Abstract
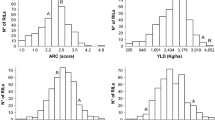
To breed a new variety of coffee (Coffea arabica) requires approximately 25 years due to the long generation time (5–6 years) of this perennial plant and the fact that it takes at least five generations of selection to obtain superior individuals. One way to reduce the number of generations is to use marker-assisted selection (MAS). To implement MAS, it is necessary to develop a genetic map and to identify markers associated with quantitative trait loci (QTLs) governing traits of interest. The objective of this study was to identify QTLs associated with yield, plant height, and bean size. An F2 mapping population consisting of 278 individuals was developed from a cross between Caturra × CCC1046. A total of 338 SSR were used to construct a framework linkage map. Subsequently, SNP markers were added to construct a more robust genetic map. R/qtl software was used to integrate SSR and SNP markers. The integrated linkage map consists of 22 linkage groups populated by 848 SSR and SNP markers, with a total map length of 3800 cM. F3 progenies of the mapping population were planted in five locations and evaluated for yield, plant height, and bean size. A major yield QTL was significant at two locations and a second was significant at one location. Two QTL were each detected for plant height and bean size.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basten CJ. (1997). QTL Cartographer: a reference manual and tutorial for qtl mapping. North Carolina State University, Raleigh NC, USA
Basten, C. J., Weir B. S. and Zeng Z. B. (2000).QTL Cartographer, version 1.14. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC.
Benson DA, Clark K, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Sayers EW (2014) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gku 1216
Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD (1986) Towards a saturated linkage map in tomato based on isozymes and random cDNA sequences. Genetics 112(4):887–898
Bridson DM, Verdcourt B. (1988). Rubiaceae, pt 2. Flora of Tropical East Africa. Kew: Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 415–747
Broman KW, Sen S (2009) A guide to QTL mapping with R/qtl. Springer, New York. ISBN 978-0-387-92124-2
Broman KW, Wu H, Sen Ś, Churchill GA (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19:889–890
Burr B, Burr FA, Thompson KH, Albertson MC, Stuber CW (1988) Gene mapping with recombinant inbreds in maize. Genetics 118:519–526
Carvalho A. (1946). Distribuiçäo geografica e classificaçäo botânica do gênero Coffea com referência especial à espécie Arabica. V. Origem e classificaçao botânica do C. arabica L. Boletim da Superintendencia dos Serviços do Cafe 21(230):174–184
Carvalho A (1959) A genética de Coffea: XXIV—mutantes de Coffea arabica procedentes da Etiópia. Bragantia 18:353–371
Chevalier A, Dagron M (1928) Recherches historiques sur les débuts de la culture du caféier en Amérique. Communications et Actes de l'Académie des Sciences Coloniales, París, 38 p
Chou H, Holmes MH (2001) DNA sequence quality trimming and vector removal. Bioinformatics 17:1093–1104
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Coulibaly I, Louarn J, Lorieux M, Hamon S, Noirot M. (2001). Genetic linkage map of a backcross between C. canephora P. and C. heterocalyx and autogamy gene location. 19. International Scientific Colloquium on Coffee. Trieste (Italia). 14–18 May 2001. Proceedings. Association Scientifique Internationale du Cafe, París (Francia)
Doerge R (2002) Mapping and analysis of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Nat Rev 3:43–52
Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl M, Green P (1998) Basecalling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8:175–185
Fernandez-Pozo N, Menda N, Edwards JD, Saha S, Tecle IY, Strickler SR, Bombarely A, Fisher-York T, Pujar A, Foerster H, Yan A, Mueller LA (2014) The Sol Genomics Network (SGN)—from genotype to phenotype to breeding. Nucleic Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1195
