Abstract
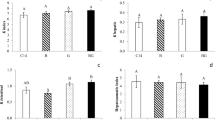
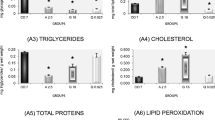
This study sought to analyze the effects of the herbicide quinclorac on body condition indices; plasma levels of corticosterone, glucose, and uric acid; activity of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione S-transferase (GST); and levels of lipid peroxidation (LPO) in the liver and caudal muscle of American bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) tadpoles. After a 7-day acclimation period, animals were exposed to four concentrations (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 μg/L) of herbicide for a further 7 days. Then, blood samples were obtained, animals were euthanized, and the liver and caudal muscle resected. Levels of corticosterone and uric acid were reduced in tadpoles exposed to the highest concentration of herbicide, and this reduction was preceded by an increase in glucose levels. In the liver tissue, LPO was increased after exposure to 0.1 μg/L quinclorac, followed by a return to baseline values in the remaining concentrations; this response was accompanied by an increase in SOD and GST and reduction of tissue protein levels. At the highest concentration, a reduction in activity of all enzymes was observed, with protein returning to control-like levels. In muscle, SOD and GST levels declined with exposures up to 0.1 g/L and 0.4 μg/L, respectively, whereas LPO decreased in animals exposed to 0.1 μg/L. These results suggest participation of nonenzymatic antioxidant defenses, as demonstrated by the reduction in uric acid levels. Exposure to the range of quinclorac concentrations used in this study slowed body mass and length gain, reduced corticosterone levels, and modulated antioxidant defenses.

ᅟ





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi, H. (1984). Catalase in vitro. Methods in Enzymology, 105, 121–126.
Albinati, R. C. B., Costa, G. B., & Neves, A. P. (1998). Efeito da densidade populacional de girinos de (Rana catesbeiana, Shaw, 1802) sobre o tempo de metamorfose e peso do ímagos. Arquivos da Escola de Medicina Veterinária da UFBA, 19, 75–86.
Alford, R. A., & Richards, S. J. (1999). Global amphibian declines: a problem in applied ecology. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 30, 133–165.
ASTM. (1998). Standard guide for conducting the frog embryo teratogenesis assay—Xenopus (FETAX) (pp. 790–805). Philadelphia: ASTM.
Bagarinao, T., & Thayaparan, K. (1986). The length-weight relationship, food habits and condition factor of wild juvenile milkfish in Sri Lanka. Aquaculture, 55, 241–246.
Banerjee, B. D., Seth, V., Bhattacharya, A., Pasha, S. T., & Chakraborty, A. K. (1999). Biochemical effects of some pesticides on lipid peroxidation and free-radical scavengers. Toxicology Letters, 107, 33–47.
Barata, C., Varo, I., Navarro, J. C., Arun, S., & Porte, C. (2005). Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in the freshwater cladoceran Daphnia magna exposed to redox cycling compounds. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C, 140, 175–186.
Barbosa, K. B. F., Costa, N. M. B., Alfenas, R. C. G., De Paula, S. O., Minim, V. P. R., & Bressan, J. (2010). Estresse oxidativo: conceito, implicações e fatores modulatórios. Revista de Nutrição, 23(4), 629–643.
Blaustein, A. R. (1994). Chicken little or Nero’s fiddle? A perspective on declining amphibian populations. Herpetologica, 50, 85–97.
Blaustein, A. R., & Johnson, P. T. J. (2003). The complexity of deformed amphibians. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 1, 87–94.
Bohrer, M. B. C. (1995). Biomonitoramento das lagoas de tratamento terciário dos efluentes líquidos industriais (Sitel) do Pólo Petroquímico do Sul, Triunfo, RS, através da comunidade zooplantônica (p. 470). Tese de Doutorado: Departamento de Ciências, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos.
Boone, M. D., Bridges, C. M., & Rothermel, B. B. (2001). Growth and development of larval green frogs (Rana clamitans) exposed to multiple doses of an insecticide. Oecologia, 129, 518–524.
Boone, M. D., Semlitsch, R. D., Little, E. E., & Doyle, M. C. (2007). Multiple stressors in amphibian communities: effects of chemical contamination, bullfrogs and fish. Ecological Applications, 17, 229–301.
