Abstract
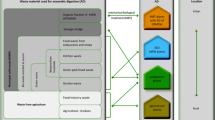
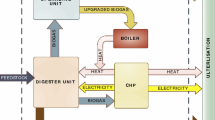
India is one among the Asia’s newly industrialized countries, in which urban centres generate large amount of municipal solid wastes due to the rapid urbanization. To demonstrate urban waste potentials for biogas production by anaerobic digestion, a comprehensive analysis on the availability of organic waste hotspots and its biogas potential for the exemplary case of Chennai, India, was undertaken. The identified hotspots and their biogas potential were plotted with Geographical Information System as thematic maps. The results of biogas potential tests revealed strong variations in the biogas potentials of individual waste streams from 240.2 to 514.2 mLN/g oDM (organic dry matter) with oDM reduction in the range of 36.4–61.5 wt.-%. Major waste generation hotspots were identified from the surveyed urban bio-reserves and the biogas potentials within an effective area of 5 km radius surrounding the hotspot were estimated. It was found that the biogas potential of individual hotspots ranged between 38.0–5938.7 m3/day. Further results revealed that the biogas potential during anaerobic co-digestion, by considering nearby bio-reserves in the effective areas of major hotspots, with and without residential organic waste, ranged between 4110.4–18–106.1 m3/day and 253.2–5969.5 m3/day, originating from 144.0–620.0 tons and 3.1–170.5 tons, respectively. Despite variations in the composition of the wastes, the Carbon/Nitrogen ratio, oDM reduction, biogas production and substrate availability were improved during co-digestion of nearby bio-reserves within the major hotspots, thereby improving the prevailing barriers in substrate management during anaerobic digestion of wastes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adama O (2007) Governing from above, solid waste management in Nigeria’s new capital city of Abuja. Acta Universitatis Stockholmiensis, Stockholm studies in human geography book series, Stockholm, pp 1–223. ISBN: 978-91-85445-67-7
Adhikari BB, Chae M, Bressler DC (2018) Utilization of slaughterhouse waste in value-added applications: recent advances in the development of wood adhesives. Polymers 10(176):1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10020176
Ahluwalia IJ (2016) Challenges of urbanisation in India. In: Besley T (ed) Contemporary issues in development economics. International Economic Association Series.Palgrave Macmillan, London
Akinbomi J, Brandberg T, Sanni SA, Taherzadeh MJ (2014) Development and dissemination strategies for accelerating biogas production in Nigeria. BioRes 9(3):5707–5737. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.9.3
Alessa L, Kliskey A, Brown G (2008) Social–ecological hotspots mapping: a spatial approach for identifying coupled social–ecological space. Landsc Urban Plan 85(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2007.09.007
Alkanok G, Demirel B, Onay TT (2014) Determination of biogas generation potential as a renewable energy source from supermarket wastes. Waste Manag 34(1):134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.09.015
Alvarez R, Riden G (2008) Semi-continuous co-digestion of solid slaughterhouse waste, manure, and fruit and vegetable waste. Renew Energy 33(4):726–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2007.05.001
Alvarez JA, Otero L, Lema JM (2010) A methodology for optimising feed composition for anaerobic co-digestion of agro-industrial wastes. Bioresour Technol 101(4):1153–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.061
Anjum M, Khalid A, Mahmood T, Arshad M (2012) Anaerobic co-digestion of municipal solid organic waste with melon residues to enhance biodegradability and biogas production. J Mater Cycles Waste 14:388–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-012-0082-9
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water & wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington
Aspé E, Martí MC, Jara A, Roeckel M (2001) Ammonia inhibition in the anaerobic treatment of fishery effluents. Water Environ Res 73(2):154–164. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143001x138813
ASTM (2014) Standard test methods for determination of carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen in analysis samples of coal and carbon in analysis samples of coal and coke. ASTM D5373. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Banks CJ, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Heaven S (2012) Trace element requirements for stable food waste digestion at elevated ammonia concentrations. Bioresour Technol 104:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.068
Barchmann T, Mauky E, Dotzauer M, Stur M, Weinrich S, Jacobi H, Liebetrau J, Nelles M (2016) Expanding the flexibility of biogas plants—substrate management, schedule synthesis and economic assessment. Landtechnik 71(6):233–251. https://doi.org/10.15150/lt.2016.3146
Bhat PA, Shafiq M, Mir AA, Ahmed P (2017) Urban sprawl and its impact on landuse/land cover dynamics of Dehradun City, India. Int J Sustain 6(2):513–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsbe.2017.10.003
Bolaane B, Ali M (2004) Sampling household waste at source: lessons learnt in Gaborone. Waste Manag Res 22:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X04044970