Ferreira A, Da Silva MF, Da Costa E, Silva L, Cruz CD (2006) Estimating the effects of population size and type on the accuracy of genetic maps. Genet Mol Biol 29(1):187–192
Geleta M, Herrera I, Monzón A, Bryngelsson T (2012) Genetic diversity of arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.) in Nicaragua as estimated by simple sequence repeat markers. Sci World J 2012:939820
Haarer A E (1956) Modern coffee production. Leonard Hill pub
Hanson WD (1959) Minimum family size for the planning of genetic experiments. Agron J 51:711–715
Harris S, Jones D B (1997) Optimization of the polymerase chain reaction. Br. Journal of Biomed Science 166–173
He P, Li JZ, Zheng XW, Shen LS, Lu CF, Chen Y, Zhu LH (2001) Comparison of molecular linkage maps and agronomic trait loci between DH and RIL populations derived from the same rice cross. Crop Sci 41:1240–1246
Hong Y, Chen X, Liang X, Liu H, Zhou G, Li S, Wen S, Holbrook CC, Guo B (2010) A SSR-based composite genetic linkage map for the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genome. BMC Plant Biol 10:17. 3
Hudson CJ, Freeman JS, Kullan ARK, Petroli CD, Sansaloni CP, Kilian A, Detering F, Grattapaglia D, Potts BM, Myburg AA, Vaillancourt RE (2012) A reference linkage map for Eucalyptus. BMC Genomics 13:240
International Coffee Organization. (2015). http://www.ico.org/prices/po-production.pdf. London, England. April
Koressaar T, Remm M (2007) Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics 23(10):1289–91
Ky CL, Barre P, Lorieux M, Trouslot P, Akaffou S, Louarn J, Charrier A, Hamon S, NoiritT M (2000) Interspecific genetic linkage map, segregation distortion and genetic conversion in coffee (Coffea sp.). Theor Appl Genet 101:669–676
Lander S, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M, Lincoln S, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lashermes P, Couturon E, Moreau N, Paillard M, Louarn J (1996) Inheritance and genetic mapping of self-incompatibility in Coffea canephora Pierre. Theor Appl Genet 93:458–462
Lashermes P, Combes MC, Prakash NS, Trouslot P, Lorieux M, Charrier A (2001) Genetic linkage map of Coffea canephora: effect of segregation distortion and analysis of recombination rate in male and female meiosis. Genome 44:589–596
Lefebvre-Pautigny F, Wu FN, Philippot M, Rigoreau M, Priyono ZM, Frasse P, Bouzayen M, Broun P, Petiard V, Tanksley SD, Crouzillat D (2010) High resolution synteny maps allowing direct comparisons between the coffee and tomato genomes. Tree Genet Genomes 6(4):565–577. doi:10.1007/s11295-010-0272-3
Leroy T, De Bellis F, Legnate H, Kanamura E, Gonzales G, Pereira LFP, Andrade AC, Charmetant P, Montagnon C, Cubry P, Marraccini P, Pot D, de Kochko A (2011) Improving the quality of African robustas: QTLs for yield- and quality-related traits in Coffea canephora. Tree Genet Genomes 7:781–798. doi:10.1007/s11295-011-0374-6
Li ZK, Yu SB, Lafitte HR, Huang N, Courtois B, Hittalmani S, Vijayakumar CHM, Liu GF, Wang GC, Shashidhar HE et al (2003) QTL × environment interactions in rice. I. Heading date and plant height. Theor Appl Genet 108:141–153
Liu HB (1998) Statistical genomics, linkage, mapping and QTL analysis. CRC, Boca Raton, 611 pp
Lopez GG, del Moncada BMP (2005) Construcción de un mapa de ligamiento genético preliminary en Coffea liberica x C. eugenioides. Cenicafé 56(4):319–338
Lopez GG, McCouch SR, del Moncada MP (2013) A genetic map of an interspecific diploid pseudo testcross population of coffee. Euphytica 192(2):305–323
Moncada P, McCouch S (2004) Simple sequence repeat diversity in diploid and tetraploid Coffea species. Genome 47:501–509
Moreno RLG (2004) Obtención de variedades de café con resistencia durable a enfermedades, usando la diversidad genética como estrategia de mejoramiento. Revista Academia Colombiana Ciencias Exactas, Físicas Naturales 28(107):187–200
