Abstract
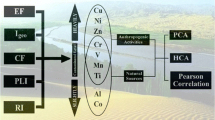
In the present study, surface sediment samples from 48 sites covering the whole water area and three main estuaries of Chaohu Lake were collected to determine the concentrations of 25 metal elements using microwave-assisted digestion combined with ICP-MS. Spatial variation, source appointments, and contamination evaluation were examined using multivariate statistical techniques and pollution indices. The results show that for the elements Cd, Pb, Zr, Hf, U, Sr, Zn, Th, Rb, Sn, Cs, Tl, Bi, and Ba, which had higher coefficients of variation (CV), the concentrations were significantly higher in the eastern lake than in the western lake, but other elements with low CV values did not show spatial differences. The accumulation of Cu, Zn, Rb, Sr, Zr, Cd, Sn, Cs, Ba, Hf, Ta, Tl, Pb, Bi, U, and Th in the surface sediments was inferred as long-term agricultural cultivation impact, but that of Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, and Ni may have been a natural occurrence. The contribution from industrial and municipal impact was negligible, despite the rapid urbanization around the studied area. Principal component analysis-multiple linear regression (PCA-MLR) predicted the contribution from agricultural activities to range from 0.45 ± 1.31 % for Co to 92.7 ± 17.7 % for Cd. The results of the pollution indices indicate that Chaohu Lake was weakly to moderately affected by Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, and Ni but was severely contaminated by Hf and Cd. The overall pollution level in the eastern lake was higher than that in the western lake with respect to the pollution level index (PLI). Therefore, our results can help comprehensively understand the sediment contamination by metals in Chaohu Lake.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agency USEP (1996) Microwave assisted acid digestion of siliceous and organically based matrices, Test methods for evaluating solid waste. USEPA, Washington, DC
Aleksander-Kwaterczak U, Helios-Rybicka E (2009) Contaminated sediments as a potential source of Zn, Pb, and Cd for a river system in the historical metalliferous ore mining and smelting industry area of South Poland. J Soils Sediments 9:13–22
Cao D-J, Yue Y-D, Huang X-M, Wei M (2004) Environmental quality assessment of Pb, Cu Fe pollution in Chaohu lake waters. China Environ Sci 24:509–512
Chen J, Li S-F (2007) Chemical speciation and total concentration of heavy metals for sediments from Lake Chaohu. Henan Sci 25:303–307
Chen L-H, Ni W-Z, Liu X-L, Sun J-B (2009) Investigation of heavy metal concentrations in commerical fertilizers commonly used. J Zhejiang Sci Tech Univ 26:223–227
Chen X-R, Chen F-R, Jia S-J, Cheng Y-N (2012) Soil geochemical baseline and background in Yangtze River-Huaihe River basin of Anhui Province. Geol China 39:302–310
Chen X, Yang XD, Dong XH, Liu EF (2013) Environmental changes in Chaohu Lake (southeast, China) since the mid 20th century: The interactive impacts of nutrients, hydrology and climate. Limnologica 43:10–17
Cheng J, Li X-D, Hua R-M, Tang J, Lu H-X (2008) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Chaohu, Lake. J Agro Environ Sci 27:1403–1408
Du L, Yi C-L, Pan S-M (2004) Grain-size characteristics and sedimentary environment in the lacustrian deposit of Chaohu Lake, the Yangtze Delta region. J Anhui Normal Univ 27:101–104
Du C-C, Liu E-F, Yang X-D, Wu Y-H, Xue B (2012) Characteristics of enrichment and evaluation of anthropogenic pollution of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Chaohu. J Lake Sci 24:59–66
Gan X-H (2008) Contaminative characteristics of sediments and their ecological impact assessment in estuary of Tongyang River at Chaohu Lake. Hefei University of Technology, Hefei
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Han YM, Cao JJ, Kenna TC, Yan BZ, Jin ZD, Wu F, An ZS (2011) Distribution and ecotoxicological significance of trace element contamination in a similar to 150 yr record of sediments in Lake Chaohu, Eastern China. J Environ Monit 13:743–752
Hu Y, Cheng H (2013) Application of stochastic models in identification and apportionment of heavy metal pollution sources in the surface soils of a large-scale region. Environ Sci Tech 47:3752–3760
Huang B-Z (2009) Comtaminative characteristics analysis of sediments and plants in estuary of Tongyang River at Chaohu Lake. Hefei University of Technology, Hefei
Jia T-F, Zhang W-G, Yu L-Z (2009) Metal element enrichment characteristics of sediments in Chaohu Lake since the 1860s and its implication to human activity. Geogr Res 28:1217–1226
Kavouras IG, Koutrakis P, Tsapakis M, Lagoudaki E, Stephanou EG, Von Baer D, Oyola P (2001) Source apportionment of urban particulate aliphatic and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) using multivariate methods. Environ Sci Technol 35:2288–2294
Keith ML, Cruft EF, Dahlberg EG (1967): Trace metals in stream sediment of southeastern Pennsylvania. Geochemical prospecting guide based on regional distribution of zinc, copper, nickel, cobalt, chromium, and vanadium. College of Earth and Mineral Sciences, Pennsylvania State University (University Park), 11 pp
Kong M, Dong Z-L, Chao J-Y, Zhang Y-M, Yin H-B (2015) Bioavailability and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Lake Chaohu. China Environ Sci 35:1223–1229
Li RZ, Shu K, Luo YY, Shi Y (2010) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in estuarine surface sediments of Tangxi River in Chaohu Lake basin. Chin Geogr Sci 20:9–17