Bouallagui H, Touhami Y, Cheikh R, Hamdi M (2005) Bioreactor performance in anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable wastes. Process Biochem 40(3–4):989–995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.03.007
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Budiman I, Muthahhari R, Kaynak C, Reichwein F, Zhang W (2018) Multiple challenges and opportunities for biogas dissemination in Indonesia. Indones J Energy 1(2):46–60. https://doi.org/10.33116/ije.v1i2.25
Chaudhuri S (2015) Urban poor, economic opportunities and sustainable development through traditional knowledge and practices. Global Bioeth 26(2):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/11287462.2015.1037141
Chen X, Yan W, Sheng K, Sanati M (2014) Comparison of high-solids to liquid anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and green waste. Bioresour Technol 154:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.054
Cuetos MJ, Gomez X, Otero M, Moran A (2008) Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste (SHW) at laboratory scale: influence of co-digestion with the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Biochem Eng J 40:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2007.11.019
Cuetos MJ, Gómez X, Otero M, Morán A (2010) Anaerobic digestion and co-digestion of slaughterhouse waste (SHW): influence of heat and pressure pre-treatment in biogas yield. Waste Manag 30(10):1780–1789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.01.034
Dasgupta MK, Mondal MK (2012) Bio energy conversion of organic fraction of Varanasi’s municipal solid waste. Energy Procedia 14:1931–1938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.12.887
Dhar H, Kumar P, Kumar S, Mukherjee S, Vaidya AN (2016) Effect of organic loading rate during anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste. Bioresour Technol 217:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.12.004
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28(3):350–356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60111a017
Edwiges T, Frare LM, Alino JHL, Triolo JM, Flotats X, Costa M (2018) Methane potential of fruit and vegetable waste: an evaluation of the semi-continuous anaerobic mono-digestion. Environ Technol:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1515262
Escamilla-Alvarado C, Poggi-Varald HM, Ponce-Noyola MT (2016) Bioenergy and bioproducts from municipal organic waste as alternative to landfilling: a comparative life cycle assessment with prospective application to Mexico. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(33):25602–25617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6939-z
Feyissa G, Zeleke G, Gebremariam E, Bewket W (2018) GIS based quantification and mapping of climate change vulnerability hotspots in Addis Ababa. Geo Environ Disasters 5(14):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-018-0106-4
Frings CS, Dunn RT (1970) A colorimetric method for determination of total serum lipids based on the sulpho-phospho-vanillin reaction. Amer J Clin Pathol 53(1):89–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/53.1.89
Fromhold M (2001) Technologieregionen in Asiens Newly Industrialized Countries: Strukturen und Beziehungssysteme am Beispiel von Bangalore, Indien und Bandung, Indonesien, LITVerlagMünster
Fuchs W, Wang X, Gabauer W, Ortner M, Li Z (2018) Tackling ammonia inhibition for efficient biogas production from chicken manure: status and technical trends in Europe and China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 97:186–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.08.038
Greater Chennai Corporation portal (2018) Solid waste management department. http://www.chennaicorporation.gov.in/NorthMonSoon2017/ZONE_1.pdf. Accessed on 4 June 2018
Greater Chennai Corporation portal (2019) Solid waste management department. http://www.chennaicorporation.gov.in/NorthMonSoon2017/ZONE_1.pdf. Accessed on 10 February 2019
Gumisiriza R, Mshandete AM, Rubindamayugi MST, Kansiime F, Kivaisi AK (2009) Enhancement of anaerobic digestion of Nile perch fish processing wastewater. Afr J Biotechnol 8(2):328–333 ISSN 1684–5315
Hansen KH, Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (1998) Anaerobic digestion of swine manure: inhibition by ammonia. Water Res 32(1):5–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/s00431354(97)00201-7
Heo NH, Park SC, Kang H (2004) Effects of mixture ratio and hydraulic retention time on single-stage anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and waste activated sludge. J Environ Sci Health A 39(7):1739–1756. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-120037874
Hills DJ (1979) Effects of carbon: nitrogen ratio on anaerobic digestion of dairy manure. Agric Wastes 1(4):267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-4607(79)90011-8
IOP (2019) Chennai population data portal (India online pages (IOP)). http://www.indiaonlinepages.com/population/chennai-current-population.html. Accessed on 10 February 2019
Jadhav AR, Chitanand MP, Shete HG (2013) Flower waste degradation using microbial consortium. IOSR J Agric Vet Sci 3(5):1–4. https://doi.org/10.9790/2380-0350104
Jensen PD, Mehta CM, Carney C, Batstone DJ (2016) Recovery of energy and nutrient resources from cattle paunch waste using temperature phased anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag 51:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.02.039
