Abstract
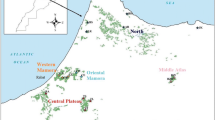
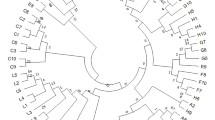
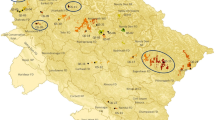
Cork oak (Quercus suber L.) is an essential species of the Mediterranean region. In Morocco, it represents a source of life and is a noble species for many populations. The Maâmora forest, situated in Morocco, is recognized as the largest forest in the Mediterranean basin and displays the highest diversity compared to other forests in its distribution area. This study aimed to establish a genetic database of 240 individuals from Maâmora forest using seven SSR markers. Through a series of statistical analyses, we determined the level of diversity and genetic structure and created a core collection. Statistical analysis of the data showed a high degree of allelic variation, generating 47 alleles with an average of 6.71 alleles per locus. Furthermore, a high percentage of polymorphisms and a high Shannon index were observed. Intra-population genetic diversity was found to be high (86%) compared to inter-population diversity (14%). A low level of genetic differentiation (Gst = 0.12) and high gene flow were identified, consistent with the results obtained from the analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA). This suggests a possible capacity for the species to adapt to environmental conditions. A core collection of 18 genotypes was constructed, which included all the private alleles that were detected in this study. This core collection exhibited similar and crucial diversity to that identified in the initial collection, as verified by a series of genetic diversity and structural analyses. This research advocates populations and individuals for further studies on adaptation in order to improve and conserve this valuable resource in the future.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaci H, Farid B (2019) The cork oak, aneglected tree resource in algeria. Algeria: agriculture, water supply and vegetation. S.l.: NOVA SCIENCE
Alberto FJ, Aitken SN, Alía R, González-Martínez SC, Hänninen H, Kremer A et al (2013) Potential for evolutionary responses to climate change – evidence from tree populations. Glob Change Biol 19(6):1645–1661. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12181
Aronson J, Pereira JS, Pausas JG (2012) Cork oak woodlands on the edge: ecology, adaptive management, and restoration. Island Press
Audigeos D, Brousseau L, Traissac S, Scotti-Saintagne C, Scotti I (2013) Molecular divergence in tropical tree populations occupying environmental mosaics. J Evol Biol 26(3):529–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeb.12069
Belahbib N, Pemonge MH, Ouassou A, Sbay H, Kremer A, Petit RJ (2001) Frequent cytoplasmic exchanges between oak species that are not closely related: Quercus suber and Q. ilex in Morocco. Mol Ecol 10(8):2003–2012. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0962-1083.2001.01330.x
Belahbib Nadia, Ouassou A, Dahmani J, Douira A (2005) Contribution à l ’ étude de l ’ introgression génétique entre Quercus suber L et Q. rotundifolia ( Lamk.) Trabut au Maroc par l ’ utilisation des marqueurs microsatellites. Bulletin de l’Institut Scientifique, Rabat 26–27(ii):31–34
Carrión JS, Parra I, Navarro C, Munuera M (2000) Past distribution and ecology of the cork oak (Quercus suber) in the Iberian Peninsula: a pollen-analytical approach. Divers Distrib 6(1):29–44. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-4642.2000.00070.x
De Dato GD, Teani A, Mattioni C, Aravanopoulos F, Avramidou EV, Stojnic S et al (2020) Genetic Analysis by nuSSR markers of silver birch (Betula pendula Roth) populations in their Southern European distribution range. Front Plant Sci 11:310. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00310
Dow BD, Ashley MV, Howe HF (1995) Characterization of highly variable (GA/CT) n microsatellites in the bur oak. Quercus Macrocarpa Theor Appl Genet 91(1):137–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220870
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4(2):359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
El Alami SL, El Aboudi A, El Antry S, El Mnouar EA, Dallahi Y, Rabhi A (2023) Effect of tree shelters and regeneration method on survival and growth of cork oak plantations in the Maamora forest Morocco. J Ecol Eng 24(7):360–374. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/165784
Feng, X., Jiang, G., & Fan, Z. (2015). Identification of outliers in a genomic scan for selection along environmental gradients in the bamboo locust , Ceracris kiangsu. Nature Publishing Group, 1‑11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13758
Giorgi F, Lionello P (2008) Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Global Planet Change 63(2–3):90–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.09.005
Graudal L, Aravanopoulos F, Bennadji Z, Changtragoon S, Fady B, Kjær ED et al (2014) Global to local genetic diversity indicators of evolutionary potential in tree species within and outside forests. Forest Ecol Manag 333:35–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2014.05.002
