Abstract
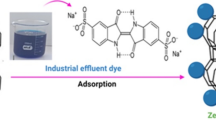
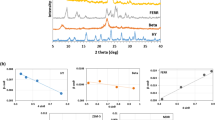
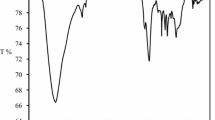
In this paper, a natural Moroccan material from the Nador area in the north east of Morocco was studied as an adsorbent to remove methyl violet 2B dye from aqueous solutions. This material has never been studied before in this region, and it will be used in its raw state. It was collected and characterized by X-ray diffraction, FTIR spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray fluorescence, thermal analysis, N2 gas adsorption–desorption, pHPZC, and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). The studies are realized with a 500-µm grain size and 182m2/g BET surface area. XRD showed the presence of significant peaks belonging to natural zeolite type clinoptilolite-Ca and minor phases. Several parameters were studied such as contact time, adsorbent mass, initial dye concentration, initial pH solution, the particle size of the material, and temperature. Out of the three isotherm models investigated after 60 min of contact time in the experiments, the Langmuir model gave the best fit to the experimental data (R2 = 0.99). The results of kinetic and thermodynamic studies revealed that the adsorption process obeyed pseudo-second-order, spontaneous (ΔG° < 0), endothermic (ΔS° > 0). The adsorption of methyl violet 2B dye is chemisorptions and physisorption. The maximum theoretical adsorption capacity was 30.30 mg·g−1 at 23 °C for a particle diameter of 500 µm. The desorption study shows that the material can be desorbed using solvents. The reuse study indicates that the same amount of natural zeolite can be used several times which makes the process efficient and sustainable. The obtained results indicate that the country of Morocco has natural zeolite among its resources and that it can be used as an efficient adsorbent for the removal of dyes.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdellaoui Y, Olguin MT, Abatal M et al (2019) Relationship between Si/AL ratio and the sorption of CD(II) by natural and modified clinoptilolite-rich tuff with sulfuric acid. Desalin Water Treat 150:157–165. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23792
Acevedo NIA, Rocha MCG, Bertolino LC (2017) Mineralogical characterization of natural clays from Brazilian Southeast region for industrial applications. Ceramica 63:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1590/0366-69132017633662045
Adeyemo AA, Adeoye IO, Bello OS (2017) Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: a review. Appl Water Sci 7:543–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0322-y
Afshin S, Rashtbari Y, Vosoughi M et al (2020) Removal of basic blue-41 dye from water by stabilized magnetic iron nanoparticles on clinoptilolite zeolite. Rev Chim 71:218–229. https://doi.org/10.37358/RC.20.2.7919
Ahmad MA, Alrozi R (2011) Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution using rambutan peel-based activated carbon: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 171:510–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.04.018
Ahmad I, Aslam M, Jabeen U et al (2022) ZnO and Ni-doped ZnO photocatalysts: synthesis, characterization and improved visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Inorganica Chim Acta 543:121167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.121167
Ahmad I, Aslam M, Jabeen U et al (2022) ZnO and Ni-doped ZnO photocatalysts: synthesis, characterization and improved visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Inorganica Chim Acta 543:121167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2022.121167
Ahmed MJ (2017) Adsorption of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from aqueous solution using activated carbons: review. J Environ Manage 190:274–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.073
Albarelli JQ, Rabelo RB, Santos DT et al (2011) Effects of supercritical carbon dioxide on waste banana peels for heavy metal removal. J Supercrit Fluids 58:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2011.07.014
Allen SJ, Mckay G, Porter JF (2004) Adsorption isotherm models for basic dye adsorption by peat in single and binary component systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:322–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.078
Aloulou H, Bouhamed H, Ghorbel A et al (2017) Elaboration and characterization of ceramic microfiltration membranes from natural zeolite: application to the treatment of cuttlefish effluents. Desalin Water Treat 95:9–17. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.21348
Alshameri A, He H, Zhu J et al (2018) Adsorption of ammonium by different natural clay minerals: characterization, kinetics and adsorption isotherms. Appl Clay Sci 159:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.007
Alshameri A, Xinghu W, Dawood AS et al (2019) Characterization of Yemeni natural zeolite (Al-Ahyuq area) and its environment applications: a review. J Ecol Eng 20:157–166. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/102842
Alver E, Metin AÜ (2012) Anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions using modified zeolite: adsorption kinetics and isotherm studies. Chem Eng J 200–202:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.038
Amrhar O, Nassali H, Elyoubi MS (2015) Adsorption of a cationic dye, methylene blue, onto Moroccan Illitic clay. J Mater Environ Sci 6:3054–3065
Anirudhan TS, Ramachandran M (2015) Adsorptive removal of basic dyes from aqueous solutions by surfactant modified bentonite clay (organoclay): kinetic and competitive adsorption isotherm. Process Saf Environ Prot 95:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.03.003
