Abstract
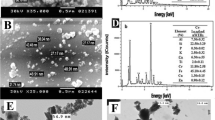
Heavy metals (HMs) in water are highly poisonous and carcinogenic agents for human health. To alleviate the toxic impacts of HMs, green remediation technologies are the need of the hour. In this regard, different nanosorbents (CMCG@ORP, ORAC, NiO/NPs, and NiO@ORAC/NCs) were synthesized in the present study, and the percentage removal of heavy metals [chromium(VI) and cadmium(II) ions] was evaluated. The nanosorbents were characterized by using FTIR, SEM, UV–Vis spectroscopy, and XRD. UV–Vis spectroscopy confirmed the synthesis of nanosorbents such as NiO/NPs and NiO@ORAC/NCs at 330.5 nm and 352.55 nm, respectively. The characterization studies show that the surface of synthesized nano-sorbents was highly coarse, uneven, and abrasive. XRD pattern deduced that the sample was of single phase, and no other impurity was detected except the face-centered cubic-phase peak of NiO. The maximum adsorption of Cd (91%) and Cr (92%) was found at initial concentrations of 100 and 60 ppm respectively at contact time = 180 min, temperature 25 °C, and with an adsorbent dose of 0.5 g. Isothermal, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies were also performed to evaluate the adsorption mechanisms and feasibility of the process. Adsorption mostly followed Freundlich isotherm which indicates the multilayer adsorption phenomenon and the negative value of Gibb’s free energy showed the spontaneous nature and feasibility of the adsorption reaction. Surface complexation, ion exchange, surface precipitation, and the phenomenon of physical adsorption occurred on the sorbent surface which led to the attachment of Cd and Cr to the tested nanosorbents. In conclusion, NiO@ORAC/NCs were the most effective in the alleviation of Cd(II) and Cr(VI) ions in contaminated water.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data related to the submitted research work is included in the manuscript.
References
Ahmed MF, Mokhtar MB (2020) Assessing cadmium and chromium concentrations in drinking water to predict health risk in Malaysia. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(8):2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17082966
Akhter F, Zoppas FM, Soomro M, Jatoi AS, Noureen F, Akhtar MN, Mehreen F (2021) Carbon-based sorbets for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution, discrepancies, and future prospects: a state-of-the-art review. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01866-3
Al-Ghouti MA, Da’ana DA (2020) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: a review. J Hazard Mater 393:122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J Chem 6730305. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Batool F, Irfan A, Hussain S, Al-Farraj ES, Iqbal S, Akbar J, Noreen S, Akhtar T, Iqbal T, Zaki MEA (2022) Development of ion character property relationship (IC-PR) for removal of 13-metal ions by employing a novel green adsorbent Aerva javanica. Molecules 27:8213. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238213
Bhowmik KL, Debnath A, Nath RK, Saha B (2017) Synthesis of MnFe2O4 and Mn3O4 magnetic nanocomposites with enhanced properties for adsorption of Cr (VI): artificial neural network modeling. Water Sci Technol 76(12):3368–3378. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.501
Cecen F, Aktas O (2011) Activated carbon for water and wastewater treatment: integration of adsorption and biological treatment, 1st ed, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany
Chen XX, Xu YM, Lau ATY (2022) Metabolic effects of long-term cadmium exposure: an overview. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:89874–89888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23620-6
Daraz U, Li Y, Ahmad I, Iqbal R, Ditta A (2023) Remediation technologies for acid mine drainage: recent trends and future perspectives. Chemosphere 311:137089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137089
Ditta A (2012) How helpful is nanotechnology in agriculture? Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 3(3):033002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/3/3/033002
Ditta A, Arshad M (2016) Applications and perspectives of using nanomaterials for sustainable plant nutrition. Nanotechnol Rev 5(2):209–229. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2015-0060
El Mouden A, El Messaoudi N, El Guerraf A, Bouich A, Mehmeti V, Lacherai A, Jada A, Sher F (2023) Multifunctional cobalt oxide nanocomposites for efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 317:137922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137922
