Abstract
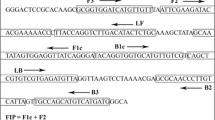
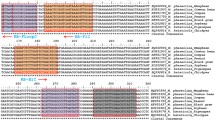
Phytophthora palmivora has caused disease in many crops including oil palm in the South America region. The pathogen has had a significant economic impact on oil palm cultivation in Colombia, and therefore poses a threat to oil palm cultivation in other regions of the World, especially in Southeast Asia, the largest producer of the crop. This study aimed to look at the ability of isolates from Malaysia, Colombia, and other regions to cross-infect Malaysian oil palm, durian, and cocoa and to develop specific biomarkers and assays for identification, detection, and diagnosis of P. palmivora as a key component for the oil palm biosecurity continuum in order to contain the disease especially at the ports of entry. We have developed specific molecular biomarkers to identify and detect Phytophthora palmivora using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and real-time loop mediated isothermal amplification (rt-LAMP) in various sample types such as soil and plants. The limit of detection (DNA template, pure culture assay) for the PCR assay is 5.94 × 10−2 ng µl−1 and for rt-LAMP is 9.28 × 10−4 ng µl−1. Diagnosis using rt-LAMP can be achieved within 30 min of incubation. In addition, PCR primer pair AV3F/AV3R developed successfully distinguished the Colombian and Malaysian P. palmivora isolates.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Some data are provided in full in the result section of this paper. Sequences data created and analysed in this research are openly available from GenBank® (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) and the accession numbers for each data is available in the paper.
References
Abdullahi UF, Naim R, Taib WRW, Saleh A, Muazu A, Aliyu S, Baig AA (2015) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), an innovation in gene amplification: bridging the gap in molecular diagnostics; a review. Indian J Sci Technol 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i17/55767
Aglietti C, Luchi N, Pepori AL, Bartolini P, Pecori F, Raio A, Capretti P, Santini A (2019) Real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification: an early-warning tool for quarantine plant pathogen detection. AMB Express 9:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0774-9
Ahmed Y, D’Onghia AM, Ippolito A, Yaseen T (2013) First report of citrus root rot caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Egypt. Plant Dis 98:155–155. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-02-13-0206-PDN
Akrofi AY (2015) Phytophthora megakarya: a review on its status as a pathogen on cacao in West Africa. Afr Crop Sci J 23:67–87
Alsultan W, Vadamalai G, Saud HM, Khairulmazmi A, Wong MY, Jaaffarand AKM, Al-Sadi AM, Rashed O, Nasehi A (2021) Phylogenetic analysis and genetic diversity of Phytophthora palmivora causing black pod Disease of cocoa in Malaysia. Plant Health Prog 22:260–271. https://doi.org/10.1094/php-02-21-0030-fi
Ann PJ (1984) Species, mating types and pathogenicity of Phytophthora distributed in citrus orchards in Taiwan. Trans Brit Mycol Soc 82:631–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(84)80103-5
Anupama KP, Nayak A, Karunasagar I, Maiti B (2020) Rapid visual detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood samples by loop-mediated isothermal amplification with hydroxynaphthol blue dye. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36:76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02851-0
Bekele B, Hodgetts J, Tomlinson JA, Boonham N, Nikolić P, Swarbrick P, Dickinson M (2011) Use of a real-time LAMP isothermal assay for detecting 16SrII and XII phytoplasmas in fruit and weeds of the Ethiopian Rift Valley. Plant Pathol 60:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2010.02384.x
Bonants P, van Weerdt Md M, Lacourt I, Cooke D, Duncan J (1997) Detection and identification of Phytophthora Fragariae Hickman by the polymerase chain reaction. Eur J Plant Pathol 103:345–355. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008640227432
Borines LM, Palermo VG, Guadalquiver GA, Dwyer C, Drenth A, Daniel R, Guest DI (2014) Jackfruit decline caused by Phytophthora palmivora (Butler). Australas Plant Pathol 43:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-013-0241-z
Bowman KD, Albrecht U, Graham JH, Bright DB (2007) Detection of Phytophthora nicotianae and P. palmivora in citrus roots using PCR-RFLP in comparison with other methods. Eur J Plant Pathol 119:143–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-007-9135-7
