Abstract
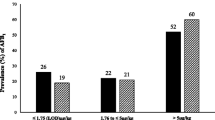
Aflatoxins are one of the major environmental contaminants in animal feed and pose a potential threat to human health due to their secretion in the milk of lactating animals. The present study was conducted with the objectives to determine the occurrence of aflatoxins (B1, B2, G1, and G2) in dairy animal concentrate feed and to evaluate the effect of season, spatial variation, and dairy farm size on the levels of aflatoxins contamination. A total of 189 dairy animal concentrate feed samples were tested for aflatoxins with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) as screening and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection (HPLC-FLD) as confirmatory techniques. Of the total, 59% feed samples were found positive for aflatoxins, while 44% samples were detected with total aflatoxins levels higher than the tolerance limit established by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and 58% samples were found with aflatoxins B1 (AFB1) levels above the European Commission (EC) legal limit. AFB1 levels in dairy animal concentrate feed were found significantly higher during rainy (41.6 μg kg−1) and winter (35.9 μg kg−1) seasons as compared to the summer season (25.5 μg kg−1). The theoretical extrapolation of the AFB1 carry-over from animal feed to milk (aflatoxins M1) in different seasons may lead to 50–100% contamination of milk at levels above the EC tolerance limit. The incidence and levels of aflatoxins especially AFB1 in animal feed, not only pose a direct effect on animals but may also pose a concern for food safety in relation to the occurrence of aflatoxins M1 in milk. Therefore, continuous surveillance of aflatoxins in dairy animal feeds is required to reduce animal and consequently human exposure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou KAH, Hassan AA, Hassan NEY, Houda El-Hamed RA (2017) Seasonal variation in prevalence of mycotoxins in feed and feedstuffs at Beni-Suef Governorate in Egypt. Eur J Acad Essays 4(4):99–109
Arroyo-Manzanares N, Huertas-Perez JF, Garcia-Campana AM, Gamiz-Gracia L (2015) Aflatoxins in animal feeds: a straightforward and cost-effective analytical method. Food Control 54:74–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.01.027
BAHFS (Basic Animal Husbandry and Fisheries Statistics) (2017) Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India, Krishi hawan, New Delhi, India. Available at: http://www.dahd.nic.in/sites/default/filess/Tables%20of%20BAH%26amp%3BFS% 202017%20%281%29.pdf. Accessed 20 Feb 2019
Bahrami R, Shahbazi Y, Nikousefat Z (2016) Occurrence and seasonal variation of aflatoxin in dairy cow feed with estimation of aflatoxin M1 in milk from Iran. Food Agric Immunol 27:388–400. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2015.1109613
Becha BB, Devi SS (2013) Aflatoxin levels in feeds and feed Ingredients of livestock and poultry in Kerala. J Vet Anim Sci 44:76–78
Bondy GS, Pestka JJ (2000) Immunomodulation by fungal toxins. J Toxicol Env Heal B 3:109–143. https://doi.org/10.1080/109374000281113
Bryden WL (2012) Mycotoxin contamination of the feed supply chain: implications for animal productivity and feed security. Anim Feed Sci Technol 173:134–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2011.12.014
Commission Directive (2003) Commission Directive 2003/100/EC of 31 October 2003 amending Annex I to directive 2002/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on undesirable substances in animal feed. Official Journal of the European Union L 285:33-37. Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT /PDF/?uri=%20CELEX:32003L0100&from=EN. Accessed 20 Dec 2018
Dhavan AS, Choudary MR (1995) Incidence of aflatoxins in animal feedstuffs: a decade’s scenario in India. J AOAC Int 78:693–698
Dutta TK, Das P (2001) Isolation of aflatoxigenic strains of Aspergillus and detection of aflatoxin B1 from feeds in India. Mycopathologia 151:29–33. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010960402254
Dwivedi S, Sahrawat K, Upadhyaya H, Ortiz R (2013) Food, nutrition and agro-biodiversity under global climate change. Adv Agron 120:1–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-407686-0.00001-4
EC (European Commission) (2002) European Commission Decision 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off J Eur Commun L 221:8–36 Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2002:221:0008:0036:EN:PDF. Accessed 24 Jan 2018
EC (European Commission) (2006) European Commission (EC) Regulation No 401/2006 of 23 February 2006 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of the levels of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L 70:12-34. Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32006R0401&from=EN. Accessed 24 Jan 2018
EN ISO (2003) EN ISO 16050:2003, Foodstuffs - determination of aflatoxin B1, and the total content of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 in cereals, nuts and derived products - high performance liquid chromatographic method. European Committee for Standardization. Available at: https://www.pau.edu/msrlibrary/iso/pdf/iso_16050_2003_ ed1_en_29628_3_cpdf.pdf. Accessed 10 Feb 2018
