Abstract
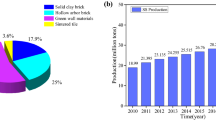
Recycling municipal sewage sludge in fired bricks not only contributes to environmental protection, but is also an alternative to natural clay resource. The complex compositions of sludge have a great influence on the brick property. This work presents a systematical investigation on fired bricks made only with sludge and shale. The physicochemical properties of the raw mixtures, macroscopic performance, microstructure, and its evolution were quantitatively determined. The coordination between shale and sludge enables the blend of raw materials to achieve the desired gradation and plasticity. Although a reduction in compressive strength was observed, the open porosity was increased to 31.6% and thermal conductivity was reduced to 0.51 W·(m·K)−1, indicating the benefit to the performance of lightweight thermal insulation bricks. The fitting results confirm the pore-forming effect induced by the organic matter in the sludge. The obtained bricks possess good performance, especially in thermal insulation properties, and environmental and economic benefits.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed for the current study are available on request.
References
Areias IOR, Vieira CMF, Colorado HA et al (2020) Could city sewage sludge be directly used into clay bricks for building construction? A comprehensive case study from Brazil. J Build Eng 31:101374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101374
ASTM (2006) Standard classification of soils for engineering purposes (unified soil classification system)
Azevedo A, de Matos P, Marvila M et al (2021) Rheology, hydration, and microstructure of portland cement pastes produced with ground açaí fibers. Appl Sci 11:3036. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11073036
Azevedo ARG, Marvila TM, Júnior Fernandes W et al (2019) Assessing the potential of sludge generated by the pulp and paper industry in assembling locking blocks. J Build Eng 23:334–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.02.012
Balshin MY (1949) Relation of mechanical properties of powder metals and their porosity and the ultimate properties of porous metal-ceramic materials. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 67:831–834
Beshah DA, Tiruye GA, Mekonnen YS (2021) Characterization and recycling of textile sludge for energy-efficient brick production in Ethiopia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:16272–16281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11878-7
Cangussu N, Vasconcelos L, Maia L (2022) Environmental benefits of using sewage sludge in the production of ceramic bricks. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18670-9
Chang Z, Long G, Zhou JL, Ma C (2020) Valorization of sewage sludge in the fabrication of construction and building materials: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 154:104606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104606
Chiang K-Y, Yen H-R, Lu C-H (2019) Recycled gypsum board acted as a mineral swelling agent for improving thermal conductivity characteristics in manufacturing of green lightweight building brick. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:34205–34219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3801-5
Cobo-Ceacero CJ, Cotes-Palomino MT, Martínez-García C et al (2019) Use of marble sludge waste in the manufacture of eco-friendly materials: applying the principles of the Circular Economy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:35399–35410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05098-x
Cusido JA, Cremades LV (2003) Gaseous emissions from ceramics manufactured with urban sewage sludge during firing processes. Waste Manage 23:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00060-08
Dai Z, Zhou H, Zhang W et al (2019) The improvement in properties and environmental safety of fired clay bricks containing hazardous waste electroplating sludge: the role of Na2SiO3. J Clean Prod 228:1455–1463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.274
De Silva GHMJS, Hansamali E (2019) Eco-friendly fired clay bricks incorporated with porcelain ceramic sludge. Constr Build Mater 228:116754.1–116754.10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116754.
