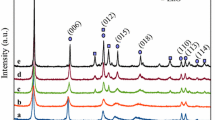
Abstract
Manganese-rich MnSAPO-34 molecular sieves were prepared by one-pot synthesis method for NO x abatement using the ammonia-selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR) technology and characterized using ICP, BET, XRD, FE-SEM, H2-TPR, NH3-TPD, XPS, and DR UV-Vis analyses. The experimental results indicate that the Mn content and chemical state, as well as the surface acidity, of the MnSAPO-34 molecular sieves significantly enhance their DeNO x efficiency at low temperatures (ca. 200–300 °C). The manganese-rich MnSAPO-34 was synthesized using a combination of triethylamine and diisopropylamine as the structural directing agents and high Mn loading (n(MnO)/n(P2O5) = 0.4). The resulting catalyst exhibits the highest activity among all of the samples with a NO x conversion value of nearly 95% and a N2 selectivity that is higher than 90% at 220–400 °C. In addition, this catalyst presents higher NO x conversion than the conventional V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts and other SAPO-based catalysts below 300 °C. Furthermore, the analytical results indicate that the manganese species in the catalyst are mainly in the form of a framework Mn(IV), which could play a significant role in the NH3-SCR process as the specific active species. The results suggest that controlling the types and content of the organic amine templates and variations in the surface acidity of the catalysts may significantly enhance the SCR activity at lower temperatures.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao B, Wang SX, Liu H, Xu JY, Fu K, Klimont Z, Hao JM, He KB, Cofala J, Amann M (2013) NO x emissions in China: historical trends and future perspectives. Atmos Chem Phys 13:9869–9897
Andonova S, Tamm S, Montreuil C, Lambert C, Olsson L (2016) The effect of iron loading and hydrothermal aging on one-pot synthesized Fe/SAPO-34 for ammonia SCR. Appl Catal B-Environ 180:775–787
Andreoli S, Deorsola FA, Galletti C, Pirone R (2015) Nanostructured MnOx catalysts for low-temperature NOx SCR. Chem Eng J 278:174–182
Balle P, Geiger B, Kureti S (2009) Selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 on Fe/HBEA zeolite catalysts in oxygen-rich exhaust. Appl Catal B-Environ 85:109–119
Bosch H, Jamssen F (1988) Formation and control of nitrogen oxide. Catal Today 2:369–379
Cao Y, Zou S, Lan L, Yang ZZ, Xu HD, Lin T, Gong MC, Chen YQ (2015) Promotional effect of Ce on Cu-SAPO-34 monolith catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia. J Mol Catal a-Chem 398:304–311
Chen F, Huang B-C, Yang Y-X, Liu X-Q, Yu C-L (2015) Synthesis, characterization and NH3-SCR activity of MnSAPO-34 molecular sieves. Acta Phys -Chim Sin 31:2375–2385
Chou B, Tsai J-L, Cheng S (2001) Cu-substituted molecular sieves as liquid phase oxidation catalysts. Micropor Mesopor Mat 48:309–317
Deka U, Lezcano-Gonzalez I, Warrender SJ, Picone AL, Wright PA, Weckhuysen BM, Beale AM (2013) Changing active sites in Cu-CHA catalysts: deNO(x) selectivity as a function of the preparation method. Micropor Mesopor Mat 166:144–152
Fan SK, Xue JJ, Yu T, Fan DQ, Hao T, Shen MQ, Li W (2013) The effect of synthesis methods on Cu species and active sites over Cu/SAPO-34 for NH3-SCR reaction. Catal Sci Technol 3:2357–2364
Fan WB, Schoonheydt RA, Weckhuysen BM (2000) Synthesis of Co-rich CoAPO-CHA molecular sieves in the presence of ethanol and caesium. Chem Commun:2249–2250
Fang C, Zhang DS, Cai SX, Zhang L, Huang L, Li HR, Maitarad P, Shi LY, Gao RH, Zhang JP (2013) Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over nanoflaky MnOx on carbon nanotubes in situ prepared via a chemical bath deposition route. Nanoscale 5:9199–9207
Frache A, Palella B, Cadoni M, Pirone R, Ciambelli P, Pastore HO, Marchese L (2002) Catalytic DeNO(x) activity of cobalt and copper ions in microporous MeALPO-34 and MeAPSO-34. Catal Today 75:359–365