Guo B, Hao X, Han L, Zhai Y, Zhou S, & Chen S (2021) Unraveling the genetic diversity and structure of Quercus liaotungensis population through analysis of microsatellite markers, 1‑19. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10922
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1993) Atterns and levels of pollen-mediated gene flow in Lathyrus latifolius. Evolution 47(1):98–110
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: synthesis report summary for policymakers paper of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. IPCC Secretariat, Geneve
Kampfer S, Lexer C, Glössl J, Steinkellner H (2004) Characterization of (GA)n microsatellite loci from Quercus Robur. Hereditas 129(2):183–186. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.1998.00183.x
Kim KW, Chung HK, Cho GT, Ma KH, Chandrabalan D, Gwag JG et al (2007) PowerCore: a program applying the advanced M strategy with a heuristic search for establishing core sets. Bioinformatics 23(16):2155–2162. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm313
Kim HN, Jin HY, Kwak MJ, Khaine I, You HN, Lee TY et al (2017) Why does Quercus suber species decline in Mediterranean areas? J Asia-Pacific Biodivers 10(3):337–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.japb.2017.05.004
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Laakili A, Belkadi B, Gaboun F, Yatrib C, Makhloufi M, El Antry S et al (2016) Analysis of dendrometric diversity among natural populations of cork oak (Quercus suber l.) from Morocco. Turkish J Agric Forest 40(2):127–135. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1407-147
Laakili A, Belkadi B, Medraoui L, Alami M, Yatrib C, Pakhrou O et al (2018) Diversity and spatial genetic structure of natural Moroccan Quercus suber L. assessed by ISSR markers for conservation. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 24(4):643–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-018-0538-z
Laaribya S, Alaoui A, Ayan S, Benabou A, Labbaci A, Ouhaddou H, Bijou M (2021) Prediction by maximum entropy of potential habitat of the cork oak (Quercus suber L.) in Maamora forest Morocco. Forestist 71(2):63–69. https://doi.org/10.5152/forestist.2021.20059
Lahssini S, Lahlaoi H, Alaoui HM, Hlal EA, Bagaram M, Ponette Q (2015) Predicting cork oak suitability in Maâmora forest using random forest algorithm. J Geogr Inf Syst 07(02):202–210. https://doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2015.72017
Lehmann T, Hawley WA, Collins FH (1996) An evaluation of evolutionary constraints on microsatellite loci using null alleles. Genetics 144(3):1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/144.3.1155
Lindner M, Maroschek M, Netherer S, Kremer A, Barbati A, Garcia-Gonzalo J et al (2010) Climate change impacts, adaptive capacity, and vulnerability of European forest ecosystems. For Ecol Manage 259(4):698–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.023
Liu H, Cheng H, Xu J, Hu J, Zhao C, Xing L et al (2023) Genetic diversity and population structure of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua in China using SSR markers. PLoS One 18(8):e0290605. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0290605
López-Aljorna A, Bueno MÁ, Aguinagalde I, Martín JP (2007) Fingerprinting and genetic variability in cork oak (Quercus suber L.) elite trees using ISSR and SSR markers. Annal Forest Sci 64(7):773–779. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:2007057
McDermott JM, McDonald BA (1993) Gene flow in plant pathosystems. Annu Rev Phytopathol 31:353–373. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.31.090193.002033
Modesto IS, Miguel C, Pina-Martins F, Glushkova M, Veloso M, Paulo OS, Batista D (2014) Identifying signatures of natural selection in cork oak (Quercus suber L) genes through SNP analysis. Tree Genet Genomes 10(6):1645–1660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-014-0786-1
Natl P, Sci A, Harbor CS, York N, Chin J, Res NA (2006) Genetic Diversity of Two Evergreen Oaks [Quercus suber ( L .) and Quercus ilex subsp. rotundifolia ( Lam )] in Portugal using AFLP Markers. Silvae Genetica 3:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1515/sg-2006-0016
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in Subdivided Populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79:3321–3323
Neophytou C, Aravanopoulos FA, Fink S, Dounavi A (2010) Detecting interspecific and geographic differentiation patterns in two interfertile oak species (Quercus petraea (Matt) Liebl and Q robur L) using small sets of microsatellite markers. Forest Ecol Manag 259(10):2026–2035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2010.02.013
Nybom H (2004) Comparison of different nuclear DNA markers for estimating intraspecific genetic diversity in plants. Mol Ecol 13(5):1143–1155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02141.x