Es-Sahbany H, Berradi M, Nkhili S, Hsissou R, Allaoui M, Loutfi M, Bassir D, Belfaquir M, El Youbi MS (2019) Removal of heavy metals (nickel) contained in wastewater-models by the adsorption technique on natural clay. Mater Today Proc 13:866–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.04.050
Farouq R, Yousef NS (2015) Equilibrium and kinetics studies of adsorption of copper (II) ions on natural biosorbent. Int J Chem Eng Appl 6(5):319. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJCEA.2015.V6.503
Fu T, Zhang B, Gao X, Cui S, Guan CY, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Peng Y (2023) Recent progresses, challenges, and opportunities of carbon-based materials applied in heavy metal polluted soil remediation. Sci Total Environ 856:158810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158810
Gorzin F, Bahri Rasht Abadi M (2018) Adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by adsorbent prepared from paper mill sludge: kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Adsorp Sci Technol 36:149–169. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617416686976
Gupta S, Graham DW, Sreekrishnan TR, Ahammad SZ (2023) Heavy metal and antibiotic resistance in four Indian and UK rivers with different levels and types of water pollution. Sci Total Environ 857:159059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159059
Hsu CJ, Xiao YZ, Chung A, Hsi HC (2023) Novel applications of vacuum distillation for heavy metals removal from wastewater, copper nitrate hydroxide recovery, and copper sulfide impregnated activated carbon synthesis for gaseous mercury adsorption. Sci Total Environ 855:158870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158870
Humelnicu D, Lazar MM, Ignat M, Dinu IA, Dragan ES, Dinu MV (2020) Removal of heavy metal ions from multi-component aqueous solutions by eco-friendly and low-cost composite sorbents with anisotropic pores. J Hazard Mater 381:120980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120980
Iroegbu AOC, Ray SS (2022) Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications. Nanotechnol Rev 11(1):1696–1721. https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2022-0105
Ismail WNW, Syah MIAI, Abd Muhet NH, Bakar NHA, Yusop HM, Samah NA (2022) Adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions by hybrid inulin-TEOS for water treatment. Civ Eng J 8(9):1787–1798. https://doi.org/10.28991/CEJ-2022-08-09-03
Ismanto A, Hadibarata T, Widada S, Indrayanti E, Ismunarti DH, Safinatunnajah N, Kusumastuti W, Dwiningsih Y, Alkahtani J (2023) Groundwater contamination status in Malaysia: level of heavy metal, source, health impact, and remediation technologies. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 46(3):467–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-022-02826-5
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283(2–3):65–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001
Katsumata H, Kaneco S, Inomata K, Itoh K, Funasaka K, Masuyama K, Suzuki T, Ohta K (2003) Removal of heavy metals in rinsing wastewater from plating factory by adsorption with economically viable materials. J Environ Manage 69(2):187–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4797(03)00145-2
Kedzierski M, Falcou-Préfol M, Kerros ME, Henry M, Pedrotti ML, Bruzaud S (2019) A machine learning algorithm for high throughput identification of FTIR spectra: application on microplastics collected in the Mediterranean Sea. Chemosphere 234:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.113
Kołodyńska D, Gęca M, Pylypchuk IV, Hubicki Z (2016) Development of new effective sorbents based on nanomagnetite. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1371-3
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelo ̈ ster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24(4):1–39
Lan D, Qin M, Liu J, Wu G, Zhang Y, Wu H (2020) Novel binary cobalt nickel oxide hol-lowed-out spheres for electromagnetic absorption applications. Chem Eng J 382:122797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122797
Li M, Kuang S, Kang Y, Ma H, Dong J, Guo Z (2022) Recent advances in the application of iron-manganese oxide nanomaterials for removal of heavy metals in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 153157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153157
Liu Y, Wang P, Gojenko B, Yu J, Wei L, Luo D, Xiao T (2021) A review of water pollution arising from agriculture and mining activities in Central Asia: facts, causes and effects. Environ Pollut 291:118209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118209