Aurich A, Hofmann J, Oltrogge R et al (2017) Improved Isolation of Microbiologically Produced (2R,3S)-Isocitric Acid by Adsorption on Activated Carbon and Recovery with Methanol. Org Process Res Dev 21:866–870. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00090
Ayari F, Srasra E, Trabelsi-Ayadi M (2005) Characterization of bentonitic clays and their use as adsorbent. Desalination 185:391–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.046
Babel S, Kurniawan TA (2003) Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: a review. J Hazard Mater 97:219–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00263-7
Bardestani R, Patience GS, Kaliaguine S (2019) Experimental methods in chemical engineering: specific surface area and pore size distribution measurements—BET, BJH, and DFT. Can J Chem Eng 97:2781–2791. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.23632
Bazrafshan E, Zarei AA, Mohammadi L et al (2021) Efficient tetracycline removal from aqueous solutions using ionic liquid modified magnetic activated carbon (IL@mAC). J Environ Chem Eng 9:106570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106570
Belaid KD, Kacha S (2011) Study of the kinetics and thermodynamics of the adsorption of a basic dye on sawdust. Rev Des Sci L’eau 24:131–144. https://doi.org/10.7202/1006107ar
Boulahbal M, Malouki MA, Canle M et al (2022) Removal of the industrial azo dye crystal violet using a natural clay: characterization, kinetic modeling, and RSM optimization. Chemosphere 306:135516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135516
Camacho LM, Deng S, Parra RR (2010) Uranium removal from groundwater by natural clinoptilolite zeolite: effects of pH and initial feed concentration. J Hazard Mater 175:393–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.017
Çoruh S, Geyikçi F, Elevli S (2011) Adsorption of neutral red dye from an aqueous solution onto natural sepiolite using full factorial design. Clays Clay Miner 59:617–625. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590607
Danish M, Birnbach J, Mohamad Ibrahim MN et al (2021) Optimization study of caffeine adsorption onto large surface area wood activated carbon through central composite design approach. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100594
Depeursinge A, Racoceanu D, Iavindrasana J, et al (2010) Fusing visual and clinical information for lung tissue classification in HRCT data. Artif Intell Med 170:ARTMED1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j
Djebbar M, Djafri F, Bouchekara M, Djafri A (2012) Adsorption of phenol on natural clay. Appl Water Sci 2:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-012-0031-8
Djilani C, Zaghdoudi R, Djazi F et al (2015) Adsorption of dyes on activated carbon prepared from apricot stones and commercial activated carbon. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 53:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.02.025
El Mrabet I, Benzina M, Zaitan H (2021) Treatment of landfill leachate from fez city by combined fenton and adsorption processes using Moroccan bentonite clay. Desalin Water Treat 225:402–412. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27142
Englert AH, Rubio J (2005) Characterization and environmental application of a Chilean natural zeolite. Int J Miner Process 75:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2004.01.003
EPA (2004) This is a reproduction of a library book that was digitized by Google as part of an ongoing effort to preserve the information in books and make it universally accessible. Biol Cent 2:v–413
Farooq Khan M, Ahmed H, Abdulkareem Almashhadani H et al (2022) Sustainable adsorptive removal of high concentration organic contaminants from water using biodegradable Gum-Acacia integrated magnetite nanoparticles hydrogel adsorbent. Inorg Chem Commun 145:110057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.110057
Farooq Khan M, Jamal A, Jacquline Rosy P et al (2022) Eco-friendly elimination of organic pollutants from water using graphene oxide assimilated magnetic nanoparticles adsorbent. Inorg Chem Commun 139:109422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109422
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2012) Microwave-assisted preparation and adsorption performance of activated carbon from biodiesel industry solid reside: influence of operational parameters. Bioresour Technol 103:398–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.116
Ghamkhari A, Mohamadi L, Kazemzadeh S et al (2020) Synthesis and characterization of poly(styrene-block-acrylic acid) diblock copolymer modified magnetite nanocomposite for efficient removal of penicillin G. Compos Part B Eng 182:107643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107643
Ghamkhari A, Mohamadi L, Kazemzadeh S et al (2020) Synthesis and characterization of poly(styrene-block-acrylic acid) diblock copolymer modified magnetite nanocomposite for efficient removal of penicillin G. Compos Part B Eng 182:107643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107643
Gómez V, Larrechi MS, Callao MP (2007) Kinetic and adsorption study of acid dye removal using activated carbon. Chemosphere 69:1151–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.076
Hadri M, El Mrabet I, Chaouki Z et al (2022) Valorization of natural diatomite mineral: application to removal of anionic dye from aqueous solution in a batch and fixed-bed reactor. J Cent South Univ 29:2084–2098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-022-5065-y