European Commission Regulation (2001) European Commission Regulation, setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in food stuffs. 466/2001/EC. pp. 1–13 (2001). Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/sfp/ fcr/fcr02_en.pdf>. Accessed 7 May 2018
Fallah AA (2010) Assessment of aflatoxin M1 contamination in pasteurized and UHT milk marketed in central part of Iran. Food Chem Toxicol 48:988–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.01.014
FDA (Food and Drug Administration) (1997) Adulterated food. Federal Food Drug and Cosmetic Act, chapter IV: definitions and standards for food, Sec 402 (a) (1), Food and Drug Administration. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/opacom/laws/fdcact/fdcact4.htm. Accessed 24 Feb 2018
Gong Y, Hounsa A, Egal S, Turner PC, Sutcliffe AE, Hall AJ, Cardwell K, Wild CP (2004) Post-weaning exposure to aflatoxin results in impaired child growth: a longitudinal study in Benin, West Africa. Environ Health Perspect 112(13):1334–1338. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.6954
Hernandez-Martinez R, Navarro-Blasco I (2015) Surveillance of aflatoxin content in dairy cow feed stuff from Navarra (Spain). Anim Feed Sci Technol 200:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2014.12.002
Heshmati A, Milani JM (2010) Contamination of UHT milk by aflatoxin M1 in Iran. Food Control 21(1):19–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2009.03.013
Hussain I, Anwar J (2008) A study on contamination of aflatoxin M1 in raw milk in Punjab Province of Pakistan. Food Control 19(4):393–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2007.04.019
IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer) (2002) Some traditional herbal medicines, some mycotoxins, naphthalene and styrene. In: IARC monograph on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France. Vol. 82. Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono82.pdf. Accessed 4 July 2018
IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer) (2012) Chemical agents and related occupations. In: IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, France. Vol. 100F. Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono100F.pdf. Accessed 24 Aug 2018
ICH (International Conference on Harmonisation) (2005) Harmonized tripartite guideline. Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology, Q2 (R1), International Conference on Harmonisation. Available at: https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf. Accessed 19 May 2018
Iqbal SZ, Mustafa HG, Asi MR, Jinap S (2014) Variation in vitamin E level and aflatoxins contamination in different rice varieties. J Cereal Sci 60(2):352–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2014.05.012
Iqbal SZ, Jinap S, Pirouz AA, Ahmad Faizal AR (2015) Aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products, occurrence and recent challenges: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 46:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.08.005
Jager AV, Tedesco MP, Souto PCMC, Oliveira CAF (2013) Assessment of aflatoxin intake in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Food Control 33(1):87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.02.016
Kabak B, Dobson AD, Var I (2006) Strategies to prevent mycotoxin contamination of food and animal feed. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 46(8):593–619. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390500436185
Khayoon WS, Saad B, Yan CB, Hashim NH, Ali ASM, Salleh MI, Salleh B (2010) Determination of aflatoxins in animal feeds by HPLC with multifunctional column clean-up. Food Chem 118:882–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.05.082
Khlangwiset P, Shephard GS, Wu F (2011) Aflatoxins and growth impairment: a review. Crit Rev Toxicol 41(9):740–755. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2011.575766
Liu Y, Wu F (2010) Global burden of aflatoxin - induced hepatocellular carcinoma: a risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect 118(6):818–824. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901388
Lunyasunya TP, Wamae LW, Musa HH, Olowofesso O, Lokwaleput IK (2005) The risks of mycotoxins contamination of dairy feed and milk on smallholder dairy farms in Kenya. Pak J Nutr 4(3):162–169. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2005.162.169
Masoero F, Gallo A, Moschini M, Piva G, Diaz D (2007) Carryover of aflatoxin from feed to milk in dairy cows with low or high somatic cell counts. Animal 1(9):1344–1350. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1751731107000663
Min L, Lia D, Tong X, Sun H, Chen W, Wang G, Zheng N, Wang J (2020) The challenges of global occurrence of aflatoxin M1 contamination and the reduction of aflatoxin M1 in milk over the past decade. Food Control 117:107352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107352
