Abstract
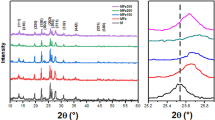
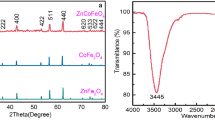
Natural ferrous minerals are readily available and recyclable catalysts in photo-Fenton-like oxidation for wastewater treatment. In this work, typical ferrous oxide and sulfide minerals including magnetite, chalcopyrite, and pyrrhotite were exploited as catalysts in heterogeneous photo-Fenton oxidation for purification of biological effluent of dyeing wastewater. In a wide initial pH range (3.0~7.5), ferrous mineral-based heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions were proven to be effective on the oxidation of recalcitrant pollutants. COD removals achieved 60.57%, 58.83%, and 57.41% using pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, and magnetite, respectively, as catalyst under ultraviolet irradiation of 220~275 nm at H2O2 concentration of 9.8 mM. The corresponding COD removals were 51.75% and 34.09% with or without ferrous sulfate additions in UV/H2O2 systems. Minerals exhibited excellent stability and reusability with photo-catalytic activity reduction of less than 10% in the reuse of 5 cycles. Dissolved iron concentrations were determined to be 1.86 mg L−1, 4.62 mg L−1, and 7.53 mg L−1 for magnetite, chalcopyrite, and pyrrhotite, respectively, at pH 3 and decreased to zero in neutral pH environment, which were much lower than those required for homogenous Fenton reaction. It was deduced that oxidation of recalcitrant pollutants was mainly catalyzed by Fe(II) on the mineral surface. The more reactive oxygen species such as hydroxyl radicals were resulted from the reaction of surface Fe (II) with H2O2, H2O2 photolysis, and charge separation of minerals under UV irradiation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asgari E, Mohammadi F, Nourmoradi H, Sheikhmohammadi A, Rostamifasih Z, Hashemzadeh B, Arfaeinia H (2020) Heterogeneous catalytic degradation of nonylphenol using persulphate activated by natural pyrite: response surface methodology modelling and optimisation. Int J Environ An Ch:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1807528
Bae S, Kim D, Lee W (2013) Degradation of diclofenac by pyrite catalyzed Fenton oxidation. Appl Catal B-Environ 134:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.12.031
Bansal P, Verma A, Mehta C, Sangal VK (2019) Potential use of waste foundry sand in dual process (photocatalysis and photo-Fenton) for the effective removal of phenazone from water: Slurry and fixed-bed approach. J Environ Manag 233:793–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.005
Benzaquén TB, Barrera DA, Carraro PM, Sapag K, Alfano OM, Eimer GA (2019) Nanostructured catalysts applied to degrade atrazine in aqueous phase by heterogeneous photo-Fenton process. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:4192–4201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2348-9
Bilici Z, Işık Z, Aktaş Y, Yatmaz HC, Dizge N (2019) Photocatalytic effect of zinc oxide and magnetite entrapped calcium alginate beads for azo dye and hexavalent chromium removal from solutions. J Water Process Eng 31:100826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100826
Biswal S, Pahlevani F, Bhattacharyya SK, Sahajwalla V (2020) A novel reforming approach of utilizing spent coffee grounds to produce iron. Resour Conserv Recycl 163:105067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105067
Brindha R, Muthuselvam P, Senthilkumar S, Rajaguru P (2018) Fe0 catalyzed photo-Fenton process to detoxify the biodegraded products of azo dye Mordant Yellow 10. Chemosphere. 201:77–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.151
Castro FD, Bassin JP, Dezotti M (2017) Treatment of a simulated textile wastewater containing the Reactive Orange 16 azo dye by a combination of ozonation and moving-bed biofilm reactor: evaluating the performance, toxicity, and oxidation by-products. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:6307–6316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7119-x
Cruz González G, Julcour C, Chaumat H, Jáuregui-Haza U, Delmas H (2018) Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by photolysis and photo-Fenton oxidation. J Environ Chem Eng 6:874–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.049
De León MA, Sergio M, Bussi J, Ortiz de la Plata GB, Alfano OM (2019) Heterogeneous photo-Fenton process using iron-modified regional clays as catalysts: photonic and quantum efficiencies. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:12720–12730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04762-6
Diao Y, Yan Z, Guo M, Wang X (2018) Magnetic multi-metal co-doped magnesium ferrite nanoparticles: an efficient visible light-assisted heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst synthesized from saprolite laterite ore. J Hazard Mater 344:829–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.029
Díez AM, Pazos M, Sanromán MA (2019) Synthesis of magnetic-photo-Fenton catalyst for degradation of emerging pollutant. Catal Today 328:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.12.042
Dinesh GK, Anandan S, Sivasankar T (2016) Synthesis of Fe-doped Bi2O3 nanocatalyst and its sonophotocatalytic activity on synthetic dye and real textile wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:20100–20110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5951-z
Emídio ES, Hammer P, Nogueira RFP (2020) Simultaneous degradation of the anticancer drugs 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide using a heterogeneous photo-Fenton process based on copper-containing magnetites (Fe3-xCuxO4). Chemosphere. 241:124990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124990
