Abstract
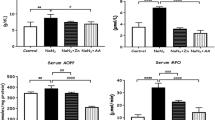
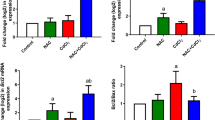
Copper (Cu) is an extensively used heavy metal and an indispensible micronutrient for living beings. However, Cu is also toxic and exerts multiple adverse health effects when humans are exposed to high levels of this metal. We have examined the effect of single acute oral dose of copper chloride (CuCl2) on parameters of oxidative stress, cellular metabolism, membrane and DNA damage in rat intestine. Adult male Wistar rats were divided into four groups and separately administered a single oral dose of 5, 15, 30 and 40 mg CuCl2/kg body weight. Rats not administered CuCl2 served as the control. Oral administration of CuCl2 led to significant alterations in the activities of metabolic and membrane-bound enzymes; brush border enzymes were inhibited by 45–75% relative to the control set. Inhibition of antioxidant enzymes diminished the metal-reducing and free radical quenching ability of the cells. Oxidative damage caused cellular oxidation of thiols, proteins and lipids. Diphenylamine and comet assays showed that CuCl2 treatment enhanced DNA damage while DNA-protein crosslinking was also increased in the intestinal cells. Examination of stained sections showed that CuCl2 treatment led to marked histological changes in the intestine. All the changes seen were in a CuCl2 dose-dependent manner with more prominent alterations at higher doses of CuCl2. These results clearly show that oral administration of CuCl2 results in oxidative damage to the intestine which can impair its digestive and absorptive functions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The materials and datasets analysed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Arnal N, Cristalli DO, de Alaniz MJT, Marra CA (2010) Clinical utility of copper, ceruloplasmin, and metallothionein plasma determinations in human neurodegenerative patients and their first-degree relatives. Brain Res 1319:118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.11.085
ATSDR (2004) Toxicological profile for copper. Agency for toxic substances and disease Registry New York
Attri S, Sharma N, Jahagirdar S, Thapa BR, Prasad R (2006) Erythrocyte metabolism and antioxidant status of patients with Wilson disease with hemolytic anemia. Pediatr Res 59:593–597. https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000203098.77573.39
Barceloux DG (1999) Copper. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 37:217–230
Barker S, Weinfeld M, Murray D (2005) DNA–protein crosslinks: their induction, repair, and biological consequences. Mutat Res 589:111–135
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1996.0292
Beutler E (1984) Red cell metabolism: a manual of biochemical methods, 3rd edn. Grune & Stratton, Orlando, FL
Bonting SL, Simon KA, Hawkins NM (1961) Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys 95:416–423
Bourlioux P, Koletzko B, Guarner F, Braesco V (2003) The intestine and its microflora are partners for the protection of the host: report on the Danone Symposium “The Intelligent Intestine,” held in Paris, June 14, 2002. Am J Clin Nutr 78:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/78.4.675
Bremner I (1998) Manifestations of copper excess. Am J Clin Nutr 67:1069S–1073S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/67.5.1069S
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Burton K (1956) A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62:315–323
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1985) Glutathione reductase. Methods Enzymol 113:484–490
Chen L, Tuo B, Dong H (2016) Regulation of intestinal glucose absorption by ion channels and transporters. Nutrients 8(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8010043
Circu ML, Aw TY (2011) Redox biology of the intestine. Free Radic Res 45:1245–1266. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2011.611509
Collins AR (1999) Oxidative DNA damage, antioxidants and cancer. Bioassays 21:238–246
Costa V, Quintanilha A, Moradas-Ferreira P (2007) Protein oxidation, repair mechanisms and proteolysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. IUBMB Life 59:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1080/15216540701225958
Crane RK, Sols A (1953) The association of hexokinase with particulate fractions of brain and other tissue homogenates. J Biol Chem 203:273–292
Culling CFA (1974) Handbook of histopathological & histochemical techniques, 3rd edn. Butterworth-Heinemann
Davanzo F, Settimi L, Faraoni L, Maiozzi P, Travaglia A, Marcello I (2004) Agricultural pesticide-related poisonings in Italy: cases reported to the Poison Control Centre of Milan in 2000-2001. Epidemiol Prev 28:330–337
Dhanraj P, Venter C, Bester MJ, Oberholzer HM (2020) Induction of hepatic portal fibrosis, mitochondria damage, and extracellular vesicle formation in Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to copper, manganese, and mercury, alone and in combination. Ultrastruct Pathol 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/01913123.2020.1731638
Escobar JA, Rubio MA, Lissi EA (1996) Sod and catalase inactivation by singlet oxygen and peroxyl radicals. Free Radic Biol Med 20:285–290