NSSO (National Sample Survey Office) (2014) Household consumption of various goods and services in India 2011–12, NSS 68th Round, National Sample Survey Office, Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of India. Available at: http://mospi.nic.in/sites/default/files/publication_ reports/Report_no558_rou68_30june14.pdf. Accessed 23 Feb 2019
Ozay G, Seyhan F, Pembeci C, Saklar S, Yilmaz A (2008) Factors influencing fungal and aflatoxins levels in Turkish hazelnuts (Corylus avellana L.) during growth, harvest, drying and storage: a 3-year study. Food Addit Contam 25(2):209–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030701711016
Patyal A, Gill JPS, Bedi JS, Aulakh RS (2020) Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in raw, pasteurized and UHT milk from Punjab, India. Curr Sci 118(1):79–86. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v118/i1/79-86
Ramesh J, Sarathchandra G, Sureshkumar V (2013) Analysis of feed samples for aflatoxin B1 contamination by HPTLC - a validated method. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 2(5):373–377
Reddy KRN (2010) An overview of mycotoxins contamination in foods and its implications for human health. Toxin Rev 29(1):3–26. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569541003598553
Saleemullah AI, Khalil IA, Shah H (2006) Aflatoxin contents of stored and artificially inoculated cereals and nuts. Food Chem 98(4):699–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.06.034
Sharma H, Jadhav VJ, Garg SR (2019) Aflatoxin M1 in milk in Hisar City, Haryana, India and risk assessment. Food Addit Contam Part B 13:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/19393210.2019.1693434
Siddappa V, Nanjegowda DK, Viswanath P (2012) Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in some samples of UHT, raw & pasteurized milk from Indian states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. Food Chem Toxicol 50(11):4158–4162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.08.034
Streit E, Schatzmayr G, Tassis P, Tzika E, Marin D, Taranu I, Tabuc C, Nicolau A, Aprodu I, Puel O, Oswald IP (2012) Current situation of mycotoxin contamination and co-occurrence in animal feed - focus on Europe. Toxins 4(10):788–809. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4100788
Streit E, Naehrer K, Rodrigues I, Schatzmayr G (2013) Mycotoxin occurrence in feed and feed raw materials worldwide: long-term analysis with special focus on Europe and Asia. J Sci Food Agric 93(12):2892–2899. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6225
Tsakiris IN, Tzatzarakis MN, Alegakis AK, Vlachou MI, Renieri EA, Tsatsakis AM (2013) Risk assessment scenarios of children’s exposure to aflatoxin M1 residues in different milk types from the Greek market. Food Chem Toxicol 56:261–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.024
Van Egmond HP, Schothorst RC, Jonker MA (2007) Regulations relating to mycotoxins in food: perspectives in a global and European context. Anal Bioanal Chem 389(1):147–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1317-9
Veldman A, Meijs JAC, Borggreve GJ, Heeresvander Tol JJ (1992) Carry-over of aflatoxin from cows’ food to milk. Anim Prod 55(2):163–168. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0003356100037417
Vijayasamundeeswari A, Mohankumar M, Karthikeyan M, Vijayanandraj S, Paranidharan V, Velazhahan R (2009) Prevalence of aflatoxin B1 contamination in pre and post-harvest maize kernels, food products, poultry and livestock feeds in Tamil Nadu, India. J Plant Prot Res 49(2):221–224
WHO (World Health Organization) (2002) Evaluation of certain mycotoxins in food (fifty-sixth report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives). WHO technical report series, No. 906, World Health Organization, Geneva. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42448/WHO_ TRS_906.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y. Accessed 16 Dec 2018
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Guru Angad Dev Veterinary Animal Sciences University, Ludhiana, Punjab (India) for providing all the necessary facilities to conduct this research.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in conceptualization and methodology. AP performed the ELISA and HPLC examination of feed samples for aflatoxins. AP and JSB interpreted the whole data and were major contributors in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
A written consent was taken from all the dairy farmers during feed sample collection.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 98 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patyal, A., Gill, J.P.S., Bedi, J.S. et al. Assessment of aflatoxin contamination in dairy animal concentrate feed from Punjab, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 37705–37715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13321-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13321-x