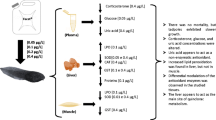
Abstract
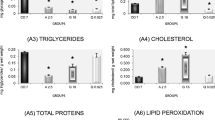
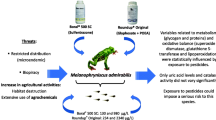
The aim of this study was to verify the effects of the isolated forms of Boral® SC 500, Glifosato® Biocarb herbicides, and a blend of both herbicides on metabolism and oxidative balance markers of Rana catesbeiana tadpoles and on their nutritional condition. Groups of tadpoles were divided into different treatments: control (no herbicides), Boral® 500 SC (sulfentrazone: 130 μg/L), Glifosato® Biocarb (glyphosate: 234 μg/L), and a blend of both herbicides. After 7 days, the liver, caudal muscle, and blood samples were taken to subsequently perform the biomarkers determination by spectrophotometry. The intestinal condition factor increased in animals exposed to glyphosate and herbicide blends, suggesting a hyperphagic effect. This hypothesis was confirmed by the rise of triglycerides and circulating very low–density lipoprotein (VLDL). There was a significant increase in the levels of uric acid in tadpoles exposed to the herbicide blend. Corticosterone levels reduced significantly in animals exposed to glyphosate and the herbicide blend. Oxidative stress markers had a tissue-dependent response. In the liver, glutathione S-transferase increased, and superoxide dismutase and catalase decreased in animals exposed to sulfentrazone and glyphosate. Lipoperoxidation was reduced in the glyphosate treatment. In the caudal muscle, superoxide dismutase and catalase activities were maintained, and there was a decline in the levels of glutathione S-transferase and TBARS only in the blend group.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armas ED, Monteiro RTR, Antunes PM, Santos MAPF, Camargo PB, Abakerli RB (2007) Diagnóstico espaço temporal da ocorrência de herbicidas nas águas superficiais e sedimentos do Rio Corumbataí e principais afluentes. Química Nova 30(5):1119–1127
Bailey DC, Todt CE, Burchfield SL, Pressley AS, Denney RD, Isaac B, Snapp IB, Rekek Negga R, Traynor WL, Fitsanakis VA (2018) Chronic exposure to a glyphosate-containing pesticide leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and increased reactive oxygen species production in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 57:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.11.005
Banerjee BD, Seth V, Bhattacharya A, Pasha ST, Chakraborty AK (1999) Biochemical effects of some pesticides on lipid peroxidation and free-radical scavengers. Toxicol Lett 107:33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(99)00029-6
Barton BA, Iwama GK (1991) Physiological changes in fish from stress in aquaculture with emphasis on the response and effects of corticosteroids. Annu Rev Fish Dis 1:3–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/42.3.517
Blaustein AR, Johnson PTJ (2003) The complexity of deformed amphibians. Front Ecol Environ 1:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1890/1540-9295(2003)001[B0087:TCODA]D2.0.CO.2
Bókony V, Móricz ÁM, Tóth Z, Gál Z, Kurali A, Mikó Z, Pásztor K, Szederkényi M, Tóth Z, Ujszegi J, Üveges B, Krüzselyi D, Capon RJ, Hoi H, Hettyey A (2016) Variation in chemical defense among natural populations of common toad, Bufo bufo, tadpoles: the role of environmental factors. J. Chem. Ecol. 42 (4): 329–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-016-0690-2
Both C, Lingnau R, Santos-Jr A, Madalozzo B, Lima LP, Grant T (2011) Widespread occurrence of the American bullfrog, Lithobates Catesbeianus (Shaw, 1802) (Anura: Ranidae), in Brazil. S AM J Herpetol 6(2):127–134. https://doi.org/10.2994/057.006.0203
Both C, Madalozzo B, Lingnau R, Grant T (2014) Amphibian richness patterns in Atlantic Forest areas invaded by American bullfrogs. Austral Ecology 39(7):864–874. https://doi.org/10.1111/aec.12155
Boveris A, Cadenas E (1982) Production of superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide in mitochondria. In: Oberley LW (ed) Superoxide dismutase, vol. 2, Boca Raton, pp 15–30
Boveris A, Chance B (1973) The mitocondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide: general properties and effect of hyperbaric oxygen. Biochem J 34:707–717
Boyland E, Chasseaud LF (1969) The role of glutathione and glutathione S-transferases in mercapturic acid byosinthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 32:173–219