Brasier CM, Griffin MJ (1979) Taxonomy of Phytophthora palmivora on cocoa. Trans Brit Mycol Soc 72:111–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(79)80015-7
Burgess TI, López-Villamor A, Paap T, Williams B, Belhaj R, Crone M, Dunstan W, Howard K, Hardy GESJ (2021) Towards a best practice methodology for the detection of Phytophthora species in soils. Plant Pathol 70:604–614. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13312
Cacciola SO, Williams NA, Cooke DEL, Duncan JM (2001) Molecular identification and detection of Phytophthora species on some important mediterranean plants including sweet chestnut. For Snow Landsc Res 76:351–356
Cahill DM, Hardham AR (1994) A dipstick immunoassay for the specific detection of Phytophthora cinnamomi in soils. Phytopathology 84:1284–1292. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-84-128
Cao YT, Wu ZH, Jian JC, Lu YS (2010) Evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the rapid detection of Vibrio harveyi in cultured marine Shellfish. Lett Appl Microbiol 51:24–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02853.x
Capote N, Pastrana AM, Aguado A, Torres T (2012) Molecular tools for detection of plant pathogenic fungi and fungicide resistance. In: Cumagun CJR (ed.) Plant Pathology. InTech, www.intechopen.com, pp 151–202. https://doi.org/10.5772/38011
Carella P, Gogleva A, Tomaselli M, Alfs C, Schornack S (2018) Phytophthora palmivora establishes tissue-specific intracellular infection structures in the earliest divergent land plant lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E3846-e3855. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717900115
Chaliha C, Srivastava R, Kalita E, Sahoo L, Verma PK (2023) Rapid and precise detection of cryptic tea pathogen Exobasidium vexans: RealAmp validation of LAMP approach. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39:52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03506-y
Chen Q, Li B, Liu P, Lan C, Zhan Z, Weng Q (2013) Development and evaluation of specific PCR and LAMP assays for the rapid detection of Phytophthora melonis. Eur J Plant Pathol 137:597–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0273-9
Concibido-Manohar E (2004) Phytophthora diseases of coconut in the Philippines. In: Drenth A, Guest DI (eds) Diversity and management of Phytophthora in Southeast Asia. ACIAR, Canberra, p 115
Dai TT, Lu CC, Lu J, Dong SM, Ye WW, Wang YC, Zheng XB (2012) Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of Phytophthora sojae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 334:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02619.x
Demeke T, Jenkins GR (2010) Influence of DNA extraction methods, PCR inhibitors and quantification methods on real-time PCR assay of biotechnology-derived traits. Anal Bioanal Chem 396:1977–1990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3150-9
Drenth A, Guest DI (2004) Phytophthora in the tropics. In: Drenth A, Guest D (eds) Diversity and management of Phytophthora in Southeast Asia. ACIAR, Canberra, pp 30–41
Drenth A, Sendall B (2001) Practical guide to detection and identification of Phytophthora. CRC Tropical Plant Protection, Australia
Drenth A, Wagels G, Smith B, Sendall B, O’Dwyer C, Irvine G, Irwin JAG (2006) Development of a DNA-based method for detection and identification of Phytophthora species. Australas Plant Pathol 35:147–159. https://doi.org/10.1071/ap06018
Duan YB, Yang Y, Wang JX, Liu CC, He LL, Zhou MG (2015) Development and application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detecting the highly benzimidazole-resistant isolates in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Sci Rep 5:17278. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17278
Ellis MA, Miller SA (1993) Using a Phytophthora-specific immunoassay kit to diagnose raspberry Phytophthora root rot. HortScience 28:642–644. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.28.6.642
Goodwin PH, English JT, Neher DA, Duniway JM, Kirkpatrick BC (1990) Detection of Phytophthora parasitica from soil and host tissue with a species-specific DNA probe. Phytopathology 80:277–281. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-80-277
Guo H, Li C-P, Shi T, Fan C-J, Huang G-X (2012) First report of Phytophthora palmivora causing root rot of cassava in China. Plant Dis 96:1072–1072. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-09-11-0780-pdn
