Abstract
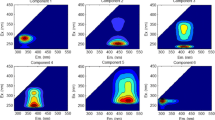
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) in wastewater can be characterized using fluorescence excitation-emission matrix and parallel factor (EEM-PARAFAC) analysis. Wastewater from animal farms or pharmaceutical plants usually contains high concentration of antibiotics. In this study, the quenching effect of antibiotics on the typical components of DOM was explored using fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC analysis. Four antibiotics (roxarsone, sulfaquinoxaline sodium, oxytetracycline, and erythromycin) at the concentration of 0.5∼4.0 mg/L and three typical components of DOM (tyrosine, tryptophan, and humic acid) were selected. Fluorescence quenching effects were observed with the addition of antibiotics. Among these four antibiotics, roxarsone (2.9∼20.2 %), sulfaquinoxaline sodium (0∼32.0 %), and oxytetracycline (0∼41.8 %) led to a stronger quenching effect than erythromycin (0∼8.0 %). From the side of DOM, tyrosine and tryptophan (0.5∼41.8 %) exhibited a similar quenching effect, but they were higher than humic acids (0∼20.2 %) at the same concentration of antibiotics. For humic acid, a significant quenching effect was observed only with the addition of roxarsone. This might be the first report about the fluorescence quenching effect caused by antibiotics. The results from this study confirmed the interference of antibiotics on the fluorescence intensity of the main components of DOM and highlighted the importance of correcting fluorescence data in the wastewater containing antibiotics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aristilde L, Sposito G (2010) Binding of ciprofloxacin by humic substances: a molecular dynamics study. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:90–98
Aristilde L, Sposito G (2013) Complexes of the antimicrobial ciprofloxacin with soil, peat, and aquatic humic substances. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:1467–1478
Baghoth SA, Sharma SK, Amy GL (2011) Tracking natural organic matter (NOM) in a drinking water treatment plant using fluorescence excitation-emission matrices and PARAFAC. Water Res 45:797–809
Baker A (2005) Thermal fluorescence quenching properties of dissolved organic matter. Water Res 39:4405–4412
Baker A, Elliott S, Lead JR (2007) Effects of filtration and pH perturbation on freshwater organic matter fluorescence. Chemosphere 67:2035–2043
Bro R (1997) PARAFAC. Tutorial and applications. Chemometr Intell Lab 38:149–171
Bro R, Kiers HAL (2003) A new efficient method for determining the number of components in PARAFAC models. J Chemometr 17:274–286
Carstea EM, Baker A, Bieroza M, Reynolds D (2010) Continuous fluorescence excitation-emission matrix monitoring of river organic matter. Water Res 44:5356–5366
Carstea EM, Baker A, Bieroza M, Reynolds DM, Bridgeman J (2014) Characterisation of dissolved organic matter fluorescence properties by PARAFAC analysis and thermal quenching. Water Res 61:152–161
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:5701–5710
Coble PG, Green SA, Blough NV, Gagosian RB (1990) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in the Black Sea by fluorescence spectroscopy. Nature 348:432–435
Cory RM, McKnight DM (2005) Fluorescence spectroscopy reveals ubiquitous presence of oxidized and reduced quinones in dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 39:8142–8149
Diaz-Cruz MS, de Alda MJL, Barcelo D (2003) Environmental behavior and analysis of veterinary and human drugs in soils, sediments and sludge. Trac-Trend Anal Chem 22:340–351
Du LF, Liu WK (2012) Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 32:309–327
Esteves da Silva JC, Machado AA, Oliveira CJ, Pinto MS (1998) Fluorescence quenching of anthropogenic fulvic acids by Cu(II), Fe(III) and UO(2)(2+). Talanta 45:1155–65
Fellman JB, Miller MP, Cory RM, D'Amore DV, White D (2009) Characterizing dissolved organic matter using PARAFAC modeling of fluorescence spectroscopy: a comparison of two models. Environ Sci Technol 43:6228–6234
Fick J, Soderstrom H, Lindberg RH, Phan C, Tysklind M, Larsson DGJ (2009) Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:2522–2527
Garbarino JR, Bednar AJ, Rutherford DW, Beyer RS, Wershaw RL (2003) Environmental fate of roxarsone in poultry litter. I. Degradation of roxarsone during composting. Environ Sci Technol 37:1509–1514
Gentry-Shields J, Wang A, Cory RM, Stewart JR (2013) Determination of specific types and relative levels of QPCR inhibitors in environmental water samples using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy and PARAFAC. Water Res 47:3467–3476
Henderson RK, Baker A, Murphy KR, Hamblya A, Stuetz RM, Khan SJ (2009) Fluorescence as a potential monitoring tool for recycled water systems: a review. Water Res 43:863–881
Hernandez D, Plaza C, Senesi N, Polo A (2006) Detection of copper(II) and zinc(II) binding to humic acids from pig slurry and amended soils by fluorescence spectroscopy. Environ Pollut 143:212–220
Hirsch R, Ternes T, Haberer K, Kratz KL (1999) Occurrence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 225:109–18
Hu ZH, Liu YL, Chen GW, Gui XY, Chen TH, Zhan XM (2011) Characterization of organic matter degradation during composting of manure-straw mixtures spiked with tetracyclines. Bioresour Technol 102:7329–7334