Fahmy HM, Ebrahim NM, Gaber MH (2020) In-vitro evaluation of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in normal and cancer lung cell lines. J Trace Elem Med Biol 60:126481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126481
Farhana A, Lappin SL (2020) Biochemistry, lactate dehydrogenase. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL)
Farooq N, Yusufi ANK, Mahmood R (2004) Effect of fasting on enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism and brush border membrane in rat intestine. Nutr Res 24:407–416
Flohé L, Günzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Gabbianelli R, Lupidi G, Villarini M, Falcioni G (2003) DNA damage induced by copper on erythrocytes of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata and mollusk Scapharca inaequivalvis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:350–356
Gaetke LM, Chow CK (2003) Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 189:147–163
Gal-Garber O, Mabjeesh SJ, Sklan D, Uni Z (2003) Nutrient transport in the small intestine: Na+,K+-ATPase expression and activity in the small intestine of the chicken as influenced by dietary sodium. Poult Sci 82:1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/82.7.1127
Gao S, Li Q, Ou-Yang C et al (2009) Lead toxicity induced antioxidant enzyme and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activities in Jatropha curcas L. radicles. Fresenius Environ Bull 5:811–815
Garcia Sampaio F, de Lima BC, Tie Oba E et al (2008) Antioxidant defenses and biochemical changes in pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) in response to single and combined copper and hypoxia exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 147:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.07.009
Gay C, Gebicki JM (2000) A critical evaluation of the effect of sorbitol on the ferric-xylenol orange hydroperoxide assay. Anal Biochem 284:217–220. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.2000.4696
Glossmann H, Neville DM (1972) gamma-Glutamyltransferase in kidney brush border membranes. FEBS Lett 19:340–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(72)80075-9
Glotfelty LG, Wong AC, Levy M (2020) Small molecules, big effects- microbial metabolites in intestinal immunity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 318:G907–G911. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00263.2019
Goldmann DR, Schlesinger H, Segal S (1976) Isolation and characterization of the brush border fraction from newborn rat renal proximal tubule cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 419:251–260
Guecheva T, Henriques JA, Erdtmann B (2001) Genotoxic effects of copper sulphate in freshwater planarian in vivo, studied with the single-cell gel test (comet assay). Mutat Res 497:19–27
Habeeb AF (1972) [37] Reaction of protein sulfhydryl groups with Ellman’s reagent. Methods Enzymol 25:457–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(72)25041-8
Halliwell B, Aruoma OI (1991) DNA damage by oxygen-derived species: Its mechanism and measurement in mammalian systems. FEBS Lett 281:9–19
Handy RD, Musonda MM, Phillips C, Falla SJ (2000) Mechanisms of gastrointestinal copper absorption in the African walking catfish: copper dose-effects and a novel anion-dependent pathway in the intestine. J Exp Biol 203:2365–2377
Hayashi M, Kuge T, Endoh D, Nakayama K, Arikawa J, Takazawa A, Okui T (2000) Hepatic copper accumulation induces DNA strand breaks in the liver cells of Long-Evans Cinnamon strain rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 276:174–178. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.3454
Husain N, Mahmood R (2019) Copper(II) generates ROS and RNS, impairs antioxidant system and damages membrane and DNA in human blood cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:20654–20668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05345-1
Ide H, Shoulkamy MI, Nakano T, Miyamoto-Matsubara M, Salem AMH (2011) Repair and biochemical effects of DNA–protein crosslinks. Mutat Res 11:113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.12.007
Itoh S, Ozumi K, Kim HW et al (2009) Novel mechanism for regulation of extracellular SOD transcription and activity by copper: role of antioxidant-1. Free Radic Biol Med 46:95–104
Jamshidi S, Beigrezaei S, Faraji H (2018) A review of probable effects of antioxidants on DNA damage. Int J Pharma Phytopharma Res 8:72–79
Jiang WD, Liu Y, Jiang J, Wu P, Feng L, Zhou XQ (2015) Copper exposure induces toxicity to the antioxidant system via the destruction of Nrf2/ARE signaling and caspase-3-regulated DNA damage in fish muscle: amelioration by myo-inositol. Aquat Toxicol 159:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.12.020
Kalita J, Kumar V, Misra UK, Bora HK (2020) Movement disorder in copper toxicity rat model: Role of inflammation and apoptosis in the corpus striatum. Neurotox Res 37:904–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00140-9
Kaunitz JD, Gunther R, Wright EM (1982) Involvement of multiple sodium ions in intestinal d-glucose transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:2315–2318. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.79.7.2315
Kempson SA, Kim JK, Northrup TE, Knox FG, Dousa TP (1979) Alkaline phosphatase in adaptation to low dietary phosphate intake. Am J Phys 237:E465–E473