Farshchi ME, Aghdasinia H, Khataee A (2018) Modeling of heterogeneous Fenton process for dye degradation in a fluidized-bed reactor: kinetics and mass transfer. J Clean Prod 182:644–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.225
Ferreira SAD, Donadia JF, Gonçalves GR, Teixeira AL, Freitas MBJG, Fernandes AAR, Lelis MFF (2019) Photocatalytic performance of granite waste in the decolorization and degradation of Reactive Orange 122. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103144
Gao J, Liu Y, Xia X, Wang L, Shao L, Cai T, Dong W (2019) Mechanisms for photo assisted Fenton of synthesized pyrrhotite at neutral pH. Appl Surf Sci 463:863–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.09.007
García-Estrada R, Esteban García B, Ramírez-Zamora RM, Sánchez Pérez JA (2020) Micropollutant degradation by the heterogeneous solar photo-Fenton process at circumneutral PH using copper slag. J Water Process Eng 38:101562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101562
García-Muñoz P, Pliego G, Zazo JA, Bahamonde A, Casas JA (2016) Ilmenite (FeTiO3) as low cost catalyst for advanced oxidation processes. J Environ Chem Eng 4:542–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.11.037
García-Muñoz P, Pliego G, Zazo JA, Bahamonde A, Casas JA (2017a) Sulfonamides photoassisted oxidation treatments catalyzed by ilmenite. Chemosphere. 180:523–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.04.047
García-Muñoz P, Pliego G, Zazo JA, Barbero B, Bahamonde A, Casas JA (2017b) Modified ilmenite as catalyst for CWPO-Photoassisted process under LED light. Chem Eng J 318:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.093
Garcia-Muñoz P, Fresno F, de la Peña O’Shea VA, Keller N (2019) Ferrite Materials for Photoassisted Environmental and Solar Fuels Applications. Top Curr Chem 378:6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-019-0270-3
Gonçalves NPF, Minella M, Fabbri D, Calza P, Malitesta C, Mazzotta E, Bianco Prevot A (2020) Humic acid coated magnetic particles as highly efficient heterogeneous photo-Fenton materials for wastewater treatments. Chem Eng J 390:124619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124619
Gou Y, Chen P, Yang L, Li S, Peng L, Song S, Xu Y (2021) Degradation of fluoroquinolones in homogeneous and heterogeneous photo-Fenton processes: a review. Chemosphere. 270:129481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129481
Han X, Liu S, Huo X, Cheng F, Zhang M, Guo M (2020) Facile and large-scale fabrication of (Mg,Ni)(Fe,Al)2O4 heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like catalyst from saprolite laterite ore for effective removal of organic contaminants. J Hazard Mater 392:122295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122295
Huang X, Zhu T, Duan W, Liang S, Li G, Xiao W (2020) Comparative studies on catalytic mechanisms for natural chalcopyrite-induced Fenton oxidation: effect of chalcopyrite type. J Hazard Mater 381:120998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120998
Legrini O, Oliveros E, Braun AM (1993) Photochemical processes for water treatment. Chem Rev 93:671–698. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00018a003
Li H, Shang J, Yang ZP, Shen WJ, Ai ZH, Zhang LZ (2017) Oxygen vacancy associated surface Fenton chemistry: surface structure dependent hydroxyl radicals generation and substrate dependent reactivity. Environ Sci Technol 51:5685–5694. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00040
Liu H, Chen Q, Yu Y, Liu Z, Xue G (2013) Influence of Fenton’s reagent doses on the degradation and mineralization of H-acid. J Hazard Mater 263:593–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.10.021
Liu X, Xu D, Zhang D, Zhang G, Zhang L (2016) Superior performance of 3 D Co-Ni bimetallic oxides for catalytic degradation of organic dye: investigation on the effect of catalyst morphology and catalytic mechanism. Appl Catal B-Environ 186:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.005
Ltaïef AH, Pastrana-Martínez LM, Ammar S, Gadri A, Faria JL, Silva AM (2018) Mined pyrite and chalcopyrite as catalysts for spontaneous acidic pH adjustment in Fenton and LED photo-Fenton-like processes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93:1137–1146. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5472
Lu J, Ayele BA, Liu X, Chen Q (2020a) Electrochemical removal of RRX-3B in residual dyeing liquid with typical engineered carbonaceous cathodes. J Environ Manag:111669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111669
Lu J, Chen Z, Ayele BA, Liu X, Chen Q (2020b) Electrocatalytic activities of engineered carbonaceous cathodes for generation of hydrogen peroxide and oxidation of recalcitrant reactive dye. J Electroanal Chem 878:114579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114579
Molina CB, Sanz-Santos E, Boukhemkhem A, Bedia J, Belver C, Rodriguez JJ (2020) Removal of emerging pollutants in aqueous phase by heterogeneous Fenton and photo-Fenton with Fe2O3-TiO2-clay heterostructures. Environ Sci Pollut R 27:38434–38445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09236-8
Navarro P, Gabaldon JA, Gomez-Lopez VM (2017) Degradation of an azo dye by a fast and innovative pulsed light/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Dyes Pigments 136:887–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.09.053
Nooshabadi AJ, Rao KH (2014) Formation of hydrogen peroxide by sulphide minerals. Hydrometallurgy. 141:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2013.10.011
