Abstract
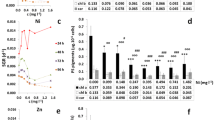
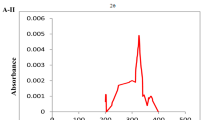
Effects of various concentrations of Cu2+ and Zn2+ (0.0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, or 1.0 mg/L) on the growth, malondialdehyde (MDA), the intracellular calcium, and physiological characteristics of green algae, Cladophora, were investigated. Low Zn2+ concentrations accelerated the growth of Cladophora, whereas Zn2+ concentration increases to 0.25 mg/L inhibited its growth. Cu2+ greatly influences Cladophora growth. The photosynthesis of Cladophora decreased under Zn2+ and Cu2+ stress. Cu2+ and Zn2+ treatment affected the content of total soluble sugar in Cladophora and has small increases in its protein content. Zn2+ induced the intracellular calcium release, and copper induced the intracellular calcium increases in Cladophora. Exposure to Cu2+ and Zn2+ induces MDA in Cladophora. The stress concent of Cu2+ was strictly correlated with the total soluble sugar content, Chla+Chlb, and MDA in Cladophora, and the stress concent of Zn2+ was strictly correlated with the relative growth rate (RGR) and MDA of Cladophora.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts polyphenoloxidase in beta vulgaris. J Plant Physiol 24(1):1–15
Babu MY, Palanikumar L, Nagarani N, Devi VJ, Kumar SR, Ramakritinan CM, Kumaraguru AK (2014) Cadmium and copper toxicity in three marine macroalgae:evaluation of the biochemical responses and DNA damage. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9604–9616
Balamurugan K, Schaffner W (2006) Copper homeostasis in eukaryotes: teetering on a tightrope. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763(7):737–746
Batistič O, Kudla J (2010) Calcium: not just another ion. Cell Bio Met Nutr 17:17–54
Boyd RS (2010) Heavy metal pollutants and chemical ecology: exploring new frontiers. J Chem Ecol 36(1):46–58
Cao DJ, Shi XD, Li H, Xie PP, Zhang HM, Deng JW, Liang YG (2015) Effects of lead on tolerance, bioaccumulation, and antioxidative defense system of green algae, Cladophora. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 112:231–237
Dodds WK, Gudder DA (1992) The ecology of Cladophora. J Phycol 28(4):415–427
González A, María de los Ángeles C, Mellado M, Cabello S, Márquez S, Morales B, Moenne A (2012) Copper-induced intracellular calcium release requires extracellular calcium entry and activation of L-type voltage-dependent calcium channels in Ulva compressa. Plant Signal Behav 7(7):728–732
Han T, Kang SH, Park JS et al (2008) Physiological responses of Ulvapertusa and U. armorican to copper exposure. Aquat Toxicol 86:176–184
Koutsogiannaki S, Evangelinos N, Koliakos G, Kaloyianni M (2006) Cytotoxic mechanisms of Zn2+ and Cd2+ involve Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE) activation by ROS. Aquat Toxicol 78(4):315–324
Lage OM, Sansonetty F, O’Connor JE, Parente AM (2001) Flow cytometric analysis of chronic and acute toxicity of copper(II) on the marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. Cytometry 44(3):226–235
Lelong A, Jolley DF, Soudant P, Hegaret H (2012) Impact of copper exposure on Pseudo-nitzschia spp. physiology and domoic acid production. Aquat Toxicol 118–119:37–47
Levy JL, Stauber JL, Jolley DF (2007) Sensitivity of marine microalgae to copper:the effect of biotic factors on copper adsorption and toxicity. Sci Total Environ 387(1–3):141–154
Li Y, Zheng YY, Qian JX, Chen XM, Shen ZL, Tao LP, Li HX, Qin HH, Li M, Shen H (2012) Preventive effects of zinc against psychological stress-induced iron dyshomeostasis, erythropoiesis inhibition, and oxidative stress status in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 147:285–291
Liu YJ, Zhao ZG, Si J, Di CX, Han J, An LZ (2009) Brassinosteroids alleviate chilling-induced oxidative damage by enhancing antioxidant defense system in suspension cultured cells of Chorispora bungeana. J Plant Growth Regul 59(3):207–214
Liu D, Chen JR, Mahmood Q, Li S, Wu JS, Ye ZQ, Peng DL, Yan WB, Lu KP (2014) Effect of Zn toxicity on root morphology, ultrastructure, and the ability to accumulate Zn in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13615–13624
Lu YJ, Jiang AL, Dou BR, Wang C, Wang CH (2010) Effect of Cd(II) and Zn(II) on growth and biochemical composition of alga Nitzschia closterium. J Dalian Fish Univ 25(2):178–182
Maksymiec W (2007) Signaling responses in plants to heavy metal stress. Acta Physiol Plant 29(3):177–187
Mazumdar K, Das S (2015) Phytoremediation of Pb, Zn, Fe, and Mg with 25 wetland plant species from a paper mill contaminated site in North East India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:701–710