Jha AK, Sharma C, Singh N, Ramesh R, Purvaja R, Gupta PK (2008) Greenhouse gas emissions from municipal solid waste management in Indian mega-cities: a case study of Chennai landfill sites. Chemosphere 71(4):750–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.024
Jørgensen PJ (2009) Biogas—green energy 36. Process, design, energy supply, environment. Faculty of Agricultural Sciences, Aarhus. http://www.lemvigbiogas.com/BiogasPJJuk.pdf
Joshi R, Ahmed S (2016) Status and challenges of municipal solid waste management in India: a review. Cogent Environ Sci 2(1139434):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311843.2016.1139434
Kafle GK, Kim SH (2012) Evaluation of the biogas productivity potential of fish waste: a lab scale batch study. J Biosyst Eng 37(5):302–313. https://doi.org/10.5307/JBE.2012.37.5.302
Kafle GK, Bhattarai S, Kim SH, Chen L (2014) Effect of feed to microbe ratios on anaerobic digestion of Chinese cabbage waste under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions: biogas potential and kinetic study. J Environ Manag 133:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.12.006
Kalia V, Sonakya V, Raizada N (2000) Anaerobic digestion of banana stem waste. Bioresour Technol 73(2):191–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(99)00172-8
Kapoor R, Ghosh P, Kumar M, Vijay VK (2019) Evaluation of biogas upgrading technologies and future perspectives: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(12):11631–11661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04767-1
Karthikeyan L, Suresh V, Krishnan V, Tudor T, Varshini V (2018) The management of hazardous solid waste in India: an overview. Environments 5(9):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5090103
Kemausuor F, Adaramola M, Morken J (2018) A review of commercial biogas systems and lessons for Africa. Energies 11(11):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11112984
Kim Y, Yoon Y, Kim C, Giersdorf J (2012) Status of biogas technologies and policies in South Korea. Renew Sust Energ Rev 16:3430–3438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.02.075
Kinobe JR, Niwagaba CB, Gebresenbet G, Komakech AJ, Vinnerås B (2015) Mapping out the solid waste generation and collection models: the case of Kampala City. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 65(2):197–205. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2014.984818
Kulkarni MB, Ghanegaonkar PM (2019) Biogas generation from floral waste using different techniques. Global J Environ Sci Manag 5(1):17–30. https://doi.org/10.22034/gjesm.2019.01.02
Kumar S, Swapnavahini K (2012) Nutrient reduction and biogas production of rose residue by anaerobic digestion in a batch reactor. Int J Adv Res Sci Technol 1(2):125–129 ISSN 2320–1126
Kumar S, Smith SR, Fowler G, Velis C, Kumar SJ, Arya S, Rena KR, Cheeseman C (2017) Challenges and opportunities associated with waste management in India. R Soc Open Sci 4(160764):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.160764
LAGA (2016) LAGA - Methodensammlung - Abfalluntersuchung. Version 3.0. Stand: 14. Oktober 2016. Bund/Länder-Arbeitsgemeinschaft Abfall
Lahiry S (2019) India’s challenges in waste management. The key to efficient waste management is to ensure segregation source and resource recovery. https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/waste/india-s-challenges-in-waste-management-56753. Accessed on 12 March 2019
Lin YP, Chu HJ, Wu CF, Chang TK, Chen CY (2011) Hotspot analysis of spatial environmental pollutants using kernel density estimation and geostatistical techniques. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8(1):75–88. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8010075
Lu X, Jin W, Xue S, Wang X (2017) Effects of waste sources on performance of anaerobic co-digestion of complex organic wastes: taking food waste as an example. Sci Rep 7(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16068-z
Mahanty B, Zafar M, Han MJ, Park HS (2014) Optimization of co-digestion of various industrial sludges for biogas production and sludge treatment: methane production potential experiments and modeling. Waste Manag 34(6):1018–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.09.001
Malayil S, Ashwath R, Natekar S, Chankaya HN (2019) Biogas conversion potential of chicken wastes. In: Ghosh S. (eds) Waste Valorisation and Recycling 2:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2784-1_24
Meeker DL, Hamilton CR (2006) An overview of the rendering industry, National Renderers Association. In: Meeker DL (ed) Essential rendering: all about the animal by-products industry. National Renderers Association, Alexandria, pp 1–16
Metson GS, Cordell D, Ridoutt B, Mohr S (2018) Mapping phosphorus hotspots in Sydney’s organic wastes: a spatially explicit inventory to facilitate urban phosphorus recycling. J Urban Ecol 4(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/jue/juy009
Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) (2015) Annual report. In: Energy, M.O.N.A.R. (Ed.), New Delhi. https://mnre.gov.in/file-manager/annual-report/2015-2016/EN/content.htm. Accessed on 10 February 2019
Ministry of Power and Energy Department (MPED) (2016) Power for all scheme statistics—Tamilnadu roadmap. https://powermin.nic.in/sies/default/files/uploads/Power_For_All_Tamilnadu_Signed.pdf. Accessed on 25 February 2019