N’Diaye A, Noirot M, Hamon S, Poncet V (2007) Genetic basis of species differentiation between Coffea liberica Hiern and C. canephora Pierre: analysis of an interspecific cross. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54(5):1011–1021. doi:10.1007/s10722-006-9195-0
Nagai, C., M. R. Jones, A. E. Byers, D. J. Adamski, R. Ming. (2006). Development and characterization of a true F2 population for genetic and QTL mapping in arabica. Proceedings of 21th ASIC International Conference on Coffee Science, 11–15 September, 2006. Montpellier, France. 2007 pp. 771–777
Paillard M, Lashermes P, Petiard V (1996) Construction of a molecular linkage map in coffee. Theor Appl Genet 93:41–47
Pearl HM, Nagai C, Moore PH, Steiger DL, Osgood RV, Ming R (2004) Construction of a genetic map for arabica coffee. Theor Appl Genet 108:829–835
Pertea G, Huang X, Liang F, Antonescu V, Sultana R, Karamycheva S, Lee Y, White J, Cheung F, Parvizi B, Tsai J, Quackenbush J (2003) TIGR Gene Indices clustering tools (TGICL): a software system for fast clustering of large EST datasets. Bioinformatics 19(5):651–652. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg034
Portis E, Mauromicale G, Mauro R, Acquadro A, Scaglione D, Lanteri S (2009) Construction of a reference molecular linkage map of globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus). Theor Appl Genet 2009(120):59–70
Prasad S H, Phanindranath R, Annapurna V, Lalremruata A, Aggarwal R (2008) Development of new genomic microsatellite markers from robusta coffee (Coffea canephora Pierre ex A. Froehner) showing broad cross-species transferability and utility in genetic studies. BMC Plant Biol 1471-2229-8-51
Spindel J, Wright M, Chen C, Cobb J, Gage J, Harrington S, Lorieux M, Ahmadi N, McCouch S (2013) Bridging the genotyping gap: using genotyping by sequencing (GBS) to add high-density SNP markers and new value to traditional bi-parental mapping and breeding populations. Theor Appl Genet 126(11):2699–2716
Texeira-Cabral TA, Sakiyama NS, Zambolin L, Pereira AA, Schuster I (2004) Single-locus inheritance and partial linkage map of Coffea arabica L. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 4:416–421
Untergrasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3—new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40(15):e115
Wang S., Basten, C. J. and Zeng Z-B. (2012). Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. (http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm)
Xing Y, Tan VJ, Hua J, Sun X, Xu C, Zhang Q (2002) Characterization of the main effects, epistatic effects and their environmental interactions of QTLs on the genetic basis of yield traits in rice. Theor Appl Genet 105(2002):248–257
Acknowledgments
We thank the Experimentation Unit at Cenicafe for valuable assistance in collecting field data, and Cenicafe and Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Colombia (Agreements No. 100 of 2004, 015 of 2006, 067 of 2007, and 102 of 2011) for financial support. We are grateful to the US National Science Foundation for a PhD fellowship for JS and for research support under Plant Genome Research Program award #1026555 to SMc.
Data archiving statement
Primer sequences of the SSR markers are provided in Table ESM 1
SNP markers sequences and polymorphism are provided in Table ESM 2.
Genotypic data for SSR and SNP markers in the F2 coffee population are provided in Table ESM 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Grattapaglia
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table ESM 1
(XLS 706 kb)
Table ESM 2
(XLSX 198 kb)
Table ESM 3
(XLSX 1000 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moncada, M., Tovar, E., Montoya, J.C. et al. A genetic linkage map of coffee (Coffea arabica L.) and QTL for yield, plant height, and bean size. Tree Genetics & Genomes 12, 5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0927-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0927-1