Hieno A, Li M, Otsubo K, Suga H, Kageyama K (2021) Multiplex LAMP detection of the genus Phytophthora and four Phytophthora species P. ramorum, P. lateralis, P. kernoviae, and P. nicotianae, with a plant internal control. Microbes Environ 36:19. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME21019
Hulme PE (2014) An introduction to plant biosecurity: past, present and future. In: Gordh G, McKirdy S (eds) The handbook of plant biosecurity: principles and practices for the identification, containment and control of organisms that threaten agriculture and the environment globally. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7365-3_1
Hussain T, Singh BP (2016) Molecular diagnosis of killer pathogen of potato: Phytophthora infestans and its management. In: Kumar P, Gupta VK, Tiwari AK, Kamle M (eds) Current trends in plant disease diagnostics and management practices. Springer, Cham, pp 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27312-9_1
Hussain T, Singh BP, Anwar F (2017) Development of specific marker for PCR diagnostic of late blight of potato caused by Phytophthora infestans using RAPD based SCAR methodology. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 16:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2015.10.001
Kaneko H, Kawana T, Fukushima E, Suzutani T (2007) Tolerance of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to a culture medium and biological substances. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:499–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbbm.2006.08.008
Kong L, Wang H-b, Wang S-s, Xu P-p, Zhang R-f, Dong S, Zheng X-b (2020) Rapid detection of potato late blight using a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. J Integr Agric 19:1274–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62816-9
König S, Schwenkbier L, Pollok S, Riedel M, Wagner S, Popp J, Weber K, Werres S (2015) Potential of Ypt1 and ITS gene regions for the detection of Phytophthora species in a lab-on-a-chip DNA hybridization array. Plant Pathol 64:1176–1189. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12357
Lee SB, Taylor JW (1990) Isolation of DNA from fungal mycelia and single spores. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky J, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press Inc, San Diego, pp 282–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-372180-8.50038-X
Lenarčič R, Morisset D, Mehle N, Ravnikar M (2013) Fast real-time detection of potato spindle tuber viroid by rt-LAMP. Plant Pathol 62:1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12017
Levy L, Shiel P, Dennis G, Lévesque CA, Clover G, Bennypaul H, Barr N, Roda A, Young R, Plazinski J, Moran J (2014) Molecular diagnostic techniques and biotechnology in plant biosecurity. In: Gordh G, McKirdy S (eds) The handbook of plant biosecurity: principles and practices for the identification, containment and control of organisms that threaten agriculture and the environment globally. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 375–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7365-3_13
Li Y, Cooke DEL, Jacobsen E, van der Lee T (2013) Efficient multiplex simple sequence repeat genotyping of the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans. J Microbiol Methods 92:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2012.11.021
Li G-R, Huang G-M, Zhu L-H, Lv D, Cao B, Liao F, Luo J-F (2019) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) detection of Phytophthora hibernalis, P. syringae and P. cambivora. J Plant Pathol 101:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-018-0136-5
Liberato JR, Suzuki MS, Denth A (2012) PaDIL Species Factsheet: Phytophthora fruit rot and root rot of papaya. https://www.padil.gov.au/
Liew ECY, Maclean DJ, Irwin JAG (1998) Specific PCR based detection of Phytophthora medicaginis using the intergenic spacer region of the ribosomal DNA. Mycol Res 102:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756297004450
Lim TK, Chan LG (1986) Fruit rot of durian caused by Phytophthora palmivora. Pertanika 9:269–276
Liu Y, Ahmed A, Munir S, He P, He P-b, Wu Y, Tang P, Wang Z, Kong BH, He Y (2023) First report of Aloe root and stem rot caused by Phytophthora palmivora in Yunnan Province, China. Plant Dis. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-05-23-0927-pdn
Luo JG, Ge JW, Tang LJ, Qiao XY, Jiang YP, Cui W, Liu M, Li YJ (2013) Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of bovine parvovirus. J Virol Methods 191:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2012.05.002