Boveris, A., & Cadenas, E. (1982). Production of superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide in mitochondria. In L. W. Oberley (Ed.), Superoxide dismutase (Vol. 2, pp. 15–30). Florida: CRC Press.
Boveris, A., & Chance, B. (1973). The mitochondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide: general properties and effect of hyperbaric oxygen. Biochemical Journal, 34, 707–717.
Boyland, E., & Chasseaud, L. F. (1969). The role of glutathione and glutathione S-transferases in mercapturic acid biosynthesis. Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology, 32, 173–219.
Buege, J. A., & Aust, S. D. (1978). Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods in Enzymology, 52, 302–310.
Bueno-Guimarães, H. M., Ferreira, C. M., Garcia, M. L., & Saldiva, P. H. (2001). Tadpole epithelium test: potential use of Rana catesbeiana histopathologic epithelial changes to evaluate aquatic pollution. Bulletin of the Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67, 202–209.
Cajaraville, M. P., Bebianno, M. J., Blasco, J., Porte, C., Sarasquete, C., & Viarengo, A. (2000). The use of biomarkers to assess the impact of pollution in coastal environments of the Iberian peninsula: a practical approach. Science of the Total Environment, 247, 295–311.
Costa, M. A. G. (2004). Poluição ambiental: herança para gerações futuras (p. 254). Orium: Santa Maria.
Costa, M. J., Monteiro, D. A., Oliveira-Neto, A. L., Rantin, F. T., & Kalinin, A. L. (2008). Oxidative stress biomarkers and heart function in bullfrog tadpoles exposed to Roundup Original®. Ecotoxicology, 17, 153–116.
Costantini, D. (2008). Oxidative stress in ecology and evolution: lessons from avian studies. Ecology Letters, 11, 1238–1251.
Costantini, D. (2014). Oxidative stress and hormesis in evolutionary ecology and physiology (p. 348). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Dornelles, M. F., & Oliveira, G. T. (2014). Effect of atrazine, glyphosate and quinclorac on biochemical parameters, lipid peroxidation and survival in bullfrog tadpoles (Lithobates catesbeianus). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 66, 415–429.
Dornelles, M. F., & Oliveira, G. T. (2015). Toxicity of atrazine, glyphosate, and quinclorac in bullfrog tadpoles exposed to concentrations below legal limits. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(2), 1610–1620.
Endemann, M., Hristoforoglu, K., Stauber, T. E., & Wilhelm, E. (2002). Assessment of age related polyploidy in Quercus robur L. somatic embryos and regenerated plants using DNA flow cytometry. Biologia Plantarum, 44(3), 339–345.
Ezemonye, L., & Tongo, I. (2009). Lethal and sublethal effects of atrazine to amphibian larvae. Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences, 2(1), 29–36.
Fang, J. K. H., Au, D. W. T., Wu, R. S. S., Chan, A. K. Y., Mok, H. O. L., & Shin, P. K. S. (2009). The use of physiological indices in rabbitfish Siganus oramin for monitoring of coastal pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 1229–1235.
Ferreira, C. M., Lombardi, J. V., Machado-Neto, J. G., Bueno-Guimarães, H. M., Soares, S. R., & Saldiva, P. H. (2004). Effects of copper oxychloride in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles: toxicological and bioaccumulative aspects. Bulletin of the Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 73, 465–470.
Fonseca, L. L., Sánchez, C., Santos, H., & Voit, E. O. (2011). Complex coordination of multi-scale cellular responses to environmental stress. Molecular BioSystems, 7(3), 731–741.
Fordham, C. L., Tessari, J. D., Ramsdell, H. S., & Keefe, T. J. (2001). Effects of malathion on survival, growth, development and equilibrium posture of bullfrog tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20(1), 179–184.
Freitas, J. S., & Alemida, E. A. (2016). Antioxidant defense system of tadpoles (Eupemphix nattereri) exposed to changes in temperature and pH. Zoological Science, 33(2), 186–194.
Galbraith, D. W., Harkins, K. R., Maddon, J. M., Ayres, N. M., Sharma, D. P., & Firoozabady, E. (1983). Rapid flow cytometric analysis of the cell-cycle in intact plant-tissues. Science, 220, 1049–1051.