De Silva GHMJS, Perera BVA (2018) Effect of waste rice husk ash (RHA) on structural, thermal and acoustic properties of fired clay bricks. J Build Eng 18:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2018.03.019
Duckworth W (1953) Discussion of Ryshkewitch Paper by Winston Duckworth*. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 36
Epa US (1992) Toxicity characteristics leaching procedure, Method 1311. Test methods for the evaluation of solid waste
Feng NQ, Chan SYN, He ZS, Tsang MKC (1997) Shale ash concrete. Cem Concr Res 27:279–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(96)00201-3
Hasselman DPH (1963) Relation between effects of porosity on strength and on Young’s modulus of elasticity of polycrystalline materials. J Am Ceram Soc 46:564–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1963.tb14615.x
Hatinoğlu MD, Sanin FD (2021) Sewage sludge as a source of microplastics in the environment: a review of occurrence and fate during sludge treatment. J Environ Manage 295:113028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113028
Head KH (1992) Manual of soil laboratory testing, Volume 1. Laboratories
Huang BB, Zhang XH, Zhu JZ (2012) Influence of sludge content on compressive strength of sintering sludge-shale bricks. Appl Mech Mater 238:101–104. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.238.101
Kornmann M (2007) Clay bricks and roof tiles, manufacturing and properties
Li X, He C, Lv Y et al (2020) Utilization of municipal sewage sludge and waste glass powder in production of lightweight aggregates. Constr Build Mater 256:119413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119413
Li X, Lv Y, Ma B, et al (2014) Utilization of oil well-derived drilling waste in shale-brick production. Environ Eng Manag J 13:173–180. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2014.021
Li X-G, Lv Y, Ma B-G et al (2011) Influence of sintering temperature on the characteristics of shale brick containing oil well-derived drilling waste. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1617–1622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-011-0526-0
Li Z, Huang B, Huang B, et al. (2015) Straight joint shear performance test of urban sludge sintered shale bricks. In: Gu JW, Chen XL, Liu EH (eds) 2015 International Conference on Energy, Materials and Manufacturing Engineering (emme 2015). E D P Sciences, Cedex A, p 04009. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/20152504009
Liew AG, Idris A, Samad AA et al (2004) Reusability of sewage sludge in clay bricks. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 6:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-003-0105-7
Liu D-G, Min X-B, Ke Y et al (2018) Co-treatment of flotation waste, neutralization sludge, and arsenic-containing gypsum sludge from copper smelting: solidification/stabilization of arsenic and heavy metals with minimal cement clinker. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7600–7607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1084-x
Martínez-García C, Eliche-Quesada D, Pérez-Villarejo L et al (2012) Sludge valorization from wastewater treatment plant to its application on the ceramic industry. J Environ Manage 95:S343–S348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.06.016
Martins ROG, Alvarenga R de CSS, Pedroti LG, et al (2018) Assessment of the durability of grout submitted to accelerated carbonation test. Constr Build Mater 159:261–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.10.111
Marvila MT, Azevedo ARG, Alexandre J et al (2019) Correlation between the properties of structural clay blocks obtained by destructive tests and ultrasonic pulse tests. J Build Eng 26:100869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100869
Mezencevova A, Yeboah NN, Burns SE et al (2012) Utilization of Savannah Harbor river sediment as the primary raw material in production of fired brick. J Environ Manage 113:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.08.030
Mohajerani A, Ukwatta A, Jeffrey-Bailey T et al (2019) A proposal for recycling the world’s unused stockpiles of treated wastewater sludge (biosolids) in fired-clay bricks. Buildings 9:14. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings9010014
Ozturk S, Sutcu M, Erdogmus E, Gencel O (2019) Influence of tea waste concentration in the physical, mechanical and thermal properties of brick clay mixtures. Constr Build Mater 217:592–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.05.114
Phonphuak N (2013) Effects of additive on the physical and thermal conductivity of fired clay brick
Phonphuak N, Kanyakam S, Chindaprasirt P (2016) Utilization of waste glass to enhance physical–mechanical properties of fired clay brick. J Clean Prod 112:3057–3062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.10.084
Qing-Fan LI (2016) Discussion on factors influencing the content of urban sludge for brick-making(II). Block-Brick-Tile
Quijorna N, Coz A, Andres A, Cheeseman C (2012) Recycling of Waelz slag and waste foundry sand in red clay bricks. Resour Conserv Recycl 65:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2012.05.004
Rani MY, Bhagawan D, Himabindu V et al (2016) Preparation and characterization of green bricks using pharmaceutical industrial wastes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:9323–9333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5191-2