Khundmiri SJ, Asghar M, Khan F, Salim S, Yusufi AN (2004) Effect of ischemia and reperfusion on enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in rat kidney. J Nephrol 17:377–383
Koppenol W (1994) Chemistry of iron and copper in radical reactions. In: Free radical damage and its control. Evans CA and Burdon RH (Eds). Elsevier Science. pp 3–24
Kumar V, Kalita J, Bora HK, Misra UK (2016) Relationship of antioxidant and oxidative stress markers in different organs following copper toxicity in a rat model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 293:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.01.007
Kwok ML, Hu XL, Meng Q, Chan KM (2020) Whole-transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) analyses of the zebrafish liver cell line, ZFL, after acute exposure to Cu2+ ions. Metallomics. 12(5):732–751. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0mt00005a
Legrand C, Bour JM, Jacob C, Capiaumont J, Martial A, Marc A, Wudtke M, Kretzmer G, Demangel C, Duval D, Hache J (1992) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity of the number of dead cells in the medium of cultured eukaryotic cells as marker. J Biotechnol 25:231–243
Letelier ME, Lepe AM, Faúndez M, Salazar J, Marín R, Aracena P, Speisky H (2005) Possible mechanisms underlying copper-induced damage in biological membranes leading to cellular toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 151:71–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2004.12.004
Letelier ME, Sánchez-Jofré S, Peredo-Silva L, Cortés-Troncoso J, Aracena-Parks P (2010) Mechanisms underlying iron and copper ions toxicity in biological systems: Pro-oxidant activity and protein-binding effects. Chem Biol Interact 188:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.06.013
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN et al (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478
Liu J, Wang Y, Zhao H, Mu M, Guo M, Nie X, Sun Y, Xing M (2020) Arsenic (III) or/and copper (II) exposure induce immunotoxicity through trigger oxidative stress, inflammation and immune imbalance in the bursa of chicken. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110127
Lorincz MT (2018) Wilson disease and related copper disorders. Handb Clin Neurol 147:279–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63233-3.00018-X
Lowry OH (1951) Protein determination with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Marnett LJ (2002) Oxy radicals, lipid peroxidation and DNA damage. Toxicology 181:219–222
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Mishra K, Ojha H, Chaudhury NK (2012) Estimation of antiradical properties of antioxidants using DPPH assay: A critical review and results. Food Chem 130:1036–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.127
Mithieux G, Gautier-Stein A (2014) Intestinal glucose metabolism revisited. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 105:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2014.04.008
Moura FA, de Andrade KQ, dos Santos JCF, Araújo ORP, Goulart MOF (2015) Antioxidant therapy for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: does it work? Redox Biol 6:617–639
Ozcelik D, Uzun H (2009) Copper intoxication; Antioxidant defenses and oxidative damage in rat brain. Biol Trace Elem Res 127:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-008-8219-3
Paul et al (2002) Role of dietary antioxidants to protect against DNA damage in adult dogs. J Nutr 132:1720S–1724S
Penhoat A, Fayard L, Stefanutti A, Mithieux G, Rajas F (2014) Intestinal gluconeogenesis is crucial to maintain a physiological fasting glycemia in the absence of hepatic glucose production in mice. Metabolism 63:104–111
Pigeolet E, Corbisier P, Houbion A, Lambert D, Michiels C, Raes M, Zachary MD, Remacle J (1990) Glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase inactivation by peroxides and oxygen derived free radicals. Mech Ageing Dev 51:283–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/0047-6374(90)90078-t
Prohaska JR (2008) Role of copper transporters in copper homeostasis. Am J Clin Nutr 88:826S–829S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/88.3.826S
Quigley JP, Gotterer GS (1969) Distribution of Na+-K+-stimulated ATPase activity in rat intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 173:456–468
Radi R (2004) Nitric oxide, oxidants, and protein tyrosine nitration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4003–4008
Ren X, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Wang X, Liu P, Li J (2020) Comparative accumulation and transcriptomic analysis of juvenile Marsupenaeus japonicus under cadmium or copper exposure. Chemosphere 249:126157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126157
Sagun KC, Juan MC, David WG (2006) Antioxidants prevent oxidative DNA damage and cellular transformation elicited by the over-expression of c-MYC. Mutat Res 593:64–79
Saha P, Manoharan P, Arthur S, Sundaram S, Kekuda R, Sundaram U (2015) Molecular mechanism of regulation of villus cell Na-K-ATPase in the chronically inflamed mammalian small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848:702–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.11.005