Mandal S, Calderon J, Marpu SB, Omary MA, Shi SQ (2021) Mesoporous activated carbon as a green adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals and Congo red: characterization, adsorption kinetics, and isotherm studies. J Contam Hydrol 243:103869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2021.103869
Mazhar S, Ditta A, Bulgariu L, Ahmad I, Ahmed M, Nadiri AA (2019) Sequential treatment of paper and pulp industrial wastewater: prediction of water quality parameters by mamdani fuzzy logic model and phytotoxicity assessment. Chemosphere 227:256–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.022
Mehmood K, Ahmad HR, Saifullah (2019) Quantitative assessment of human health risk posed with chromium in waste, ground, and surface water in an industrial hub of Pakistan. Arab J Geosci 12:1-11https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4470-5
Mohan S, Gandhimathi R (2009) Removal of heavy metal ions from municipal solid waste leachate using coal fly ash as an adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.03.104
Murtaza G, Ditta A, Ahmed Z, Usman M, Faheem M, Tariq A (2021) Co-biosorption potential of Acacia nilotica bark in removing Ni and amino azo benzene from contaminated wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 233:261–271. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27514
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8
Nandiyanto ABD, Al Husaeni DN, Ragadhita R, Fiandini M, Al Husaeni DF, Maryanti R (2023) Analysis of adsorption isotherm characteristics for removing curcumin dyes from aqueous solutions using avocado seed waste carbon microparticles accompanied by computational calculations. J Eng Sci Technol 18(1):706–720
Narasimharao K, Lingamdinne LP, Al-Thabaiti S, Mokhtar M, Alsheshri A, Alfaifi SY, Chang YY, Koduru JR (2022) Synthesis and characterization of hexagonal MgFe layered double hydroxide/graphene oxide nanocomposite for efficient adsorptive removal of cadmium ion from aqueous solutions: isotherm, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism. J Water Process Eng 47:102746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102746
Ngala RA, Awe MA, Nsiah P (2018) The effects of plasma chromium on lipid profile, glucose metabolism, and cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus. A case-control study. Plos One 13(7):e0197977. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197977
Niazi NK, Bibi I, Shahid M, Ok YS, Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Wang H, Murtaza B, Islam E, Nawaz MF (2018) Arsenic removal by Japanese oak wood biochar in aqueous solutions and well water: investigating arsenic fate using integrated spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. Sci Total Environ 621:1642–1651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.063
Paithankar JG, Saini S, Dwivedi S, Sharma A, Chowdhuri DK (2021) Heavy metal associated health hazards: an interplay of oxidative stress and signal transduction. Chemosphere 262:128350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128350
Pereira SK, Kini S, Prabhu B, Jeppu GP (2022) A simplified modeling procedure for adsorption at varying pH conditions using the modified Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm. Appl Water Sci 13(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01800-6
Pomoni DI, Koukou MK, Vrachopoulos MG, Vasiliadis L (2023) A review of hydroponics and conventional agriculture based on energy and water consumption, environmental impact, and land use. Energies 16(4):1690. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041690
Rajahmundry GK, Garlapati C, Kumar PS, Alwi RS, Vo D-VN (2021) Statistical analysis of adsorption isotherm models and its appropriate selection. Chemosphere 276:130176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130176
Rizvi A, Khan MS (2019) Putative role of bacterial biosorbent in metal sequestration revealed by SEM–EDX and FTIR. Indian J Microbiol 59(2):246–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00780-7
Seow YX, Tan YH, Mubarak NM, Kansedo J, Khalid M, Ibrahim ML, Ghasemi M (2022) A review on biochar production from different biomass wastes by recent carbonization technologies and its sustainable applications. J Environ Chem Eng 10(1):107017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.107017
Shah R, Khan RS, Jan AU, Ullah S, Ditta A, Islam Z, Ullah R, Ullah R, Soufan W, Almutairi KF, Rajendran K, Elango D, Sabagh AE (2023) Plant growth regulators with a balanced supply of nutrients enhance the phytoextraction efficiency of Parthenium hysterophorus for cadmium in contaminated soil. ACS Omega 8(21):18940–18950. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c01429