Georgieva, N. V. (2005). Oxidative stress as a factor of disrupted ecological oxidative balance in biological systems—a review. Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 8(1), 1–11.
Gervasi, S. S., Urbina, J., Hua, J., Chestnut, T., Relyea, R. A., & Blaustein, A. R. (2013). Experimental evidence for American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) susceptibility to chytrid fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis). EcoHealth, 10(2), 166–171.
Glantzounis, G. K., Tsimoyiannis, E. C., Kappas, A. M., & Galaris, D. A. (2005). Uric acid and oxidative stress. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 11, 4145–4151.
Goulet, B. N., & Hontela, A. (2003). Toxicity of cadmium, endosulfan, and atrazine in adrenal steroidogenic cells of two amphibian species, Xenopus laevis and Rana catesbeiana. Environmental Toxicology, 22(9), 2106–2113.
Habig, W. H., & Jakoby, W. B. (1981). Glutathione S-transferases (rat and human). Methods in Enzymology, 77, 218–234.
Harris, R. N. (1999). The anuran tadpole—evolution and maintenance. In R. W. McDiarmid & R. Altig (Eds.), Tadpoles—the biology of anuran larvae (pp. 280–294). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Houlihan, J. E., Findlay, C. S., Schmidt, B. R., Meyers, A. H., & Kuzmin, S. L. (2001). Quantitative evidence for global amphibian population declines. Nature, 404, 752–755.
IBGE. (2014). Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. http://www.ibge.gov.br (acessed 20.10.2014).
IRGA. (2014). Instituto Rio Grandense do Arroz. http://www.irga.rs.gov.br (acessed 20.10.2014).
Isaksson, C. (2010). Pollution and its impact on wild animals: a meta-analysis on oxidative stress. EcoHealth, 7, 342–350.
Jena, S. D., Behera, M., Dandapat, J., & Mohanty, N. (2009). Nonenzymatic antioxidant status and modulation of lipid peroxidation in the muscles of Labeo rohita by sublethal exposure of CuSO4. Veterinary Research Communications, 33, 421–429.
Jones, L., Gossett, R. D., Banks, S. W., & McCallum, M. L. (2010). Antioxidant defense system in tadpoles of the American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus) exposed to paraquat. Journal of Herpetology, 44, 222–228.
Kavitha, P., & Rao, V. (2007). Oxidative stress and locomotor behavior response as biomarkers for assessing recovery status of mosquito Wsh, Gambusia aynis after lethal effect of an organophosphate pesticide, monocrotophos. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 87, 182–188.
Kehrer, J. P. (1993). Free radicals as mediators of tissue injury and disease. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 34, 21–48.
Kiesecker, J. M., Blaustein, A. R., & Belden, L. K. (2001). Complex causes of amphibian population declines. Nature, 410, 681–684.
Lambropoulou, D. A., Sakkas, V. A., Hela, D. G., & Albanis, T. A. (2002). Application of solid phase microextraction in the monitoring of priority pesticides in the kalamas river (N.W. Greece). Journal of Chromatography, 963(1–2), 107–116.
Landis, W. G., & Yu, M. H. (2004). Introduction to environmental toxicology: impacts of chemicals upon ecological systems (3rd ed.p. 487). Florida: CRC Press.
Lima, E. S., & Abdalla, D. S. P. (2001). Peroxidação lipídica: mecanismos e avaliação em amostras biológicas. Revista Brasileira de Ciências Farmacêuticas, 37, 293–303.
Limón-Pacheco, J., & Gonsebatt, M. E. (2009). The role of antioxidants and antioxidant-related enzymes in protective responses to environmentally induced oxidative stress. Mutation Research, 674, 137–147.
Livingstone, D. R. (2001). Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(8), 656–666.
Llesuy, S. F., Milei, J., Molina, H., Boveris, A., & Milei, S. (1985). Comparison of lipid peroxidation and myocardial damage induced by adriamycin and 4′-epiadriamycin in mice. Tumori, 71(3), 241–249.
Mann, R. M., Hyne, R. V., Choung, C. B., & Wilson, S. P. (2009). Amphibians and agricultural chemicals: Review of the risks in a complex environment. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2903–2927.
Marchesan, E., Zanella, R., Avila, L. A., Camargo, E. R., Machado, S. L. O., & Macedo, V. R. M. (2007). Rice herbicide monitoring in two Brazilian river during the rice growing season. Scientia Agricola, 64, 131–137.