Saleha Banu B, Ishaq M, Danadevi K, Padmavathi P, Ahuja YR (2004) DNA damage in leukocytes of mice treated with copper sulfate. Food Chem Toxicol 42:1931–1936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2004.07.007
Schultz SG (1977) Sodium-coupled solute transport of small intestine: a status report. Am J Phys 233:E249. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.4.E249
Shonk CE, Boxer GE (1964) Enzyme patterns in human tissues. I. Methods for the determination of glycolytic enzymes. Cancer Res 24:709–721
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Slaoui M, Fiette L (2011) Histopathology procedures: from tissue sampling to histopathological evaluation. Methods Mol Biol 691:69–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-849-2_4
Squitti R, Gorgone G, Binetti G, Ghidoni R, Pasqualetti P, Draicchio F, Albini E, Benedetti L, Lucchini R, Rossini PM (2007) Metals and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease from industrial areas with exposition to environmental toxins or metal pollution. G Ital Med Lav Ergon 29:294–296
Suzuki YJ, Carini M, Butterfield DA (2010) Protein carbonylation. Antioxid Redox Signal 12:323–325. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.2887
Takahashi H, Kikuchi K, Nakayama H (1993) Effect of chronic hypoxia on oxidative enzyme activity in rat skeletal muscle. Ann Physiol Anthropol 12:363–369. https://doi.org/10.2114/ahs1983.12.363
Talbot J, Hahn P, Kroehling L, Nguyen H, Li D, Littman DR (2020) Feeding-dependent VIP neuron-ILC3 circuit regulates the intestinal barrier. Nature 579:575–580. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2039-9
Tamura T, Stadtman TC (1996) A new selenoprotein from human lung adenocarcinoma cells: purification, properties, and thioredoxin reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1006–1011
Thorsen K, Drengstig T, Ruoff P (2014) Transepithelial glucose transport and Na+/K+ homeostasis in enterocytes: an integrative model. Am J Phys Cell Phys 307:C320–C337. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00068.2013
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Tokar EJ, Boyd WA, Freedman JH, Waalkes MP (2013) Toxic effects of metals. Casarett and Doull’s toxicology: the basic science of poisons (Klaassen CD, Ed), McGraw Hill, New York 981–1030
Umair M, Alfadhel M (2019) Genetic disorders associated with metal metabolism. Cells 8(12):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121598
Villalba JM, Canalejo A, Burón MI et al (1993) Thiol groups are involved in NADH-ascorbate free radical reductase activity of rat liver plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 192:707–713. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1993.1472
Wang Z, Dong C (2019) Gluconeogenesis in cancer: function and regulation of PEPCK, FBPase, and G6Pase. Trends Cancer 5:30–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2018.11.003
Whibley N, Tucci A, Powrie F (2019) Regulatory T cell adaptation in the intestine and skin. Nat Immunol 20:386–396. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0351-z
Yang HC, Wu YH, Yen WC, Liu HY, Hwang TL, Stern A, Chiu DT (2019) The redox role of G6PD in cell growth, cell death, and cancer. Cells 8(9):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091055
Zamberlan DC, Halmenschelager PT, Silva LFO, da Rocha JBT (2020) Copper decreases associative learning and memory in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci Total Environ 710:135306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135306
Zhang CH, Wang Y, Sun QQ, Xia LL, Hu JJ, Cheng K, Wang X, Fu XX, Gu H (2018) Copper nanoparticles show obvious in vitro and in vivo reproductive toxicity via ERK mediated signaling pathway in female mice. Int J Biol Sci 14:1834–1844. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.27640
Zhitkovich A, Costa M (1992) A simple, sensitive assay to detect DNA-protein crosslinks in intact cells and in vivo. Carcinogenesis 13:1485–1489
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Shaikh Nisar Ali for assistance in animal handling and Dr. Husain Arif for help in the comet assay.
Funding
We are extremely grateful for the funding received by the department from UGC-SAP DRS-III, DST-FIST-II and DST-PURSE programs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception, data analysis, and visualization were performed by NH, AAK and RM. NH and SH contributed to material preparations and lab experiments. RM designed the study. The first draft of the manuscript was written by NH, with contribution from SH, and finalized by RM. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This study is directed in accordance with the Animal Ethics Committee of the Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Life Sciences, Aligarh Muslim University (Registration number: 714/GO/Re/S/02/CPCSEA).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Husain, N., Hasan, S., Khan, A.A. et al. Copper chloride inhibits brush border membrane enzymes, alters antioxidant and metabolic status and damages DNA in rat intestine: a dose-dependent study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 43711–43724 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13804-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13804-x