Ishii SKL, Boyer TH (2012) Behavior of reoccurring PARAFAC components in fluorescent dissolved organic matter in natural and engineered systems: a critical review. Environ Sci Technol 46:2006–2017
Larsson DGJ, de Pedro C, Paxeus N (2007) Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J Hazard Mater 148:751–755
Li D, Yang M, Hu J, Ren L, Zhang Y, Li K (2008a) Determination and fate of oxytetracycline and related compounds in oxytetracycline production wastewater and the receiving river. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:80–86
Li WH, Sheng GP, Liu XW, Yu HQ (2008b) Characterizing the extracellular and intracellular fluorescent products of activated sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res 42:3173–3181
Li WT, Chen SY, Xu ZX, Li Y, Shuang CD, Li AM (2014) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in municipal wastewater using fluorescence PARAFAC analysis and chromatography multi-excitation/emission scan: a comparative study. Environ Sci Technol 48:2603–2609
Murphy KR, Hambly A, Singh S, Henderson RK, Baker A, Stuetz R, Khan SJ (2011) organic matter fluorescence in municipal water recycling schemes: toward a unified PARAFAC model. Environ Sci Technol 45:2909–2916
Nebbioso A, Piccolo A (2013) Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM): a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:109–124
Ni BJ, Fang F, Xie WM, Sun M, Sheng GP, Li WH, Yu HQ (2009) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances produced by mixed microorganisms in activated sludge with gel-permeating chromatography, excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy measurement and kinetic modeling. Water Res 43:1350–1358
Persson T, Wedborg M (2001) Multivariate evaluation of the fluorescence of aquatic organic matter. Anal Chim Acta 434:179–192
Plaza C, Brunetti G, Senesi N, Polo A (2006a) Fluorescence characterization of metal ion-humic acid interactions in soils amended with composted municipal solid wastes. Anal Bioanal Chem 386:2133–2140
Plaza C, Brunetti G, Senesi N, Polo A (2006b) Molecular and quantitative analysis of metal ion binding to humic acids from sewage sludge and sludge-amended soils by fluorescence spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 40:917–923
Provenzano MR, D'Orazio V, Jerzykiewicz M, Senesi N (2004) Fluorescence behaviour of Zn and Ni complexes of humic acids from different sources. Chemosphere 55:885–892
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall ABA (2006) A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65:725–759
Sheng GP, Yu HQ (2006) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res 40:1233–1239
Shi L, Wang W, Yuan SJ, Hu ZH (2014) Electrochemical stimulation of microbial roxarsone degradation under anaerobic conditions. Environ Sci Technol 48:7951–7958
Spencer RGM, Bolton L, Baker A (2007) Freeze/thaw and pH effects on freshwater dissolved organic matter fluorescence and absorbance properties from a number of UK locations. Water Res 41:2941–2950
Stedmon CA, Bro R (2008) Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial. Limnol Oceanogr-Meth 6:572–579
Stedmon CA, Markager S, Bro R (2003) Tracing dissolved organic matter in aquatic environments using a new approach to fluorescence spectroscopy. Mar Chem 82:239–254
Wu J, Zhang H, He PJ, Shao LM (2011) Insight into the heavy metal binding potential of dissolved organic matter in MSW leachate using EEM quenching combined with PARAFAC analysis. Water Res 45:1711–1719
Yamashita Y, Jaffe R (2008) Characterizing the interactions between trace metals and dissolved organic matter using excitation-emission matrix and parallel factor analysis. Environ Sci Technol 42:7374–7379
Yamashita Y, Tanoue E (2003) Chemical characterization of protein-like fluorophores in DOM in relation to aromatic amino acids. Mar Chem 82:255–271
Yan MQ, Fu QW, Li DC, Gao GF, Wang DS (2013) Study of the pH influence on the optical properties of dissolved organic matter using fluorescence excitation-emission matrix and parallel factor analysis. J Lumin 142:103–109
Zhang FF, Harir M, Moritz F, Zhang J, Witting M, Wu Y, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Fekete A, Gaspar A, Hertkorn N (2014) Molecular and structural characterization of dissolved organic matter during and post cyanobacterial bloom in Taihu by combination of NMR spectroscopy and FTICR mass spectrometry. Water Res 57:280–294
Zhao J, Nelson DJ (2005) Fluorescence study of the interaction of Suwannee River fulvic acid with metal ions and Al3 + -metal ion competition. J Inorg Biochem 99:383–396
Acknowledgments
This research was partly supported by the Key Special Program on the S&T for the Pollution Control (2012ZX07103-001), the NSFC (51578205, 51538012, 51378017, 51479046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Céline Guéguen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, PF., Hu, ZH., Yu, HQ. et al. Fluorescence quenching effects of antibiotics on the main components of dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 5667–5675 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5800-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5800-0