Gao F, Walter ED, Washton NM, Szanyi J, Peden CHF (2013a) Synthesis and evaluation of Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts for ammonia selective catalytic reduction. 1. Aqueous solution ion exchange. ACS Catal 3:2083–2093
Gao RH, Zhang DS, Liu XG, Shi LY, Maitarad P, Li HR, Zhang JP, Cao WG (2013b) Enhanced catalytic performance of V2O5-WO3/Fe2O3/TiO2 microspheres for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Catal Sci Technol 3:191–199
Gao RH, Zhang DS, Maitarad P, Shi LY, Rungrotmongkol T, Li HR, Zhang JP, Cao WG (2013c) Morphology-dependent properties of MnOx/ZrO2 CeO2 nanostructures for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J Phys Chem C 117:10502–10511
Hartmann M, Kevan L (1999) Transition-metal ions in aluminophosphate and silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves: location, interaction with adsorbates and catalytic properties. Chem Rev 99:635–664
Heck RM (1999) Catalytic abatement of nitrogen oxides-stationary applications. Catal Today 53:519–523
Kang M (2000) Effect of cobalt incorporated into the framework of SAPO-34 (CoAPSO-34s) on NO removal. J Mol Catal a-Chem 161:115–123
Kwak JH, Tonkyn RG, Kim DH, Szanyi J, Peden CH (2010) Excellent activity and selectivity of Cu-SSZ-13 in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH 3. J Catal 275:187–190
Li JH, Chang HZ, Ma L, Hao JM, Yang RT (2011) Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts—a review. Catal Today 175:147–156
Lietti L, Forzatti P, Berti F (1996) Role of the redox properties in the SCR of NO by NH3 over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts. Catal Lett 41:35–39
Lok BM, Messina CA, Patton RL, Gajek RT, Cannan TR, Flanigen EM (1984) Silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves: another new class of microporous crystalline inorganic solids. J Am Chem Soc 106:6092–6093
Long RQ, Yang RT (2001) Fe-ZSM-5 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: a comparative study of different preparation techniques. Catal Lett 74:201–205
Martinez-Franco R, Moliner M, Franch C, Kustov A, Corma A (2012) Rational direct synthesis methodology of very active and hydrothermally stable Cu-SAPO-34 molecular sieves for the SCR of NOx. Appl Catal B-Environ 127:273–280
Martinez-Franco R, Moliner M, Concepcion P, Thogersen JR, Corma A (2014) Synthesis, characterization and reactivity of high hydrothermally stable Cu-SAPO-34 materials prepared by “one-pot” processes. J Catal 314:73–82
Nova I, Lietti L, Casagrande L, Dall’Acqua L, Giamello E, Forzatti P (1998) Characterization and reactivity of TiO2-supported MoO3 De-No-x SCR catalysts. Appl Catal B-Environ 17:245–258
Pan S, Luo H, Li L, Wei Z, Huang B (2013) H2O and SO2 deactivation mechanism of MnOx/MWCNTs for low-temperature SCR of NOx with NH3. J Mol Catal A Chem 377:154–161
Pappas DK, Boningari T, Boolchand P, Smirniotis PG (2016) Novel manganese oxide confined interweaved titania nanotubes for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx by NH 3. J Catal 334:1–13
Qi GS, Yang RT, Chang R (2003) Low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over USY-supported manganese oxide-based catalysts. Catal Lett 87:67–71
Rajić N, Stojaković D, Hoçevar S, Kaučič V (1993) On the possibility of incorporating Mn (II) and Cr (III) in SAPO-34 in the presence of isopropylamine as a template. Zeolites 13:384–387
Sato S, Yu-u Y, Yahiro H, Mizuno N, Iwamoto M (1991) Cu-ZSM-5 zeolite as highly active catalyst for removal of nitrogen monoxide from emission of diesel engines. Appl Catal 70:L1–L5
Sena FC, de Souza BF, de Almeida NC, Cardoso JS, Fernandes LD (2011) Influence of framework composition over SAPO-34 and MeAPSO-34 acidity. Appl Catal a-Gen 406:59–62
Turrina A, Eschenroeder ECV, Bode BE, Collier JE, Apperley DC, Cox PA, Casci JL, Wright PA (2015) Understanding the structure directing action of copper-polyamine complexes in the direct synthesis of Cu-SAPO-34 and Cu-SAPO-18 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Micropor Mesopor Mat 215:154–167
Wang L, Huang B, Su Y, Zhou G, Wang K, Luo H, Ye D (2012a) Manganese oxides supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: catalytic activity and characterization. Chem Eng J 192:232–241