Mir MA, Hussain A, Verma C (2016) Design considerations and operational performance of anaerobic digester: a review. Cogent Eng 3(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2016.1181696
Mittal S, Ahlgren EO, Shukla PR (2018) Barriers to biogas dissemination in India: a review. Energy Policy 112:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.10.027
Mondal C, Das A, Chatterjee SG (2016) A time-lag model for biogas production by anaerobic digestion. J Renew Sustain Energy 8(6):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4966160
Morales-Polo C, Cledera-Castro M, Moratilla-Soria BY (2018) Reviewing the anaerobic digestion of food waste: from waste generation and anaerobic process to its perspectives. Appl Sci 8(10):1–35. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101804
Mozhiarasi V, Speier CJ, Benish Rose PM, Mondal MM, Pragadeesh S, Weichgrebe D, Srinivasan SV (2019) Variations in generation of vegetable, fruit and flower market waste and effects on biogas production, exergy and energy contents. J Mater Cycles Waste 3:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00828-2
Mshandete A, Kivaisi A, Rubindamayugi M, Mattiasson B (2004) Anaerobic batch co-digestion of sisal pulp and fish wastes. Bioresour Technol 95(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.01.011
Nandan A, Yadav BP, Baksi S, Bose D (2017) Recent scenario of solid waste management in India. World Sci News 66:56–74
Neelmani J, Sudeshna S (2014) Urbanization in India: an impact assessment. Int J Appl Sociol 4(2):60–65. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ijas.20140402.04
Nges IA, Mbatia B, Björnsson L (2012) Improved utilization of fish waste by anaerobic digestion following omega-3 fatty acids extraction. J Environ Manag 110:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.06.011
Okuo DO, Waheed MA, Bolaji BO (2016) Evaluation of biogas yield of selected ratios of cattle, swine, and poultry waste. Int J Green Energy 13(4):366–372. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2014.961460
Open Government data (OGD) platform, India (2018) Monthly data on Energy and Peak Demand. https://data.gov.in/resources/monthly-data-energy-and-peak-demand. Accessed on 22 February 2019
Pagliaccia P, Gallipoli A, Gianico A, Gironia F, Montecchio D, Pastore C, Bitonto L, Braguglia CM (2019) Variability of food waste chemical composition: impact of thermal pre-treatment on lignocellulosic matrix and anaerobic biodegradability. J Environ Manag 236:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.01.084
Palatsi J, Viñas M, Guivernau M, Fernandez B, Flotats X (2011) Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste: main process limitations and microbial community interactions. Bioresour Technol 102(3):2219–2227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.121
Parizeau K, Maclaren V, Chanthy L (2006) Waste characterization as an element of waste management planning: lessons learned from a study in Siem Reap, Cambodia. Resour Conserv Recycl 49:110–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2006.03.006
Patil VS, Deshmukh HV (2015) Anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste for biogas generation: a review. Int Res J Environ Sci 4(6):80–83
Pavi S, Kramer LE, Gomes LP, Miranda LAS (2017) Biogas production from co-digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and fruit and vegetable waste. Bioresour Technol 228:362–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.01.003
Philippe F, Culot M (2009) Household solid waste generation and characteristics in cape Haitian city, Republic of Haiti. Resour Conserv Recycl 54:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.06.009
Population Reference Bureau (PRB) (2016) World population data sheet. https://www.prb.org/2018-world-population-data-sheet-with-focus-on-changing-age-structures/. Accessed on 20 June 2019
Rabii A, Aldin S, Dahman Y, Elbeshbishy E (2019) A review on anaerobic co-digestion with a focus on the microbial populations and the effect of multi-stage digester configuration. Energies 12(6):2–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12061106
Saboor A, Khan S, Shah AA, Hasan F, Khan H, Badshah M (2017) Enhancement of biomethane production from cattle manure with codigestion of dilute acid pretreated lignocellulosic biomass. Int J Green Energy 14(7):632–637. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2017.1313740
Salminen E, Rintala J (2002) Anaerobic digestion of organic solid poultry slaughterhouse waste—a review. Bioresour Technol 83(1):13–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(01)00199-7
Scano EA, Asquer C, Pistis A, Ortu L, Demontis V, Cocco D (2014) Biogas from anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable wastes: experimental results on pilot-scale and preliminary performance evaluation of a full-scale power plant. Energy Convers Manag 77:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2013.09.004
Singh A, Kuila A, Adak S, Bishai M, Banerjee R (2012) Utilization of vegetable wastes for bioenergy generation. Agric Res 1(3):213–222