Odong TL, Jansen J, van Eeuwijk FA, van Hintum TJL (2013) Quality of core collections for effective utilisation of genetic resources review, discussion and interpretation. Theor Appl Genet 126(2):289–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1971-y
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6(1):288–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2005.01155.x
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—an update. Bioinformatics 28(19):2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460
Pina-Martins F, Baptista J, Pappas G, Paulo OS (2019) New insights into adaptation and population structure of cork oak using genotyping by sequencing. Glob Change Biol 25(1):337–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14497
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/155.2.945
Radu, R. G., Curtu, L. A., Spârchez, G., & Şofletea, N. (2014). Genetic diversity of Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst.] in Romanian Carpathians. Annals of Forest Research, 0(0), 1. https://doi.org/10.15287/afr.2014.178
Said DL, Najib PG, Assmaa MA (2010) Towards a coordinated development of the forest in Maamora (Morocco). Kastamonu Univ J Forest Facult 10(2):172–179
Saini P, Saini P, Kaur JJ, Francies RM, Gani M, Rajendra AA et al (2020) Molecular approaches for harvesting natural diversity for crop improvement. In R. K. Salgotra & S. M. Zargar (Éd.), Rediscovery of genetic and genomic resources for future food security (p. 67‑169). Singapore: Springer Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0156-2_3
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Selkoe KA, Toonen RJ (2006) Microsatellites for ecologists: a practical guide to using and evaluating microsatellite markers. Ecol Lett 9(5):615–629. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00889.x
Sheller M, Tóth EG, Ciocîrlan E, Mikhaylov P, Kulakov S, Kulakova N et al (2023) Genetic diversity and population structure of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) in Middle Siberia. Forests 14(1):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14010119
Sork VL, Aitken SN, Dyer RJ, Eckert AJ, Legendre P, Neale DB (2013) Putting the landscape into the genomics of trees: approaches for understanding local adaptation and population responses to changing climate. Tree Genet Genomes 9(4):901–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-013-0596-x
Soto A, Lorenzo Z, Gil L (2007) Differences in fine-scale genetic structure and dispersal in Quercus ilex L. and Q. suber L.: consequences for regeneration of Mediterranean open woods. Heredity 99(6):601–607. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6801007
Sousa F, Costa J, Ribeiro C, Varandas M, Pina-Martins F, Simões F et al (2022) Population structure in Quercus suber L. revealed by nuclear microsatellite markers. PeerJ 10:e13565. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.13565
Steinkellner H, Fluch S, Turetschek E, Lexer C, Streiff R, Kremer A et al (1997) No title found. Plant Mol Biol 33(6):1093–1096. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005736722794
Tang T, Wang F, Guo J, Guo X, Duan Y, You J (2021) Duohua Huangjing ( Polygonatum cyrtonema ) seedling basal stem rot caused by Fusarium redolens in China. Plant Dis 105(9):2717. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-03-21-0597-PDN
Vanhove M, Pina-Martins F, Coelho AC, Branquinho C, Costa A, Batista D et al (2021) Using gradient forest to predict climate response and adaptation in cork oak. J Evol Biol 34(6):910–923. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeb.13765
Vessella F, López-Tirado J, Simeone MC, Schirone B, Hidalgo PJ (2017) A tree species range in the face of climate change: cork oak as a study case for the Mediterranean biome. Eur J Forest Res 136(3):555–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-017-1055-2
Acknowledgements
We express our deep gratitude to all forest technicians who contributed to the collection of plant material throughout Morocco.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AFE wrote the paper. AFE, AM, ML, BB, and F-MA developed conceptual ideas, designed the study, and examined the document. AFE and EAS conducted sampling in field. AFE, KR, and AM contributed to the analysis of samples in the laboratory and data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Data archiving statement
In this manuscript, there is no raw data such as nucleic acid sequences, protein sequences, genetic maps, SSR, and expression data. Nevertheless, all the original metaphase pictures are in possession of the authors and available for the reviewers or for submission in any database if it is necessary.
Additional information
Communicated by J. Chen
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Assemar, F.E., Alami, M., Rabeh, K. et al. Genetic diversity and population structure in Quercus suber L. revealed by nuclear microsatellite markers and generation of a core collection. Tree Genetics & Genomes 20, 5 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-024-01638-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-024-01638-w