Shinogi Y, Yoshida H, Koizumi T et al (2003) Basic characteristics of low-temperature carbon products from waste sludge. Adv Environ Res 7:661–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(02)00040-0
Singh SK, Kulkarni S, Kumar V, Vashistha P (2018) Sustainable utilization of deinking paper mill sludge for the manufacture of building bricks. J Clean Prod 204:321–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.028
Sun C, Guo L, Zheng Y et al (2021) The hydrolysis and reduction of mixing primary sludge and secondary sludge with thermophilic bacteria pretreatment. Process Saf Environ Prot 156:288–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.10.026
Sutcu M, Alptekin H, Erdogmus E et al (2015) Characteristics of fired clay bricks with waste marble powder addition as building materials. Constr Build Mater 82:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.02.055
Teixeira SR, Santos GTA, Souza AE et al (2011) The effect of incorporation of a Brazilian water treatment plant sludge on the properties of ceramic materials. Appl Clay Sci 53:561–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2011.05.004
Wang HB, Lin ZZ, He ZY (2012) A New Brick Prepared from Municipal Sewage Sludge and Shale. Adv Mater Res 374–377:18–23
Wang S, Yu L, Yang F et al (2022a) Resourceful utilization of quarry tailings in the preparation of non-sintered high-strength lightweight aggregates. Constr Build Mater 334:127444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127444
Wang Z, Chen Y, Xu L et al (2022b) Insight into the local C-S-H structure and its evolution mechanism controlled by curing regime and Ca/Si ratio. Constr Build Mater 333:127388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127388
Wu K, Han H, Li H et al (2021) Experimental study on concurrent factors influencing the ITZ effect on mass transport in concrete. Cement Concr Compos 123:104215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104215
Wu K, Hu Y, Zhang L et al (2022) Promoting the sustainable fabrication of bricks from municipal sewage sludge through modifying calcination: microstructure and performance characterization. Constr Build Mater 324:126401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126401
Xu L, Yang K, Kang W et al (2022) A comparative physio-chemical study of steel slag blended cementitious materials in presence of hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose. Constr Build Mater 342:127940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127940
Yang Z, Lin Q, Lu S et al (2014) Effect of CaO/SiO2 ratio on the preparation and crystallization of glass-ceramics from copper slag. Ceram Int 40:7297–7305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.071
Yaras A, Sutcu M, Erdogmus E, Gencel O (2021) Recycling and immobilization of zinc extraction residue in clay-based brick manufacturing. J Build Eng 41:102421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102421
Yaras A, Sutcu M, Gencel O, Erdogmus E (2019) Use of carbonation sludge in clay based building materials processing for eco-friendly, lightweight and thermal insulation. Constr Build Mater 224:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.080
Zat T, Bandieira M, Sattler N et al (2021) Potential re-use of sewage sludge as a raw material in the production of eco-friendly bricks. J Environ Manage 297:113238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113238
Zhang Y, Lian G, Dong C et al (2020) Optimizing and understanding the pressurized vertical electro-osmotic dewatering of activated sludge. Process Saf Environ Prot 140:392–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.05.016
Zhou W, Yang F, Zhu R et al (2020) Mechanism analysis of pore structure and crystalline phase of thermal insulation bricks with high municipal sewage sludge content. Constr Build Mater 263:120021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120021
Zhou Y, Wang Z, Zhu Z et al (2022) Time-varying structure evolution and mechanism analysis of alite particles hydrated in restricted space. Constr Build Mater 341:127829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127829
Funding
This work has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51978505, 52172022), the Shanghai Rising-Star Program (20QC1400600), and the National Key Technology R&D Programs (2016YFC0700802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kai Wu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. Yuan Hu: Methodology, Writing—original draft. Linglin Xu: Writing—original draft, Data curation. Lintao Zhang: Methodology, Investigation, Writing—original draft. Xiong Zhang: Project administration, Supervision. Yufeng Su: Methodology, Investigation. Zhenghong Yang: Writing—review and editing, Methodology, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
I am free to contact any of the people involved in the research to seek further clarification and information.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Hu, Y., Xu, L. et al. Recycling of sewage sludge in clay-free thermal insulation brick: assessment of microstructure, performance, and environment impact. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 89184–89197 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22003-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22003-1