Song L, Li D, Fang H, Cao X, Liu R, Niu Q, Li Y (2019) Revealing the correlation of biomethane generation, DOM fluorescence, and microbial community in the mesophilic co-digestion of chicken manure and sheep manure at different mixture ratio. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(19):19411–19424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05175-1
Sosnowski P, Wieczorek A, Ledakowicz S (2003) Anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and organic fraction of municipal solid wastes. Adv Environ Res 7(3):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(02)00049-7
Speier CJ, Mondal MM, Weichgrebe D (2018) Data reliability of solid waste analysis in Asia’s newly industrialised countries. Int J Environ Waste Manag 22(1/2/3/4):124–146. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEWM.2018.094101
The world bank data (2019) WHAT A WASTE 2.0, A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050. http://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/trends_in_solid_waste_management.html. Accessed on 10 October 2019
Times of India (2018) Article published on 7 September 2018. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/articleshow/65713697.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppsthttps://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chennai/power-demand-2000mw-more-than-last-year/articleshow/65713697.cms. Accessed on 12 February 2019
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA (1991) Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74(10):3583–3597. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(91)78551-2
Van P, Minh HG, Phu PST, Fujiwara T (2018) A new kinetic model for biogas production from co-digestion by batch mode. Global J Environ Sci Manage 4(3):251–262. https://doi.org/10.22034/gjesm.2018.03.001
VDI-Guideline 4630 (2006) Fermentation of organic materials. Characterization of substrate, sampling, collection of material data, fermentation tests. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin
Velmurugan B, Ramanujam A (2011) Anaerobic digestion of vegetable wastes for biogas production in a fed-batch reactor. Int J Emerg Sci 1(3):478–486 ISSN: 2222-4254
Verdaguer M, Molinos-Senante M, Poch M (2016) Optimal management of substrates in anaerobic co-digestion: an ant colony algorithm approach. Waste Manag 50:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.01.047
Vij D (2012) Urbanization and solid waste management in India: present practices and future challenges. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 37:437–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.03.309
Wang X, Lu X, Li F, Yang G (2014) Effects of temperature and carbon-nitrogen (C/N) ratio on the performance of anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure, chicken manure and rice straw: focusing on ammonia inhibition. PLoS One 9(5):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0097265
Ware A, Power N (2016) Biogas from cattle slaughterhouse waste: energy recovery towards an energy self-sufficient industry in Ireland. Renew Energy 97:541–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.05.068
World population review data (2019) World Population by Country. http://worldpopulationreview.com. Accessed on 10 October 2019
Yan H, Zhao C, Zhang J, Zhang R, Xue C, Liu G, Chen C (2017) Study on biomethane production and biodegradability of different leafy vegetables in anaerobic digestion. AMB Express 7(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-017-0325-1
Yong Z, Dong Y, Zhang X, Tan T (2015) Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and straw for biogas production. Renew Energy 78:527–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.01.033
Yousuf A, Khan MR, Pirozzi D, Wahid Z (2016) Financial sustainability of biogas technology: barriers, opportunities, and solutions. Energy Source Part B 11(9):841–848. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567249.2016.1148084
Zhang C, Su H, Baeyens J, Tan T (2014) Reviewing the anaerobic digestion of food waste for biogas production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 38:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.038
Zhang J, Loh KC, Lee J, Wang CH, Dai Y, Tong Y (2017) Three-stage anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and horse manure. Sci Rep 7(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01408-w
Zhu J, Wu S, Shen J (2019) Anaerobic co-digestion of poultry litter and wheat straw affected by solids composition, free ammonia and carbon/nitrogen ratio. J Environ Sci Health A 54(3):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2018.1546494
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) and the Indian Department of Science and Technology (DST) under the Indo-German Science and Technology Centre (IGSTC) (Grant number 01DQ15007A) under the 2+2 Project “RESERVES - Resource and energy reliability by co-digestion of veg-market and slaughterhouse waste”. The authors also thank the Director, CSIR-Central Leather Research Institute for providing support for this researchwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velusamy, M., Speier, C.J., Michealammal, B.R.P. et al. Bio-reserves inventory—improving substrate management for anaerobic waste treatment in a fast-growing Indian urban city, Chennai. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 29749–29765 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07321-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07321-1