Luo J, Taniwaki MH, Iamanaka BT, Vogel RF, Niessen L (2014) Application of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for direct identification of pure cultures of Aspergillus flavus, A. nomius, and A. caelatus and for their rapid detection in shelled Brazil nuts. Int J Food Microbiol 172:5–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.12.001
Madihah AZ, Maizatul-Suriza M, Idris AS (2020) Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (rt-LAMP) for detection of coconut cadang-cadang viroid (CCCVd) variants in oil palm. J Oil Palm Res 32:453–463. https://doi.org/10.21894/jopr.2020.0049
Maizatul-Suriza M, Dickinson M, Idris AS (2019) Molecular characterization of Phytophthora palmivora responsible for bud rot disease of oil palm in Colombia. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2618-9
Maizatul-Suriza M, Suhanah J, Madihah AZ, Idris AS, Mohidin H (2021) Phylogenetic and pathogenicity evaluation of the marasmioid fungus Marasmius palmivorus causing fruit bunch rot disease of oil palm. For Pathol 51:e12660. https://doi.org/10.1111/efp.12660
Martin RR, James D, Lévesque CA (2000) Impacts of molecular diagnostic technologies on plant disease management. Annu Rev Phytopathol 38:207–239. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.38.1.207
Mazlan S, Jaafar NM, Wahab A, Rajandas H, Zulperi D (2019) Major diseases of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) in Malaysia. Pertanika J Sch Res Reviews 5:10–21
McKirdy S, Rodoni B, Moran J, Sharma S (2012) Microbial threat–a growing challenge for plant biosecurity. Microbiol Aust 33:12–14. https://doi.org/10.1071/MA12012
Miles TD, Martin FN, Coffey MD (2015) Development of rapid isothermal amplification assays for detection of Phytophthora spp. in plant tissue. Phytopathology 105:265–278. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-05-14-0134-R
Misman N, Samsulrizal NH, Noh AL, Wahab MA, Ahmad K, Ahmad Azmi NS (2022) Host range and control strategies of Phytophthora palmivora in Southeast Asia perennial crops. Pertanika J Trop Agric Sci 45:991
Mohamed Azni INA, Sundram S, Ramachandran V (2019) Pathogenicity of Malaysian Phytophthora palmivora on cocoa, durian, rubber and oil palm determines the threat of bud rot disease. For Pathol 49:e12557. https://doi.org/10.1111/efp.12557
Mori Y, Nagamine K, Tomita N, Notomi T (2001) Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:150–154. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2001.5921
Mori Y, Kitao M, Tomita N, Notomi T (2004) Real-time turbidimetry of LAMP reaction for quantifying template DNA. J Biochem Biophys Methods 59:145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbbm.2003.12.005
Mostowfizadeh-Ghalamfarsa R, Mirsoleimani Z (2012) Species-specific identification and detection of Phytophthora pistaciae, the causal agent of pistachio gummosis. Phytopathol Mediterr 52:30–45
Mumford R, Boonham N, Tomlinson J, Barker I (2006) Advances in molecular phytodiagnostics–new solutions for old problems. Eur J Plant Pathol 116:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-006-9037-0
Nagamine K, Hase T, Notomi T (2002) Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol Cell Probes 16:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1006/mcpr.2002.0415
Nair S, Manimekalai R, Ganga Raj P, Hegde V (2016) Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for detection of coconut root wilt disease and arecanut yellow leaf disease phytoplasma. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2078-4
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:e63–e63. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.12.e63
O’Gara E, Sangchote S, Fitzgerald L, Wood D, AngChing S, Guest DI, Drenth A (2004a) Infection biology of Phytophthora palmivora Butl. in Durio zibethinus L. (Durian) and responses induced by phosphonate. In: Drenth A, Guest DI (eds) Diversity and management of Phytophthora in Southeast Asia. Canberra, ACIAR, pp 42–52
O’Gara E, Vawdrey L, Martin T, Sangchote S, van Thanh H, Guest DI, Drenth A (2004b) Screening for resistance to Phytophthora. In: Drenth A (ed) Guest DI eds Diversity and management of Phytophthora in Southeast Asia. ACIAR, Canberra, Australia, pp 194–199
Opel KL, Chung D, McCord BR (2010) A study of PCR inhibition mechanisms using real time PCR. J Forensic Sci 55:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2009.01245.x