Wang L, Li W, Qi GS, Weng D (2012b) Location and nature of Cu species in Cu/SAPO-34 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J Catal 289:21–29
Wang P, Zhao H, Sun H, Yu H, Quan X (2014) Porous metal–organic framework MIL-100 (Fe) as an efficient catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH 3. RSC Adv 4:48912–48919
Weckhuysen BM, Rao RR, Martens JA, Schoonheydt RA (1999) Transition metal ions in microporous crystalline aluminophosphates: isomorphous substitution. Eur J Inorg Chem 1999:565–577
Wei YX, He YL, Zhang DH, Xu L, Meng SH, Liu ZM, Su BL (2006) Study of Mn incorporation into SAPO framework: synthesis, characterization and catalysis in chloromethane conversion to light olefins. Micropor Mesopor Mat 90:188–197
Wei YX, Zhang DZ, Xu L, Chang FX, He YL, Meng SH, Su BL, Liu ZM (2008) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance of metal-incorporated SAPO-34 for chloromethane transformation to light olefins. Catal Today 131:262–269
Wijayanti K, Andonova S, Kumar A, Li JH, Kamasamudram K, Currier NW, Yezerets A, Olsson L (2015) Impact of sulfur oxide on NH3-SCR over Cu-SAPO-34. Appl Catal B-Environ 166:568–579
Wu XD, Liu SA, Weng DA, Lin F, Ran R (2011) MnOx-CeO2-Al2O3 mixed oxides for soot oxidation: activity and thermal stability. J Hazard Mater 187:283–290
Xie LJ, Liu FD, Ren LM, Shi XY, Xiao FS, He H (2014) Excellent performance of one-pot synthesized Cu-SSZ-13 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Environ Sci Technol 48:566–572
Xu L, Du A, Wei Y, Wang Y, Yu Z, He Y, Zhang X, Liu Z (2008) Synthesis of SAPO-34 with only Si (4Al) species: effect of Si contents on Si incorporation mechanism and Si coordination environment of SAPO-34. Micropor Mesopor Mat 115:332–337
Yan CD, Cheng H, Yuan ZS, Wang SD (2015) The role of isolated Cu2+ location in structural stability of Cu-modified SAPO-34 in NH3-SCR of NO. Environ Technol 36:169–177
Yang S, Qi F, Xiong S, Dang H, Liao Y, Wong PK, Li J (2016) MnO x supported on Fe–Ti spinel: a novel Mn based low temperature SCR catalyst with a high N 2 selectivity. Appl Catal B Environ 181:570–580
Yu T, Wang J, Shen MQ, Li W (2013) NH3-SCR over Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts with various acid contents and low Cu loading. Catal Sci Technol 3:3234–3241
Yu T, Fan DQ, Hao T, Wang J, Shen MQ, Li W (2014) The effect of various templates on the NH3-SCR activities over Cu/SAPO-34 catalysts. Chem Eng J 243:159–168
Zhang L, Wang D, Liu Y, Kamasamudram K, Li JH, Epling W (2014) SO2 poisoning impact on the NH3-SCR reaction over a commercial Cu-SAPO-34 SCR catalyst. Appl Catal B-Environ 156:371–377
Zhang L, Li LL, Cao Y, Yao XJ, Ge CY, Gao F, Deng Y, Tang CJ, Dong L (2015) Getting insight into the influence of SO2 on TiO2/CeO2 for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Appl Catal B-Environ 165:589–598
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Song Z, Ning P, Li H, Liu X (2016) A novel and environmentally friendly SO 4 2−/CeO 2 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH 3. J Ind Eng Chem 34:165–171
Zhao L, Li C, Zhang X, Zeng G, Zhang J (2016) Oxidation of elemental mercury by modified spent TiO2-based SCR-DeNOx catalysts in simulated coal-fired flue gas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1471–1481
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC-51478191) and Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (2014A020216003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 108 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Chen, F., Dong, L. et al. Manganese-rich MnSAPO-34 molecular sieves as an efficient catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3: one-pot synthesis, catalytic performance, and characterization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 7499–7510 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8375-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8375-0