Brausch MJ, Smith NP (2007) Toxicity of three polyethoxylated tallowamine surfactant formulations to laboratory e field collected fairy shrimp, Thamnocephalus platyurus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52:217–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-006-0151-y
Bucciarelli T, Sacchetta P, Pennelli A, Cornelio L, Romagnoli R, Merino S, Petruzelli R, Di Ilio C. 1999. Characterization of toad glutathione transferase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1431:189–198
Carey C, Heyer WR, Wilkinson J, Alford RA, Arntzen JW, Halliday T, Hungerford L, Lips KR, Middleton EM, Orchard SA, Rand AS (2001) Amphibian declines and environmental change: use of remote-sensing data to identify environmental correlates. Conserv Biol 15:903–913. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.2001.015004903.x
Cattaneo R, Clasen B, Loro VL, Menezes CC, Pretto A, Baldisserotto B, Santi A, Avila LA (2011) Toxicological Responses of Cyprinus carpio Exposed to a Commercial Formulation Containing Glyphosate. Bull Environm Contam Toxicol 87 (6):597-602.
Coltro ML, da Silva PR, Valgas AAN, Miguel CM, Freitas BS, Oliveira GT (2017) Influence of the herbicide quinclorac (Facet®) on corticosterone levels, plasma metabolites, and antioxidant balance in liver and muscle tissues of tadpoles of Rana catesbeiana Shaw, 1802. Water, Air and Soil Poll 228(7):228–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3404-7
CONCEA – Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal. 2015. Diretrizes da Prática de Eutanásia do CONCEA. Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação. Brasília, Brasil.
Costa MJ, Monteiro DA, Oliveira-Neto AL, Rantin FT, Kalinin AL (2008) Oxidative stress biomarkers e heart function in bullfrog tadpoles exposed to roundup original. Ecotoxicol. 17(3):153–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0178-5
Costantini D (2014) Oxidative stress and hormesis in evolutionary ecology and physiology: a marriage between mechanistic and evolutionary approaches. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Costantini D, Marasco V, Møller AP (2011) A meta-analysis of glucocorticoids as modulators of oxidative stress in vertebrates. J Comp Physiol B 181:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-011-0566-2
Cunha ER, Delariva RL (2009) Introdução da rã-touro, Lithobates catesbeianus (SHAW, 1802): uma revisão. SaBios. 4:2
Dallegrave E, Mantese FD, Coelho RS, Pereira JD, Dalsenter PR, Langeloh A (2003) The teratogenic potential of the herbicide glyphosate-roundup in Wistar rats. Toxicol Lett 142:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00483-6
Damalas CA, Eeleftherohorinos IG (2001) Dicamba and atrazine antagonism on sulfonylurea herbicides used for Johnsongrass (Sorghum halepense) control in corn (Zea mays). Weed Technol 15(1):62–67
Denver RJ (2009) Structural and functional evolution of vertebrate neuroendocrine stress systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1163:1–16
Dornelles MF, Oliveira GT (2014) Effect of atrazine, glyphosate and quinclorac on biochemical parameters, lipid peroxidation e survival in bullfrog tadpoles (Lithobates catesbeianus). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66:415–429 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9967-4
Dornelles MF, Oliveira GT (2016) Toxicity of atrazine, glyphosate, and quinclorac in bullfrog tadpoles exposed to concentrations below legal limits. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1610–1620 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5388-4
El-Banna SG, Attia AM, Hafez AA, El-Kazaz SA (2009) Effect of garlic consumption on blood lipid and oxidant/ antioxidant parameters in rat males exposed to chlorpyrifos. Slovak J Anim Sci 42:111–117. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB12.2797
Freitas JS, Teresa FB, de Almeida EA (2017) Influence of temperature on the antioxidant responses and lipid peroxidation of two species of tadpoles (Rhinella schneideri and Physalaemus nattereri) exposed to the herbicide sulfentrazone (Boral 500SC®). Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 197:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.04.005
Giesy JP, Dobson S, Solomon KR (2000) Ecotoxicological risk assessment for roundup herbicide. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 167:35–120 https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4612-1156-3_2