McElroy S. (2006). Registration of the new active ingredient, Quinclorac (chemical code 128974), contained in the new pesticide product. Ortho Weed B Gon Max Plus Crabgrass Control (EPA Reg. No. 239–2689). http://pmep.cce.cornell.edu/profiles/herb-growthreg/naa-rimsulfuron/quinclorac/ortho_reg_1006.pdf. Accessed 9 Feb 2017.
Meirelles, C. E., Oliveira, V. L., Garcia, E. G., Filho, J. P. A., Lima, V. E., Santos, H. N. G., Puga, F. R., & Almeida, W. F. (1991). Agrotóxicos riscos e prevenção (p. 130). Fundacentro: São Paulo.
Modesto K.A. (2009) Efeitos de dois herbicidas à base de glifosato para um peixe neotropical, com enfoque nos biomarcadores bioquímicos. Dissertação (Mestrado). Universidade Estadual de Londrina: Paraná, 69 p.
Moraes, B. S., Loro, V. L., Glusczak, L., Pretto, A., Menezes, C., Marchezan, E., & Machado, S. O. (2007). Effects of four rice herbicides on some metabolic and toxicology parameters of teleost fish (Leporinus obtusidens). Chemosphere, 68(8), 1597–1601.
Morsy, G. M., El-Ala, K. S. A., & Ali, A. A. (2016). Studies on fate and toxicity of nanoalumina in male albino rats: oxidative stress in the brain, liver and kidney. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 32(2), 200–214.
Moura, M. A. M., Franco, D. A. S., & Matallo, M. B. (2008). Impacto de herbicidas sobre os recursos hídricos. Revista Tecnologia & Inovação Agropecuária, 1, 142–153.
Navarro-Martín, L., Lanctôt, C., Jackman, P., Park, B. J., Doe, K., Paulid, B. D., & Trudeau, V. L. (2014). Effects of glyphosate-based herbicides on survival, development, growth and sex ratios of wood frogs (Lithobates sylvaticus) tadpoles. I: chronic laboratory exposures to VisionMax®. Aquatic Toxicology, 154, 278–290.
Nunes, A., Silva, A., & Soares, E. (2011). The use of hepatic and somatic indices and histological information to characterize the reproductive dynamics of Atlantic sardine Sardina pilchardus from the Portuguese coast. Marine and Coastal Fisheries: Management, and Ecosystem Science, 3, 127–144.
Nunes, B. S., Travasso, R., Gonçalves, F., & Castro, B. B. (2015). Biochemical and physiological modifications in tissues of Sardina pilchardus: spatial and temporal patterns as a baseline for biomonitoring studies. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 3, 1–14.
Oruç, E. Ö., & Usta, D. (2007). Evaluation of oxidative stress responses and neurotoxicity potential of diazinon in different tissues of Cyprinus carpio. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 23, 45–55.
Ossana, N. A., Castañé, P. M., & Salibián, A. (2013). Use of Lithobates catesbeianus tadpoles in a multiple biomarker approach for the assessment of water quality of the Reconquista River (Argentina). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 65(3), 486–497.
Paetow, L. J., McLaughlin, J. D., Pauli, B. D., & Marcogliese, D. J. (2013). Mortality of American bullfrog tadpoles Lithobates catesbeianus infected by Gyrodactylus jennyae and experimentally exposed to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health, 25(1), 15–26.
Paulino, M. G., Sakuragui, M. M., & Fernandes, M. (2012). Effects of atrazine on the gill cells and ionic balance in a neotropical fish, Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere, 86, 1–7.
Peakall, D. B. (1992). Animal biomarkers as pollution indicators (p. 291). London: Chapman & Hall.
Peres, F., & Moreira, J. C. (2003). É veneno ou é remédio? Agrotóxicos, saúde e ambiente (p. 384). Rio de Janeiro: Fiocruz.
Persch, T. S. P., Weimer, R. N., Freitas, B. S., & Oliveira, G. T. (2017). Metabolic parameters and oxidative balance in juvenile Rhamdia quelen exposed to rice paddy herbicides: Roundup®, Primoleo®, and Facet®. Chemosphere. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.092.
