Abstract
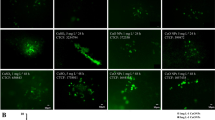
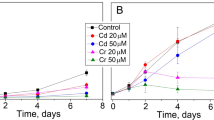
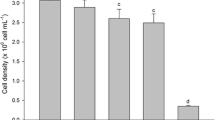
Green algae of the genus Cladophora have been reported as being bioindicators of metal contamination all over the world. The degree of total as well as intracellular copper (Cu) uptakes by the alga after 24-h prolonged exposure with 0 (control), 50 and 500 µM Cu doses, was compared with selected physiological markers. Increased intracellular Cu content in the Cladophora thalli was followed by decreased potassium (K) content, alteration of assimilation pigments composition, decreased integrity of chlorophyll a and its fluorescence. Increase of intracellular Cu was followed by the increases of TBARS and superoxide contents. While K content, chlorophyll a/b, chlorophyll a fluorescence and TBARS contents in C. prolifera were significantly altered as result of the lowest, 50 µM Cu dose tested, levels of chlorophyll a + b and soluble proteins did not change even after application of the 500 µM Cu dose.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Dw:
-
Dry weight
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- PPFD:
-
Photosynthetic photon flux density
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances
References
Bačkor M, Loppi S (2009) Interactions of lichens with heavy metals. Biol Plant 53:214–222
Bačkor M, Váczi P, Barták M, Buďová J, Dzubaj A (2007) Uptake, photosynthetic characteristics and membrane lipid peroxidation levels in the lichen photobiont Trebouxia erici exposed to copper and cadmium. Bryologist 110:100–107
Bačkor M, Kováčik J, Dzubaj A, Bačkorová M (2009) Physiological comparison of copper toxicity in the lichens Peltigera rufescens (Weis) Humb. and Cladina arbuscula subsp. mitis (Sandst.) Ruoss. Plant Growth Regul 58:279–286
Baumann HA, Morrison L, Stengel DB (2009) Metal accumulation and toxicity measured by PAM—chlorophyll fluorescence in seven species of marine macroalgae. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1063–1075
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chettri MK, Cook CM, Vardaka E, Sawidis T, Lanaras T (1998) The effect of Cu, Zn and Pb on the chlorophyll content of the lichen Cladonia convoluta and Cladonia rangiformis. Environ Exp Bot 39:1–10
Clark RB (2001) Marine pollution, 5th edn. Oxford University Press, UK
Garty J (2001) Biomonitoring atmospheric heavy metals with lichens: theory and application. Crit Rev Plant Sci 20:309–371
Kalinowska R, Pawlik-Skowrońska B (2010) Response of two terrestrial green microalgae (Chlorophyta, Trebouxiophyceae) isolated from Cu-rich and unpolluted soils to copper stress. Environ Pollut 158:2778–2785
Kennish MJ (1996) Practical handbook of estuarine and marine pollution. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kováčik J, Klejdus B, Bačkor M, Štork F, Hedbavny J (2011) Physiological responses of root-less epiphytic plants to acid rain. Ecotoxicology 20:348–357
Pawlik-Skowrońska B, Pirszel J, Brown MT (2007) Concentrations of phytochelatins and glutathione found in natural assemblages of seaweeds depend on species and metal concentrations of the habitat. Aquat Toxicol 83:190–199
Piovár J, Stavrou E, Kaduková J, Kimáková T, Bačkor M (2011) Influence of long-term exposure to copper on lichen photobiont Trebouxia erici and free-living alga Scenedesmus quadricauda. Plant Growth Regul 63:81–88
Rocchetta I, Küpper H (2009) Chromium- and copper-induced inhibition of photosynthesis in Euglena gracilis analysed on the single-cell level by fluorescence kinetic microscopy. New Phytologyst 182:405–420
Roncarati F, Saez CA, Greco M, Gledhill M, Bitonti MB, Brown MT (2015) Response differences between Ectocarpus siliculosus populations to copper stress involve cellular exclusion and induction of the phytochelatin biosynthetic pathway. Aquat Toxicol 159:167–175
Ronen R, Galun M (1984) Pigment extraction from lichens with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and estimation of chlorophyll degradation. Environ Exp Bot 24:239–245
Sabatini SE, Leonardi PI, Rodríguez MC (2011) Responses to sublethal copper exposure in two strains of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Volvocales, Chlorophyceae) in autotrophic and mixotrophic conditions. Phycologia 50:78–88
Saez CA, Roncarati F, Moenne A, Moody JA, Brown MT (2015) Copper-induced intra-specific oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in strains of the brown alga Ectocarpus siliculosus with different pollution histories. Aquat Toxicol 159:81–89
Schützendübel A, Pole A (2002) Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J Exp Bot 53:1351–1365
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radical Biol Med 18:321–336
Vavilin DV, Ducruet JM, Matorin DN, Venediktov PS, Rubin AB (1998) Membrane lipid peroxidation, cell viability and photosystem II activity in the green alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa subjected to various stress conditions. J Photochem Photobiol B 42:233–239
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolutions. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Wissel H, Mayr C, Lücke A (2008) A new approach for the isolation of cellulose from aquatic plants tissue and freshwater sediments for stable isotopic analysis. Org Geochem 39:1545–1561
Zulkifly SB, Graham JM, Young EB, Mayer RJ, Piotrowski MJ, Smith I, Graham LE (2013) The genus Cladophora Kützing (Ulvophyceae) as a globally distributed ecological engineer. J Phycol 49:1–17
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Slovak Grant Agency (VEGA 1/1238/12). The authors offer their thanks to Kenneth Andrew Dvorsky M.Sc. M.Ed. (University of Toronto, Canada) for comments on the manuscript and Dr. Andrija Želimir Lovrić (Herbarium Adriaticum, Zagreb, Croatia) for help with algal identification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bačkorová, M., Maslaňáková, I. & Bačkor, M. Copper uptake and copper-induced physiological changes in the marine alga Cladophora prolifera (Roth.) Kütz. (Chlorophyta, Ulvophyceae). Braz. J. Bot 39, 447–452 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-016-0251-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-016-0251-5