Li F, Huang J, Zeng G, Yuan X, Li X, Liang J, Wang X, Tang X, Bai B (2013) Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. J Geochem Explor 132:75–83
Liu Q-Y, Dai X-R, Wang L-Q (2008) The distribution characteristics of organic carbon in sediments of the Chaohu Lake. Shanghai Geol 105:13–17
Liu F, Deng D-G, Yang W, Shao Y-Q, Zhu P-F, Gong Z, Ge Q (2012) Distribution characteristics and bioavailability of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chaohu Lake. J Soil Water Conserv 26:149–153
Liu Z-L, Li J, Yang Y-Q, Chen R-R, Wu S-J (2013) Research and application of microwave assisted digestion procedure for the determination of 23 elements in sediments by ICP-AES/ICP-MS. Environ Chem 32:2370–2377
Mar SS, Okazaki M (2012) Investigation of Cd contents in several phosphate rocks used for the production of fertilizer. Microchem J 104:17–21
Pedro S, Duarte B, Castro N, Almeida PR, Cacador I, Costa JL (2015) The Lusitanian toadfish as bioindicator of estuarine sediment metal burden: the influence of gender and reproductive metabolism. Eco Indic 48:370–379
Ren C, Wu Y, Zhang S, Wu L-L, Liang X-G, Chen T-H, Zhu C-Z, Sojinu SO, Wang J-Z (2015) PAHs in sediment cores at main river estuaries of Chaohu Lake: implication for the change of local anthropogenic activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1687–1696
Roussiez V, Ludwig W, Probst J-L, Monaco A (2005) Background levels of heavy metals in surficial sediments of the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean): An approach based on 133Cs normalization and lead isotope measurements. Environ Pollut 138:167–177
Shang G-P, Shang J-C (2005) Causes and control countermeasures of eutrophication in Chaohu Lake. China Chin Geogr Sci 15:348–354
Shang G-P, Shang J-C (2007) Spatial and temporal variations of eutrophication in Western Chaohu Lake. China Environ Monitor Assess 130:99–109
Sun Y, Sun M (2007) Determination of 42 trace elements in seawater by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after APDC chelate co-precipitation combined with iron. Anal Lett 40:2391–2404
Sun Y-S, Cao D-J, Huang X-M, Li Y (2008) Environmental quality assessment of heavy metals in sediment along Chaohu Lake. Anhui Agr Sci Bull 14:55–56
Tang W-Z, Shan B-Q, Zhang H, Mao Z-P (2010) Heavy metal sources and associated risk in response to agricultural intensification in the estuarine sediments of Chaohu Lake Valley, East China. J Hazard Mater 176:945–951
Tang W, Shan B, Zhang H, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Ding Y, Rong N, Zhu X (2014) Heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of representative limnetic ecosystems in Eastern China. Sci Rep 4:1–7
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang J-Z, Zhang K, Liang B, Zeng EY (2011) Occurrence, source apportionment and toxicity assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of Chaohu, one of the most polluted lakes in China. J Environ Monit 13:3336–3342
Wang J-Z, Li H-Z, You J (2012a) Distribution and toxicity of current-use insecticides in sediment of a lake receiving waters from areas in transition to urbanization. Environ Pollut 161:128–133
Wang J-Z, Zhang K, Liang B (2012b) Tracing urban sewage pollution in Chaohu Lake (China) using linear alkylbenzenes (LABs) as a molecular marker. Sci Total Environ 414:356–363
Wang JZ, Yang ZY, Chen TH (2012c) Source apportionment of sediment-associated aliphatic hydrocarbon in a eutrophicated shallow lake. China Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:4006–4015
Wang J-Z, Chen T-H, Zhu C-Z, Peng S-C (2014) Trace organic pollutants in sediments from Huaihe River, China: evaluation of sources and ecological risk. J Hydrol 512:463–469
Xu F (1997) Exergy and structural exergy as ecological indicators for the development state of the Lake Chaohu ecosystem. Ecol Model 99:41–49
Yao S-C, Li S-J (2004) Sedimentary records of eutrophication for the last 100 years in Chaohu Lake. Acta Sediment Sin 22:343–347
Zan F, Huo S, Xi B, Su J, Li X, Zhang J, Yeager KM (2011) A 100 year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu. China J Environ Monit 13:2788–2797
Zhang H, Shan B (2008) Historical records of heavy metal accumulation in sediments and the relationship with agricultural intensification in the Yangtze鈥揌uaihe region. China Sci Total Environ 399:113–120
Zheng L-G, Liu G-J, Kang Y, Yang R-K (2010) Some potential hazardous trace elements contamination and their ecological risk in sediments of western Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 166:379–386
Zheng Z-X, Pan C-R, Ding F (2011) Distribution and environmental pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chaohu Lake, China. J Agro Environ Sci 30:161–165
Acknowledgments
Many thanks go to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41390240) and the State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse Foundation (No. PCRRF14002) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Céline Guéguen
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 13435 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JZ., Peng, SC., Chen, TH. et al. Occurrence, source identification and ecological risk evaluation of metal elements in surface sediment: toward a comprehensive understanding of heavy metal pollution in Chaohu Lake, Eastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 307–314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5246-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5246-4