Han R, Zhang J, Han P et al (2009) Study of equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters about methylene blue adsorption onto natural zeolite. Chem Eng J 145:496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.05.003
Hassani AH, Seif S, Javid AH, Borghei M (2008) Comparison of adsorption process by GAC with novel formulation of coagulation - flocculation for color removal of textile wastewater. Int J Environ Res 2:239–248
Ho YS (2004) Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 59:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000013305.99473.cf
Iqbal M (2016) Vicia faba bioassay for environmental toxicity monitoring: a review. Chemosphere 144:785–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.048
Iqbal M, Nisar J (2015) Cytotoxicity and mutagenicity evaluation of gamma radiation and hydrogen peroxide treated textile effluents using bioassays. J Environ Chem Eng 3:1912–1917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.06.011
Jin X, Jiang MQ, Shan XQ et al (2008) Adsorption of methylene blue and orange II onto unmodified and surfactant-modified zeolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 328:243–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2008.08.066
Kausar A, Iqbal M, Javed A et al (2018) Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: a review. J Mol Liq 256:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Kinashi K, Kambe Y, Misaki M et al (2012) Synthesis, characterization, photo-induced alignment, and surface orientation of poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene-alt-azobenzene)s. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 50:5107–5114. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.26338
Kooh MRR, Dahri MK, Lim LBL et al (2016) Batch adsorption studies of the removal of methyl violet 2B by soya bean waste: isotherm, kinetics and artificial neural network modelling. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5582-9
Kooh MRR, Dahri MK, Lim LBL (2017) Removal of the methyl violet 2B dye from aqueous solution using sustainable adsorbent Artocarpus odoratissimus stem axis. Appl Water Sci 7:3573–3581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0496-y
Kragović MM, Daković AS, Milićević SZ et al (2009) Uticaj sorpcije organskog katjona na tačku nultog naelektrisanja prirodnog zeolita. Hem Ind 63:325–330. https://doi.org/10.2298/HEMIND0904325K
Kragović M, Stojmenović M, Petrović J et al (2019) Influence of alginate encapsulation on point of zero charge (pH pzc ) and thermodynamic properties of the natural and Fe(III)-modified zeolite. Procedia Manuf 32:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.02.216
Li M, Zhu X, Zhu F et al (2011) Application of modified zeolite for ammonium removal from drinking water. Desalination 271:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.12.047
Mahmoodi NM (2013) Nickel ferrite nanoparticle: synthesis, modification by surfactant and dye removal ability. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1419-7
Mahmoud DK, Salleh MAM, Karim WAWA et al (2012) Batch adsorption of basic dye using acid treated kenaf fibre char: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 181–182:449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.11.116
Marzal P, Cabrera C, Gabald C (2005) Sorption characteristics of heavy metal ions by a natural zeolite. J Chem Technol Biotechnol Int Res Process Environ Clean Technol 481:477–481. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1189
Mehr HV, Saffari J, Mohammadi SZ, Shojaei S (2020) The removal of methyl violet 2B dye using palm kernel activated carbon: thermodynamic and kinetics model. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:1773–1782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02271-0
Miyah Y, Lahrichi A, Idrissi M et al (2017) Assessment of adsorption kinetics for removal potential of crystal violet dye from aqueous solutions using Moroccan pyrophyllite. J Assoc Arab Univ Basic Appl Sci 23:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaubas.2016.06.001
Mohammadi L, Zafar MN, Bashir M et al (2021) Modeling of phenol removal from water by NiFe2O4nanocomposite using response surface methodology and artificial neural network techniques. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105576
Mokhtari-Shourijeh Z, Montazerghaem L, Olya ME (2018) Preparation of porous nanofibers from electrospun polyacrylonitrile/polyvinylidene fluoride composite nanofibers by inexpensive salt using for dye adsorption. J Polym Environ 26:3550–3563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1238-z
Munir M, Nazar MF, Zafar MN et al (2020) Effective adsorptive removal of methylene blue from water by didodecyldimethylammonium bromide-modified brown clay. ACS Omega 5:16711–16721. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01613
Munir M, Nazar MF, Zafar MN (2021) Removal of amaranth dye over surfactant modified dull pink clay from aqueous medium. Int J Environ Anal Chem 101:2848–2865. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1711899
Musa SA, Abdulhameed AS, Baharin SNA et al (2023) Coal-based activated carbon via microwave-assisted ZnCl2 activation for methyl violet 2B dye removal: optimization, desirability function, and adsorption mechanism. Minerals 13(3):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/min13030438
Nippes RP, Macruz PD, Molina LCA, Scaliante MHNO (2022) Hydroxychloroquine adsorption in aqueous medium using clinoptilolite zeolite. Water Air Soil Pollut 233(8):287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05787-3