Gill JPK, Sethi N, Mohan A, Datta S, Girdhar M (2018) Glyphosate toxicity for animals. Environ Chem Lett 16:401–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0689-0
Gripp HS, Freitas JS, Almeida EA, Bisinoti MC, Moreira AB (2017) Biochemical effects of fipronil and its metabolites on lipid peroxidation and enzymatic antioxidantv defense in tadpoles (Eupemphix nattereri: Leiuperidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.027
Hatzios KK (1998) Supplement to herbicide handbook. Weed Science Society of America, Lawrence, pp 67–69
Hayes T (1997) Steroids as potential modulators of thyroid hormone activity in anuran metamorphosis. Am Zool 37:185–194
Hermes-Lima M (2004) Oxygen in biology and biochemistry: role of free radicals. In: Storey KB (ed) Functional metabolism: regulation and adaptation. John Wiley and Sons, New Jersey
Hermes-Lima M, Storey KB (1993) In vitro oxidative inactivation of glutathione S-transferase from a freeze tolerant reptile. Mol Cell Biochem 124(2):149–158 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00929207
Howe CM, Berrill M, Pauli BD, Helbring CC, Werry K, Veldhoen N (2004) Toxicity of glyphosate-based pesticides to four North American frog species. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1928–1938. https://doi.org/10.1897/03-71
Iguchi EY (2012) Alterações comportamentais em Geophagus brasiliensis submetidos à ação do herbicida glifosato. Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso (Bacharelado em Ciências Biológicas). Instituto de Biociências, Letras e Ciências Exatas, UNESP, São José do Rio Preto, SP.e 21p
Jones L, Gossett DR, Banks SW, McCallum ML (2010) Antioxidant defense system in tadpoles of the American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) exposed to paraquat. J Herpetol 44(2):222–228
Kiesecker JM, Blaustein AR, Belden LK (2001) Complex causes of amphibian population declines. Nature. 410:681–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/35070552
Kollman W, Segawa R (1995) Interim report of the pesticide chemistry database 1995. Environmental Hazards Assessment Program. EH95-04. Environmental Protection Agency, Department of Pesticide Regulation, California
Lajmanovich RC, Attademo AM, Peltzer PM, Junges CM, Cabagna MC (2011) Toxicity of four herbicide formulations with glyphosate on Rhinella arenarum (Anura: Bufonidae) tadpoles: B-esterases and glutathione s-transferase inhibitors. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:681–689 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9578-2
Lau ETC, Karraker NE, Leung KMY (2015) Temperature-dependent acute toxicity of methomyl pesticide on larvae of 3 Asian amphibian species. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:2322–2327. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3061
Lima LC, Ribeiro LP, Leite RC (2006) Estresse em peixes. Rev Bras Reprod Anim 30:113–117
Lima ES, Abdalla DSP (2001) Peroxidação lipídica: mecanismos e avaliação em amostras biológicas. Braz J Pharm Sci 37(3):293–303
Lushchak VI, Bagnyukova TV (2006) Effects of different environmental oxygen levels on free radical processes in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol [B] 144 (3):283-289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2006.02.014
Martinez CO, Silva CMMS, Fay EF, Abakerli RB, Maia AHN, Durrant LR (2010) Microbial degradation of sulfentrazone in a Brazilian rhodic hapludox soil. Braz J Microbiol 41:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822010000100030
Mesléard F, Gauthier-Clerc M, Lambret P (2016) Impact of the insecticide Alphacypermetrine e herbicide Oxadiazon, used singly or in combination, on the most abundant frog in French rice fields, Pelophylax perezi. Aquat Toxicol 176:24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.04.004
Modesto KA, Martinez CBR (2010) Roundup causes oxidative stress in liver and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in muscle and brain of the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere. 78:294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.10.047
Moura MAM, Franco DAS, Matallo MB (2008) Impacto de herbicidas sobre os recursos hídricos. Rev Tecnol Inov Agropec:142–151