McCready RM, Guggolz J, Silviera V, Owens HS (1950) Determination of starch and amylose in vegetables. Anal Chem 22(9):1156–1158
Ming C, Huifeng W, Xiaoli L, Jianmin Z, Xuan W, Jiasen L, Lin H (2012) Effects of heavy metals on the expression of a zinc-inducible metallothionein-III gene and antioxidant enzyme activities in Crassostrea gigas. Ecotoxicology 21(7):1928–1936
Mota R, Pereira SB, Meazzini M, Fernandes R, Santos A, Evans CA, Philippis RD, Wright PC, Tamagnini P (2015) Effects of heavy metals on Cyanothece sp. CCY 0110 growth, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) production, ultrastructure and protein profiles. J Proteomics 120:75–94
Nugroho AP, Frank H (2011) Producing Cu-loaded algae for feeding experiments:effects of copper on Parachlorella kessleri. Toxicol Environ Chem 93(3):537–548
Peers G, Price NM (2006) Copper-containing plastocyanin used for electron transport by an oceanic diatom. Nature 441(7091):341–344
Perales-Vela HV, Gonzalez-Moreno S, Montes-Horcasitas C, Cañizares-Villanueva RO (2007) Growth, photosynthetic and respiratory responses to sub-lethal copper concentrations in Scenedesmus incrassatulus (Chlorophyceae). Chemosphere 67(11):2274–2281
Raven JA, Evans MCW, Korb RE (1999) The role of trace metals in photosynthetic electron transport in O2-evolving organisms. Photosynth Res 60(2–3):111–149
Shahbaz M, Tseng MH, Stuiver CEE, Koralewska A, Posthumus FS, Venema JH, Parmar S, Schat H, Hawkesford MJ, Kok LJD (2010) Copper exposure interferes with the regulation of the uptake, distribution and metabolism of sulfate in Chinese cabbage. J Plant Physiol 167(6):438–446
Shaked Y, Xu Y, Leblanc K et al (2006) Zinc availability and alkaline phosphatase activity in Emilianiah: implications for Zn-P co-limitation in the ocean [J]. Limnol Oceanogr Sl:299–309
Singh OV, Labana S, Pandey G, Budhiraja R, Jain RK (2003) Phytoremediation: an overview of metallic ion decontamination from soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61(5–6):405–412
Tang YT, Qiu RL, Zeng XW, Ying RR, Yu FM, Zhou XY (2009) Lead, zinc, cadmium hyperaccumulation and growth stimulation in Arabis paniculata Franch. Environ Exp Bot 66(1):126–134
Todeschini V, Lingua G, D’Agostino G, Carniato F, Roccotiello E, Berta G (2011) Effects of high zinc concentration on poplar leaves: a morphological and biochemical study. Environ Exp Bot 71(1):50–56
Vinod K, Awasthi G, Chauchan PK (2012) Cu and Zn tolerance and responses of the biochemical and physiochemical system of wheat. J Stress Physiol Biochem 8(3):203–213
Wu HY, Zhan XD, Shichun S (2010) Variations of antioxidant enzyme activity and malondialdehyde content in nemertean Cephalothrix hongkongiensis after exposure to heavy metals. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 28(4):917–923
Xu L, Wang TY, Ni K, Liu SJ, Wang P, Xie SW, Meng J, Zheng XQ, Lu YL (2014) Ecological risk assessment of arsenic and metals in surface sediments from estuarine and coastal areas of the Southern Bohai Sea, China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 20(2):388–401
Youssef MA, El-Khodery SA, Ibrahim HMM (2012) Antioxidant trace elements in serum of draft horses with acute and chronic lower airway disease. Biol Trace Elem Res 150(1–3):123–129
Yu ZG, Zhang J, Wu Y et al (1994) Toxic effect of copper on benthic green aigae in the yellow sea. Acta Sci Circumst 14(4):494–500
Zhou H, Xiang SD (1998) The effect of copper, zinc, lead, cadmium on the growth and the ultrastructure of selenastrum minutum. J Hangzhou Univ (Nat Sci) 25(2):85–92
Acknowledgments
This research is completed under the financial aid of the Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of China (41430752) and supported by the Opening Project of State Key Laboratory of Tea Plant Biology and Utilization also.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Highlights
• Low Zn2+ concentrations accelerated the growth of Cladophora; Cu2+ greatly influences Cladophora growth.
• Cu2+ and Zn2+ treatment affected the content of total soluble sugar in Cladophora, but not its protein content.
• Zn2+ induced the intracellular calcium release, and copper induced the intracellular calcium increases in Cladophora.
• Exposure to Cu2+ and Zn2+ induces MDA in Cladophora.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Dj., Xie, Pp., Deng, Jw. et al. Effects of Cu2+ and Zn2+ on growth and physiological characteristics of green algae, Cladophora . Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 16535–16541 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4847-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4847-2