Rodrigues, N. R. & Almeida, F. S. (1998). Guia de herbicidas (pp. 137–142). 4th ed. Londrina: IAPAR.
Saygili, E. I., Konukoglu, D., Papila, S., & Aksay, T. (2003). Levels of plasma vitamin E, vitamin C, TBARS and cholesterol in male patients with colorectal tumors. Biochemistry (Moscow), 68(3), 325–328.
Silva, D. R. O., Avila, L. A., Agostinetto, D., Dal, M. T., Oliveira, E., Zanella, R., & Noldin, J. A. (2009). Monitoramento de agrotóxicos em águas superficiais de regiões orizícolas no sul do Brasil. Ciência Rural, 39, 2383–2389.
Sol, S. Y., Johnson, L. L., Boyd, D., Olson, O. P., Lomax, D. P., & Collier, T. K. (2008). Relationships between anthropogenic chemical contaminant exposure and associated changes in reproductive parameters in male English sole (Parophrys vetulus) collected from Hylebos Waterway, Puget Sound, Washington. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 55, 627–638.
Squadrito, G. L., Cueto, R., Splenser, A. E., Valavanidis, A., Zhang, H., Uppu, R. M., & Pryor, W. A. (2000). Reaction of uric acid with peroxynitrite and implications for the mechanism of neuroprotection by uric acid. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 376, 333–337.
Takada, Y., & Noguchi, T. (1983). The degradation of urate in liver peroxisomes. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 258(8), 4762–4764.
Tsangaris, C., Kormas, K., Strogyloudi, E., Hatzianestis, I., Neofitou, C., Andral, B., & Galgani, F. (2010). Multiple biomarkers of pollution effects in caged mussels on the Greek coastline. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C: Toxicology and Pharmacology, 151(3), 369–378.
Van der Oost, R., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. E. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13, 57–149.
Vazzoler, A. E. A. M. (1996). Biologia da reprodução de peixes teleósteos: teoria e prática (p. 196). Eduem: Maringá.
Vieira, M. I. (1993). Rã-touro gigante: características e reprodução (p. 80). São Paulo: Aquaroli Books.
Vitt, L. J., & Caldwell, J. P. (2009). Herpetology: an introductory biology of amphibians and reptiles (3rd ed.p. 697). London: Elsevier.
Wright, M. L., Guertin, C. J., Duffy, J. L., Szatkowski, M. C., Visconti, R. F., & Alves, C. D. (2003). Developmental and diel profiles of plasma corticosteroids in bullfrog: Rana catesbeiana. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A, 135, 585–595.
Yang, T. H., Lai, N. C., Graham, J. B., & Somero, G. N. (1992). Respiratory, blood, and heart enzymatic adaptations of Sebastolobus alascanus (Scorpaenidae: Teleostei) in the oxygen minimum zone: a comparative study. Biological Bulletin, 183, 490–499.
Yin, X., Jiang, S., Yu, J., Zhu, G., Wu, H., & Mao, C. (2014). Effects of spirotetramat on the acute toxicity, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation in Chinese toad (Bufo bufo gargarizans) tadpoles. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 37, 1229–1235.
Yoshikawa, T., & Naito, Y. (2002). What is oxidative stress? Journal of the Japan Medical Association, 124(11), 1549–1553.
Zanella, R., Primel, E. G., Machado, S. L. O., Gonçalves, F. F., & Marchezan, E. (2002). Monitoring of the herbicide clomazone in environmental water samples by solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Chromatographia, 55, 573–577.
Zanette, J., Monserrat, J. M., & Bianchini, A. (2015). Biochemical biomarkers in barnacles Balanus improvisus: pollution and seasonal effects. Marine Environmental Research, 103, 74–79.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Graduate Program in Zoology for the financial support provided. We also thank Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for awarding a grant to the first author and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for awarding a Level 2 Investigator grant to the corresponding author (process no. 307303/20128) during the course of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animals were transported in plastic bags to the Conservation Physiology laboratory of Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul (PUCRS), where all experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with an Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee authorization (permit no. 14/00384).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Lima Coltro, M., da Silva, P.R., Valgas, A.A.N. et al. Influence of the Herbicide Facet® on Corticosterone Levels, Plasma Metabolites, and Antioxidant System in the Liver and Muscle of American Bullfrog Tadpoles. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 241 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3404-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3404-7