Nelson DL, Cox MM (2014) Princípios de Bioquímica: Lehninger. Artmed, Porto Alegre
Nunes BS, Travasso R, Gonçalves F, Castro BB (2015) Biochemical and physiological modifications in tissues of Sardina pilchardus: spatial and temporal patterns as a baseline for biomonitoring studies. Front Environ Sci 3:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2015.00007
Nunes C, Silva A, Soares E, Ganias K (2011) The use of hepatic e somatic indices e histological information to characterize the reproductive dynamics of Atlantic sardine Sardina pilchardus from the Portuguese coast. Mar Coast Fish 3:127–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/19425120.2011.556911
Osipe JB, Teixeira ES, Osipe R, Sorace MAF, Cossa CA, Neto AMO (2008) Association of sulfentrazone and glyphosate for weed control in RR® soybean. Revista Brasileira de Herbicidas 7(1):15–25 www.rbherbicidas.com.br
Pandey A, Rudraiah M (2015) Analysis of endocrine disruption effect of Roundup® in adrenal gland of male rats. Toxicol Rep 2:1075–1085
Passos ABR, Freitas MAM, Torres LG, Silva AA, Queiroz MEL, Lima CF (2013) Sorption and desorption of sulfentrazone in Brazilian soils. J Environ Sci Health B 48(8):646–650. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2013.777313
Păunescu A, Ponepal CM (2011) Effect of Roundup® herbicide on physiological indices in marsh frog Pelophylax ridibundus. Scientific Papers, Bucharest 54:269–274
Persch TS, Weimer RN, Freitas BS, Oliveira GT (2017) Metabolic parameters and oxidative balance in juvenile Rhamdia quelen exposed to rice paddy herbicides: Roundup®, Primoleo® and Facet®. Chemosphere. 174:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.092
Pignati WA, Souza e Lima FAN, de Lara SS, Correa MLM, Barbosa JR, Costa Leão LH, Pignatti MG (2017) Spatial distribution of pesticide use in Brazil: a strategy for health surveillance. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-812320172210.17742017
Preuss JF (2017) Distribuição espaço-temporal da rã invasora, Lithobates catesbeianus (Anura, Ranidae) (Shaw, 1802) em dois remanescentes florestais da Mata Atlântica no sul do Brasil. Biota Amazônia 7(2):26–30 https://doi.org/10.18561/2179-5746/biotaamazonia
Queiroz GMP, da Silva MR, Bianco RJF, Pinheiro A, Kaufmann V (2011) Transporte De Glifosato Pelo Escoamento Superficial e Por Lixiviação Em Um Solo Agrícola. Quím Nova 34(2):190–195. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422011000200004
Relyea RA (2005) The impact of insecticides and herbicides on the biodiversity and productivity of aquatic communities. Ecol Appl 15:618–627. https://doi.org/10.1890/03-5342
Rissoli RZ, Abdalla FC, Costa MJ, Rantin FT, Mckenzie DJ, Kalinin AL (2016) Effects of glyphosate and the glyphosate based herbicides Roundup Original® and Roundup Transorb® on respiratory morphophysiology of bullfrog tadpoles. Chemosphere. 156:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.083
Rossi SC, Silva MD, Piancini LD, Oliveira Ribeiro CA, Cestari MM, Silva de Assis HC (2011) Sublethal effects of waterborne herbicides in tropical freshwater fish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87:603–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0397-6
Salbego J, Pretto A, Gioda CR, Menezes CC, Lazzari R, Neto JR, Baldisserotto B, Loro VL (2010) Herbicide formulation with glyphosate affects growth, acetylcholinesterase activity, and metabolic and hematological parameters in piava (Leporinus obtusidens). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58:740–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9464-y
Santos-Pereira M, Rocha CFD (2015) Invasive bullfrog Lithobates catesbeianus (Anura: Ranidae) in the Paraná state, Southern Brazil: a summary of the species spread. Revista Brasileira de Zoociências 16:141–147
Santos LFJ, Oliveira-Bahia VRL, Nakaghi LSO, De Stefani MV, Gonçalves AM, Pizauro Junior JM (2016) Ontogeny of the digestive enzymes of tadpoles of Lithobates catesbeianus. Copeia. 104(4):838–842. https://doi.org/10.1643/CG-16-432
Solomon KR, Carr JA, Du Preez LH, Giesy JP, Kendall RJ, Smith EE, Van Der Kraak GJ (2008) Effects of atrazine on fish, amphibians, and aquatic reptiles: a critical review. Crit Rev Toxicol 38:721–772. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440802116496
