Abstract
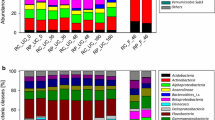
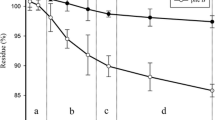
Benzo(a)pyrene degradation was compared in soil that was either composted, incubated at a constant temperature of 22 °C, or incubated under a temperature regime typical of a composting process. After 84 days, significantly more (61%) benzo(a)pyrene was removed from composted soil compared to soils incubated at a constant temperature (29%) or at composting temperatures (46%). Molecular fingerprinting approaches indicated that in composted soils, bacterial community changes were driven by both temperature and organic amendment, while fungal community changes were primarily driven by temperature. Next-generation sequencing data revealed that the bacterial community in composted soil was dominated by Actinobacteria (order Actinomycetales), Firmicutes (class Bacilli), and Proteobacteria (classes Gammaproteobacteria and Alphaproteobacteria), regardless of whether benzo(a)pyrene was present or not. The relative abundance of unclassified Actinomycetales (Actinobacteria) was significantly higher in composted soil when degradation was occurring, indicating a potential role for these organisms in benzo(a)pyrene metabolism. This study provides baseline data for employing straw-based composting strategies for the removal of high molecular weight PAHs from soil and contributes to the knowledge of how microbial communities respond to incubation conditions and pollutant degradation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annweiler E, Richnow HH, Antranikian G, Hebenbrock S, Garms C, Franke S, Francke W, Michaelis W (2000) Naphthalene degradation and incorporation of naphthalene-derived carbon into biomass by the thermophilic Bacillus thermoleovorans. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:518–523
Antizar-Ladislao B, Russell NJ (2006) In-vessel composting as a sustainable bioremediation technology of contaminated soils and waste. In: Cato MA (ed) Environmental research trends. Nova Science Publisher, New York, pp. 19–61
Alonso-Gutiérrez J, Albaigés J, Jiminéz N, Viñas M, Solanas AM, Novoa B (2009) Bacterial communities from shoreline environments (Costa da Morte, Northwestern Spain) affected by the prestige oil spill. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(11):3407–3418
Bogan BW, Schoenike B, Lamar RT, Cullen D (1996) Manganese peroxidase mRNA and enzyme activity levels during bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soil with Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2381–2386
Boonchan S, Britz ML, Stanley GA (2000) Degradation and mineralization of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by defined fungal-bacterial cocultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(3):1007–1019
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(Supplement 1):4516–4522
Cébron A, Beguiristain T, Bongoua-Devisme J, Denonfoux J, Faure P, Lorgeoux C, Ouvrard S, Parisot N, Peyret P, Leyval C (2015) Impact of clay mineral, wood sawdust or root organic matter on the bacterial and fungal community structures in two aged PAH-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:13724–13738
Cébron A, Louvel B, Faure P, France-Lanord C, Chen Y, Murrell JC, Leyval C (2011) Root exudates modify bacterial diversity of phenanthrene degraders in PAH-polluted soil but not phenanthrene degradation rates. Environ Microbiol 13(3):722–736
Cébron A, Norini MP, Beguiristain T, Leyval C (2008) Real-time PCR quantification of PAH-ring hydroxylating dioxygenase (PAH-RHDalpha) genes from Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria in soil and sediment samples. J Microbiol Methods 73(2):148–159
Coover MP, Sims RC (1987) The effetc of temperature on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon persistence in un unacclimated agricultural soil. Hazardous Waste and Hazard Mater 4:69–82
Crampon M, Bureau F, Akpa-Vinceslas M, Bodilis J, Machour N, Le Derf F, Portet-Koltalo F (2014) Correlations between PAH bioavailability, degrading bacteria, and soil characteristics during PAH biodegradation in five diffusely contaminated dissimilar soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(13):8133–8145
de Gannes V, Eudoxie G, Hickey WJ (2013) Prokaryotic successions and diversity in composts as revealed by 454-pyrosequencing. Bioresour Technol 133:573–580
de Menezes A, Clipson N, Doyle E (2012) Comparative metatranscriptomics reveals widespread community responses during phenanthrene degradation in soil. Environ Microbiol 14(9):2577–2588
Eida MF, Nagaoka T, Wasaki J, Kouno K (2012) Isolation and characterization of cellulose-decomposing bacteria inhabiting sawdust and coffee residue composts. Microbes Environ 27(3):226–233
Feitkenhauer H, Müller R, Märkl H (2003) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and long chain alkanes at 60–70°C by Thermus and Bacillus spp. Biodegradation 14:367–372