Pignatello JJ, Oliveros E, MacKay A (2007) Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 37:273–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380601163809
Qin Q, Liu Y, Li X, Sun T, Xu Y (2018) Enhanced heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue by reduced CuFe2O4. RSC Adv 8:1071–1077. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA12488K
Qin M, Lu B, Feng S, Zhen Z, Chen R, Liu H (2019) Role of exposed facets and surface OH groups in the Fenton-like reactivity of lepidocrocite catalyst. Chemosphere. 230:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.071
Rakhshaee R, Darvazeh J (2017) Comparing performance of three forms of hematite in fixed bed reactor for a photocatalytic decolorization: experimental design, model fitting and optimization of conditions. Process Saf Environ Prot 107:122–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.02.006
Samsami S, Mohamadi M, Sarrafzadeh M-H, Rene ER, Firoozbahr M (2020) Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: overview and perspectives. Process Saf Environ Prot 143:138–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.05.034
Serna-Galvis EA, Giraldo-Aguirre AL, Silva-Agredo J, Florez-Acosta OA, Torres-Palma RA (2017) Removal of antibiotic cloxacillin by means of electrochemical oxidation, TiO2 photocatalysis, and photo-Fenton processes: analysis of degradation pathways and effect of the water matrix on the elimination of antimicrobial activity. Environ Sci Pollut R 24:6339–6352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6257-5
Shan R, Han J, Gu J, Yuan H, Luo B, Chen Y (2020) A review of recent developments in catalytic applications of biochar-based materials. Resour Conserv Recycl 162:105036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105036
Sidney Santana C, Freire Bonfim DP, da Cruz IH, da Silva BM, Fabiano DP (2020) Fe2O3/MCM-41 as catalysts for methyl orange degradation by Fenton-like reactions. Environ Prog Sustain. n/a:e13507. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13507
Stupar SL, Grgur BN, Radišić MM, Onjia AE, Ivanković ND, Tomašević AV, Mijin DŽ (2020) Oxidative degradation of Acid Blue 111 by electro-assisted Fenton process. J Water Process Eng 36:101394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101394
Sun M, Wu N-N, Zhai L-F, Ru X-R (2015) Manipulate an air–cathode fuel cell toward recovering highly active heterogeneous electro-Fenton catalyst from the Fe(II) in acid mine drainage. Miner Eng 84:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2015.09.015
Talukdar K, Jun B-M, Yoon Y, Kim Y, Fayyaz A, Park CM (2020) Novel Z-scheme Ag3PO4/Fe3O4-activated biochar photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light catalytic performance toward degradation of bisphenol A. J Hazard Mater 398:123025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123025
Torres-Palma RA, Nieto JI, Combet E, Pétrier C, Pulgarin C (2010) An innovative ultrasound, Fe2+ and TiO2 photoassisted process for bisphenol a mineralization. Water Res 44:2245–2252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.12.050
Torres-Pinto A, Sampaio MJ, Teixo J, Silva CG, Faria JL, Silva AMT (2020) Photo-Fenton degradation assisted by in situ generation of hydrogen peroxide using a carbon nitride photocatalyst. J Water Process Eng 37:101467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101467
Villegas-Guzman P et al (2017) A green solar photo-Fenton process for the elimination of bacteria and micropollutants in municipal wastewater treatment using mineral iron and natural organic acids. Appl Catal B Environ 219:538–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.07.066
Wang Y, Gao Y, Chen L, Zhang H (2015) Goethite as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of methyl orange. Catal Today 252:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.01.012
Zhou Y, Huang M, Wang X, Gao J, Fang G, Zhou D (2020) Efficient transformation of diethyl phthalate using calcium peroxide activated by pyrite. Chemosphere. 253:126662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126662
Zhu R, Zhu Y, Xian H, Yan L, Fu H, Zhu G, Xi Y, Zhu J, He H (2020) CNTs/ferrihydrite as a highly efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for the degradation of bisphenol A: the important role of CNTs in accelerating Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycling. Appl Catal B-Environ 270:118891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118891
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFC0400500, 2019YFC0400502); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (19D111321, 20D111318); and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Graduate Student Innovation Fund of Donghua University (CUSF-DH-D-2019082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jun Lu: methodology, data curation, writing original draft, and writing—review and editing; Quanyuan Chen: conceptualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing; Qi Zhao: investigation; Xiaochen Liu: resources, software; Juan Zhou: supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo Torres-Palma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 397 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Chen, Q., Zhao, Q. et al. Catalytic activity comparison of natural ferrous minerals in photo-Fenton oxidation for tertiary treatment of dyeing wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 30373–30383 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14042-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14042-x