retention. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:45662–45674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10404-z
Vicente G, Melero JA, Morales G (2010) Acetalisation of bio-glycerol with acetone to produce solketal over sulfonic mesostructured silicas. Green Chem 12:899–990. https://doi.org/10.1039/b923681c
Wen Z, Wan T, Vijeta A (2021) Photocatalytic C−H azolation of arenes using heterogeneous carbon nitride in batch and flow. Chemsuschem 14:5265–5270. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202101767
Yang S, Sun H, Yang S (2023) Investigation of sorption-enhanced hydrogen production by glycerol steam reforming in bubbling fluidized bed. Fuel 349:128731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.128731
Yang X, Wang X, Qiao X (2020) Effect of hydrothermal aging treatment on decomposition of NO by Cu-ZSM-5 and modified mechanism of doping Ce against this influence. Materials 13(4):888–904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma1304088
Zahid I, Ayoub M, Abdullah BB (2020) Production of fuel additive solketal via catalytic conversion of biodiesel-derived glycerol. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:20961–20978. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c04123
Zeng L, Liu F, Zhao T, Cao J (2021) Superior ZSM-5@γ-Al2O3 composite catalyst for methanol and ethanol coconversion to light olefins. ACS Omega 6:19067–19075. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c02369
Zhang F, Ren X, Huang H (2018) High-performance phosphate supported on HZSM-5 catalyst for dehydration of glycerol to acrolein. Chinese J Chem Eng 26:1031–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.01.005
Zhou CH, Beltramini JN, Lu GQ (2008) Chemoselective catalytic conversion of glycerol as a biorenewable source to valuable commodity chemicals. Chem Soc Rev 37:527–549. https://doi.org/10.1039/b707343g
Zhou R, Jiang Y, Zhao H (2021) Synthesis of solketal from glycerol over modified SiO2 supported p-phenolsulfonic acid catalyst. Fuel 291:120207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120207
Živković S, Veljković M (2018) Environmental impacts the of production and use of biodiesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0649-z
Acknowledgements
The author expresses gratitude to the Director of Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal, India, for facilitating the necessary resources and support essential for the successful completion of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jamna Prasad Gujar: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, data curation, writing the original draft; Bharat Modhera: supervision, methodology, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
No human and/or animal studies were involved in this study.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Consent to publish
All co-authors have provided their consent for the publication of this manuscript in Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: George Z. Kyzas
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Solketal synthesis over metal (M) impregnated with ZSM-5 catalyst was studied.
• Optimal reaction conditions were identified (60 °C, glycerol:acetone 1:4, 0.2-g catalyst, 60 min, 1200 rpm) with solketal formation confirmed by GC-MS.
• The Cu-ZSM-5 catalyst exhibited significant glycerol conversion (99%) and solketal selectivity (96%).
• Cu-ZSM-5 catalyst reusability is vital for economically possible solketal production, showing consistent performance across cycles.
• The ketalization reaction is sustainable and produces no harmful by-products.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gujar, J.P., Modhera, B. Green synthesis of solketal from glycerol using metal-modified ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts: process optimization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 28353–28367 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33031-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33031-4