Gardes M, Bruns TD (1993) ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes—application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol Ecol 2:113–118
Griffiths RI, Whiteley AS, O’Donnell AG, Bailey MJ (2000) Rapid method for coextraction of DNA and RNA from natural environments for analsis of ribosomal DNA- and rRNA-based microbial community composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5488–5491
Harms H, Bosma TNP (1997) Mass transfer limitation of microbial growth and pollutant degradation. J Ind Microbiol 18:97–105
Hatayama K, Shoun H, Ueda Y, Nakamura A (2006) Tuberibacillus calidus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a compost pile and reclassification of Bacillus naganoensis Tomimura et al. 1990 as Pullulanibacillus naganoensis gen. nov., comb. nov. and Bacillus laevolacticus Andersch et al. 1994 as Sporolactobacillus laevolacticus comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2545–2551
Herlemann DPR, Lundin D, Labrenz M, Jürgens K, Zheng Z, Aspeborg H, Andersson AF (2013) Metagenomic de novo assembly of an aquatic representative of the verrucomicrobial class Spartobacteria. MBio 4(3):e00569–e00512
Hiller E, Jurkovič Ľ, Bartal M (2008) Effect of temperature on the distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil and sediment. Soil Water Res 3(4):231–240
Iwai S, Johnson TA, Chai B, Hashsham SA, Tiedje JE (2011) Comparison of the specificities and efficacies of primers for aromatic dioxygenase gene analysis of environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3551–3557
Jones RT, Robeson MS, Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. The ISME J 3(4):442–453
Juhasz AL, Naidu R (2000) Bioremediation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review of the microbial degradation of benzo(a)pyrene. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 45(1):57–88
Kanaly RA, Harayama S (2010) Advances in the field of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation by bacteria. Microb Biotechnol 3(2):136–164
Koukkou A-I, Vandera E (2011) Hydrocarbon-degrading soil bacteria: current research. In: Koukkou A-I (ed) Microbial bioremediation of non-metals: current research. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, pp. 93–117
Kozich JJ, Westcott SL, Baxter NT, Highlander SK, Schloss PD (2013) Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(17):5112–5120
Lane DJ, Pace B, Olsen GJ, Stahl DA, Sogin ML, Pace NR (1985) Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 82:6955–6959
Liu WT, Marsh TL, Cheng H, Forney LJ (1997) Characterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4516–4522
Liu ZZ, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2008) Accurate taxonomy assignments from 16S rRNA sequences produced by highly parallel pyrosequencers. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e120
Liu H, Wang C, Zhang Z, Wu W, Hao Z, Sun H (2011) Isolation of highly-effective benzo[a]pyrene degrading strain and its degradation capacity. Environmental Science 32:2696–2702
Louvel B, Cébron A, Leyval C (2011) Root exudates affect phenanthrene biodegradation, bacterial community and functional gene expression in sand microcosms. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65(7):947–953
Mahmoudi N, Slater GF, Juhasz AL (2013) Assessing limitations for PAH biodegradation in long-term contaminated soils using bioaccessibility assays. Water, Air, Soil Pollution 224:1–11
Margesin R, Schinner F (2001) Biodegradation and bioremediation of hydrocarbons in extreme environments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:650–663
Martin F, Malagnoux L, Violet F, Jakoncic J, Jouanneau Y (2013) Diversity and catalytic potential of PAH-specific ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases from a hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5125–5135
Messina E, Danaro R, Crisafi F, Smedile F, Capello S, Genovese M, Genovese L, Giuliano L, Russo D, Ferrer M, Golyshin P, Yakimov MM (2016) Genome sequence of obligate marine polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-degrading bacterium Cycloclasticus sp. 78-ME, isolated from petroleum deposits of the sunken tanker Amoco Milford Haven, Mediterranean Sea. Mar Genomics 25:11–13
Muckian L, Grant R, Doyle E, Clipson N (2007) Bacterial community structure in soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 68(8):1535–1541
Müller R, Antranikian G, Maloney S, Sharp R (1998) Thermophilic degradation of environmental pollutants. In: Antranikian G (ed) Biotechnology of extremophiles. (Advances in biochemical engineering/bio-technology, vol 61). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp. 155–169
Peng J, Zhang Y, Su J, Qiu Q, Jia Z, Zhu YG (2013) Bacterial communities predominant in the degradation of 13C(4)-4,5,9,10-pyrene during composting. Bioresour Technol 143:608–614
Peng JJ, Cai C, Qiao M, Li H, Zhu YG (2010) Dynamic changes in functional gene copy numbers and microbial communities during degradation of pyrene in soils. Environ Pollut 158(9):2872–2879