Nooraee Nia N, Rahmani M, Kaykhaii M, Sasani M (2017) Evaluation of Eucalyptus leaves as an adsorbent for decolorization of methyl violet (2B) dye in contaminated waters: thermodynamic and kinetics model. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:825–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0338-4
Nwosu FO, Ajala OJ, Owoyemi RM, Raheem BG (2018) Preparation and characterization of adsorbents derived from bentonite and kaolin clays. Appl Water Sci 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0827-2
Olad A, Naseri B (2010) Preparation, characterization and anticorrosive properties of a novel polyaniline/clinoptilolite nanocomposite. Prog Org Coatings 67:233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2009.12.003
Özcan AS, Erdem B, Özcan A (2004) Adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto Na-bentonite and DTMA-bentonite. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.07.035
Özcan A, Öncü EM, Özcan AS (2006) Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto natural sepiolite. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 277:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.11.017
Özer D, Dursun G, Özer A (2007) Methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution by dehydrated peanut hull. J Hazard Mater 144:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.092
Perraki T, Orfanoudaki A (2004) Mineralogical study of zeolites from Pentalofos area, Thrace, Greece. Appl Clay Sci 25:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-1317(03)00156-X
Ren TZ, Zhu XH, Ma TY, Yuan ZY (2013) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by periodic mesoporous titanium phosphonate materials. Adsorpt Sci Technol 31:535–548. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.31.6.535
Riaz Q, Ahmed M, Zafar MN et al (2022) NiO nanoparticles for enhanced removal of methyl orange: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamic and desorption studies. Int J Environ Anal Chem 102:84–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1715383
Ribeiro TH, Rubio J, Smith RW (2003) A dried hydrophobic aquaphyte as an oil filter for oil/water emulsions. Spill Sci Technol Bull 8:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1353-2561(03)00130-0
Saeidi N, Parvini M, Niavarani Z (2015) High surface area and mesoporous graphene/activated carbon composite for adsorption of Pb(II) from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 3:2697–2706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.09.023
Seraj S, Ferron RD, Juenger MCG (2016) Calcining natural zeolites to improve their effect on cementitious mixture workability. Cem Concr Res 85:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2016.04.002
Sprynskyy M, Golembiewski R, Trykowski G, Buszewski B (2010) Heterogeneity and hierarchy of clinoptilolite porosity. J Phys Chem Solids 71:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2010.05.006
Su CXH, Teng TT, Alkarkhi AFM, Low LW (2014) Imperata cylindrica (cogongrass) as an adsorbent for methylene blue dye removal: process optimization. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1941-x
Toth J (1971) State equation of the solid-gas interface layers. Acta Chim Hung 69:311–328
Veli S, Alyüz B (2007) Adsorption of copper and zinc from aqueous solutions by using natural clay. J Hazard Mater 149:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.109
Vijetha P, Ramesh Naidu M, Satyasree N, Rajasekhar Reddy P (2017) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using Tamarindus indica. Res J Pharm Technol 10:2557–2560. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2017.00452.8
Visa M (2016) Synthesis and characterization of new zeolite materials obtained from fly ash for heavy metals removal in advanced wastewater treatment. Powder Technol 294:338–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2016.02.019
Wang S, Zhu ZH (2006) Characterisation and environmental application of an Australian natural zeolite for basic dye removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 136:946–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.038
Xavier KCM, Dos Santos MDSF, Santos MRMC et al (2014) Effects of acid treatment on the clay palygorskite: XRD, surface area, morphological and chemical composition. Mater Res 17:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392014005000057
Zafar B, Shafqat SS, Zafar MN et al (2022) NaHCO3 assisted multifunctional Co3O4, CuO and Mn2O3 nanoparticles for tartrazine removal from synthetic wastewater and biological activities. Mater Today Commun 33:104946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104946
Zaitan H, Bianchi D, Achak O, Chafik T (2008) A comparative study of the adsorption and desorption of o-xylene onto bentonite clay and alumina. J Hazard Mater 153:852–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.070
Zhou Y, Pervin F, Biswas MA et al (2006) Fabrication and characterization of montmorillonite clay-filled SC-15 epoxy. Mater Lett 60:869–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2005.10.042
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Meryem El rharib, Konouz Hamidallah, and Zaina Zaroual. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Meryem El rharib and Zaina Zaroual, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
rharib, M.E., Hamidallah, K., Zaroual, Z. et al. Characterization and application of natural Moroccan material for methyl violet 2B dye removal from aqueous solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28307-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28307-0