Shikuku VO, Mishra T (2021) Adsorption isotherm modeling for methylene blue removal on-to magnetic kaolinite clay: a comparison of two-parameter isotherms. Appl Water Sci 11(6):103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01440-2
Shrestha R, Ban S, Devkota S, Sharma S, Joshi R, Tiwari AP, Kim HY, Joshi MK (2021) Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):105688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105688
Taamneh Y, Sharadqah S (2017) The removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using natural Jordanian zeolite. Appl Water Sci 7:2021–2028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0382-7
Ünlü N, Ersoz M (2006) Adsorption characteristics of heavy metal ions onto a low-cost biopolymeric sorbent from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 136(2):272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.013
Wang P, Cao M, Wang C, Ao Y, Hou J, Qian J (2014) Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption of methylene blue by a magnetic graphene-carbon nanotube composite. Appl Surf Sci 290:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.11.010
Wang YH, Lin SH, Juang RS (2003) Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using various low-cost adsorbents. J Hazard Mater 102(2–3):291–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00218-8
Worch, E. (2012) Adsorption technology in water treatment; de Gruyter, W., Ed, Deutscher Kunstverlag: Berlin, Germany, p 332
World Health Organization (WHO) (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality-1, recommendations, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Zaini MS, Arshad M, Syed-Hassan SS (2023) Adsorption isotherm and kinetic study of methane on palm kernel shell-derived activated carbon. J Bioresour Bioprod 8(1):66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2022.11.002
Zeb BS, Ping Z, Lin Q, Akhter MS, Ditta A, Mahmood Q, Hashem A, Dawoud TM, Abd_Allah EF (2023) Model anaerobic microbe Photobacterium phosphoreum: a potential biosensor for different metals and volatile fatty acids toxicity during wastewater treatment. Pol J Environ Stud 32(5):1–8. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/166351
Zhang P, Yang D, Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Cen Y, Zhang W, Geng W, Rong T, Liu Y, Shao J (2020) Re-examining the drive forces of China’s industrial wastewater pollution based on GWR model at the provincial level. J Clean Prod 262:121309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121309
Zhang Q, Kazim FM, Ma S, Qu K, Li M, Wang Y, Hu H, Cai W, Yang Z (2021) Nitrogen dopants in nickel nanoparticles embedded carbon nanotubes promote overall urea oxidation. Appl Catal B Environ 280:119436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119436
Zuo Q, Zheng H, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Zhang B (2023) Facile green preparation of single-and two-component modified activated carbon fibers for efficient trace heavy metals removal from drinking water. Chemosphere 137799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137799
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K., H.K.N., F.B., A.M., E.A.A., G.S., F.M., M.M., and A.D. Data curation, S.K. Formal analysis, S.K., H.K.N., F.B., A.M., E.A.A., G.S., F.M., M.M., and A.D. Investigation, S.K. Methodology, H.K.N., F.B., and A.M. Project administration, H.K.N., F.B., and A.M. Resources, S.K., H.K.N., F.B., A.M., E.A.A., G.S., F.M., M.M., and A.D. Software, S.K., H.K.N., F.B., A.M., E.A.A., G.S., F.M., M.M., and A.D. Supervision, H.K.N., F.B., and A.M. Validation, S.K., H.K.N., F.B., A.M., E.A.A., G.S., F.M., M.M., and A.D. Visualization, S.K., H.K.N., F.B., A.M., E.A.A., G.S., F.M., M.M., and A.D. Writing — original draft, S.K., H.K.N., and F.B. Writing — review and editing, S.K., H.K.N., F.B., A.M., E.A.A., G.S., F.M., M.M. and A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors agree with the content of the manuscript and gave explicit permission to submit and publish this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kanwal, S., Naeem, H.K., Batool, F. et al. Adsorption potential of orange rind–based nanosorbents for the removal of cadmium(II) and chromium(VI) from contaminated water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 110658–110673 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30164-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30164-w