Rajapaksha R, Tobor-Kapłon M, Bååth E (2004) Metal toxicity affects fungal and bacterial activities in soil differently. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(5):2966–2973
Reddy K and Adams J (2015) Sustainable remediation of contaminated sites. Momentum Press
Ren G, Ren W, Teng Y, Li Z (2015) Evident bacterial community changes but only slight degradation when polluted with pyrene in a red soil. Front Microbiol 6:22. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00022
Rentz JA, Alvarez PJJ, Schnoor JL (2008) Benzo(a)pyrene degradation by Sphingomonas yanoikuyae JAR02. Environ Pollut 151(3):669–677
Riah-Anglet W, Trinsoutrot-Gattin I, Martin-Laurent F, Laroche-Ajzenberg E, Norini M-P, Latour X, Laval K (2015) Soil microbial community structure and function relationships: a heat stress experiment. Appl Soil Ecol 86:121–130
Rousk J, Bååth E (2007) Fungal and bacterial growth in soil with plant materials of different C/N ratios. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62(3):258–267
Salvo VS, Gallizia I, Moreno M, Fabiano M (2005) Fungal communities in PAH-impacted sediments of Genoa-Voltri Harbour (NW Mediterranean, Italy). Mar Pollut Bull 50(5):553–559
Sawulski P, Clipson N, Doyle E (2014) Effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on microbial community structure and PAH ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase gene abundance in soil. Biodegradation 25(6):835–847
Scallan U, Liliensiek A, Clipson N, Connolly J (2008) RiboSort: a program for automated data preparation and exploratory analysis of microbial community fingerprints. Mol Ecol Resour 8(1):95–98
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541
Sharp CE, Brady AL, Sharp GH, Grasby SE, Stott MB, Dunfield PF (2014) Humboldt’s spa: microbial diversity is controlled by temperature in geothermal environments. The ISME J 8(6):1166–1174
Song M, Luo C, Jiang L, Zhang D, Wang Y, Zhang G (2015) Identification of benzo(a)pyrene-metabolizing bacteria in forest soils by using DNA-based stable-isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(21):7368–7376
Storey S, Ashaari MM, McCabe G, Harty M, Dempsey R, Doyle O, Clipson N, Doyle EM (2014) Microbial community structure during fluoranthene degradation in the presence of plants. J Appl Microbiol 117(1):74–84
Storey S, Chualain DN, Doyle O, Clipson N, Doyle E (2015) Comparison of bacterial succession in green waste composts amended with inorganic fertiliser and wastewater treatment plant sludge. Bioresour Technol 179:71–77
Sul WJ, Asuming-Brempong S, Wang Q, Tourlousse DM, Penton CR, Deng Y, Rodrigues JL, Adiku SG, Jones JW, Zhou J (2013) Tropical agricultural land management influences on soil microbial communities through its effect on soil organic carbon. Soil Biol Biochem 65:33–38
Vidali M (2001) Bioremediation: an overview. Pure Appl Chem 73(7):1163–1172
Vila J, Tauler M, Grifoll M (2015) Bacterial PAH degradation in marine and terrestrial habitats. Curr Opin Biotechnol 33:95–102
Viñas M, Sabaté J, Espuny MJ, Solanas AM (2005) Bacterial community dynamics and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation during bioremediation of heavily creosote-contaminated soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):7008–7018
Viamajala S, Peyton BM, Richards LA, Petersen JN (2007) Solubilization, solution equilibria, and biodegradation of PAH’s under thermophilic conditions. Chemosphere 66:1094–1106
Wickle W (2000) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil—a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163:229–248
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phyliogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gefland DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 315–322
Whitman W, Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse HJ, Trujillo M, Ludwig W, K-i S, Parte A (2012) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology: volume 5: the Actinobacteria. Springer, New York
Zeinali M, Vossoughi M, Ardestani SK (2007) Characterization of a moderate thermophilic Nocardia species able to grow on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:622–628
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the UCD China Scholarship Scheme, the SLAB scholarship program of the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education and the International Islamic University Malaysia, and the Ireland Wales Programme 2007–2013 (GIFT project). The authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Ray O’Haire from UCD School of Agriculture and Food Science for his technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Temperature regime used (GIF 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, F., Storey, S., Ashaari, M.M. et al. Benzo(a)pyrene degradation and microbial community responses in composted soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 5404–5414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8251-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8251-3