Sounderraj SFL, Sekhar P, Kumar PS, Lesley N (2011) Effect of systemic pesticide phosphamidon on haematological aspects of common frog Rana tigrina. Int J Pharm Biol Arch 2:1776–1780
Tavares-Dias M, Martins ML, Moraes FR (2000) Relação hepatossomática e esplenosomática em peixes teleósteos de cultivo intensivo. Rev Bras Zool 17:273–281
Thorngren JL, Harwood AD, Murphy TM, Huff Hartz KE, Fung CY, Lydy MJ (2017) Fate and risk of atrazine and sulfentrazone to non-target species at an agriculture site. Environ Toxicol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3664
Tsahar E, Arad Z, Izhaki I, Guglielmo CG (2006) The relationship between uric acid and its oxidative product allantoin: a potential indicator for the evaluation of oxidative stress in birds. J Comp Phys [B] 176:653–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-006-0088-5
UNICA (2015) União da industria da Cana-de-açucar. Unicadata. http://www.unicadata.com.br
USEPA - US Environmental Protection Agency 2009 Sulfentrazone registration review. EPA-HQ-OPP-2009-0624, Washington
Van Der Kraak GJ, Hosmer AJ, Hanson ML, Kloas W, Solomon KR (2014) Effects of atrazine in fish, amphibians, e reptiles: an analysis based on quantitative weight of evidence. Crit Rev Toxicol 44:1–66. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2014.967836
Vidal RA (2002) Ação dos herbicidas: absorção, translocação e metabolização. Evangraf, Porto Alegre
Vieira MI (1993) Rã touro gigante: características e reprodução. Infotec, São Paulo
Vutukuru SS (2005) Acute effects of hexavalent chromium on survival, oxygen consumption, hematological parameters and some biochemical profiles of the indian major carp, Labeo rohita. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2:456–462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2005030010
Webster NR, Nunn JF (1988) Molecular structure of free radicals and their importance in biological reactions. Br J Anaesth 60:98–108
Whiles MR, Lips KR, Pringle CM, Kilham SS, Bixby RJ, Brenes R, Montgomery C (2006) The efects of amphibian population declines on the structure and function of Neotropical stream ecosystems. Front Ecol Environ 4(1):27–34
Wright ML, Guertin CJ, Duffy JL, Szatkowski MC, Visconti RF, Alves CD (2003) Developmental and diel profiles of plasma corticosteroids in the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana. Comp Bioch Phys [A] 135:585–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1095-6433(03)00140-5
Yin X, Jiang S, Yu J, Zhu G, Wu H, Mao C (2014) Effects of spirotetramat on the acute toxicity, oxidative stress, e lipid peroxidation in Chinese toad (Bufo bufo gargarizans) tadpoles. Enviroln Toxicol Pharm 37:1229–1235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.04.016
Zanette J, Monserrat JM, Bianchini A (2015) Biochemical biomarkers in barnacles Balanus improvises: pollution and seasonal effects. Mar Environ Res 103:74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.11.001
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Laboratório de Fisiologia da Conservação group, especially the biologist Luiza Petroli Ruckheim for the support in the practical work. We also thank the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for the mastership grant provided to the first author and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the productive grant provided to the corresponding author (process no. 307071/2015-4).
Funding
This study was financially supported by the PPG—Ecology and Evolution of Biodiversitye of the PUCRS and by National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), process no. 307071 / 2015-4 .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures followed the Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal (CONCEA 2015) guide and were approved by the Comitê de Ética para Uso de Animais da Universidade (protocol no. 15/00471—CEUA/PUCRS).
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PPTX 48 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkens, A.L.L., Valgas, A.A.N. & Oliveira, G.T. Effects of ecologically relevant concentrations of Boral® 500 SC, Glifosato® Biocarb, and a blend of both herbicides on markers of metabolism, stress, and nutritional condition factors in bullfrog tadpoles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 23242–23256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05533-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05533-z