Parida M, Sannarangaiah S, Dash PK, Rao PVL, Morita K (2008) Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): a new generation of innovative gene amplification technique; perspectives in clinical diagnosis of infectious diseases. Rev Med Virol 18:407–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.593
Parveez GKA, Omar AR, Ahmad M-N, Mat Taib H, Mohd-Bakri MA, Sitti-Rahma AH, Tuan-Ismail TNM, Loh SK, Ong-Abdullah M, Zakaria K, Zainab I (2023) Oil palm economic performance in Malaysia and R&D progress in 2022. J Oil Palm Res 35:193–216. https://doi.org/10.21894/jopr.2023.0028
Pongpisutta R, Sangchote S (2004) Morphological and host range variability in Phytophthora palmivora from durian in Thailand. In: Drenth A, Guest DI (eds) Diversity and Management of Phytophthora in Southeast Asia. ACIAR, Canberra, p 53
Raftoyannis Y, Dick MW (2006) Zoospore encystment and pathogenicity of Phytophthora and Pythium species on plant roots. Microbiol Res 161:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2005.04.003
Ristaino JB, Saville AC, Paul R, Cooper DC, Wei Q (2020) Detection of Phytophthora infestans by loop-mediated isothermal amplification, real-time LAMP, and droplet digital PCR. Plant Dis 104:708–716. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-06-19-1186-re
Sagaff SAS, Ali NS, Mahyudin MM, Wong MY, Yusop MR (2022) Emerging and existing major leaf diseases of Hevea brasiliensis in Malaysia. J Curr Opin Crop Sci 3:34–47
Sankar MS, Nath VS, Misra RS, Lajapathy Jeeva M (2013) Incidence and identification of cassava tuber rot caused by Phytophthora palmivora. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 46:741–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2012.751284
Sarria GA, Torres GA, Aya HA, Ariza JG, Rodríguez J, Varón F, Vélez DC, Martínez G (2008) Phytophthora sp. es el responsable de las lesiones iniciales de la Pudrición del cogollo (PC) de la palma de aceite en Colombia. Revista Palmas 29:31–41
Sarria GA, Martinez G, Varon F, Drenth A, Guest DI (2016) Histopathological studies of the process of Phytophthora palmivora infection in oil palm. Eur J Plant Pathol 145:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0810-9
Si Ammour M, Bilodeau GJ, Tremblay DM, Van der Heyden H, Yaseen T, Varvaro L, Carisse O (2017) Development of real-time isothermal amplification assays for on-site detection of Phytophthora infestans in potato leaves. Plant Dis 101:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-12-16-1780-re
Siegieda DG, Panek J, Frąc M (2021) Shining a LAMP (Loop-mediated isothermal amplification) on the molecular detection of phytopathogens Phytophthora spp. and Phytophthora cactorum in strawberry fields. Pathogens 10:1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111453
Sun J, Najafzadeh MJ, Vicente V, Xi L, De Hoog GS (2010) Rapid detection of pathogenic fungi using loop-mediated isothermal amplification, exemplified by Fonsecaea agents of chromoblastomycosis. J Microbiol Methods 80:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2009.10.002
Surabattula R, Vejandla MP, Mallepaddi PC, Faulstich K, Polavarapu R (2013) Simple, rapid, inexpensive platform for the diagnosis of malaria by loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Exp Parasitol 134:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2013.03.031
Tashiro N, Uematsu S, Ide Y, Matsuzaki M (2012) First report of Phytophthora palmivora as a causal pathogen of citrus brown rot in Japan. J Gen Plant Pathol 78:233–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-012-0378-6
Tomita N, Mori Y, Kanda H, Notomi T (2008) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of gene sequences and simple visual detection of products. Nat Protoc 3:877–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.57
Tomlinson J (2013) In-field diagnostics using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. In: Dickinson M, Hodgetts J (eds) Phytoplasma: methods and protocols - methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-089-2_25
Tomlinson JA, Barker I, Boonham N (2007) Faster, simpler, more-specific methods for improved molecular detection of Phytophthora ramorum in the field. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4040–4047. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00161-07
Tomlinson JA, Dickinson MJ, Boonham N (2010) Rapid detection of Phytophthora ramorum and P. kernoviae by two-minute DNA extraction followed by isothermal amplification and amplicon detection by generic lateral flow device. Phytopathology 100:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-100-2-0143
Tomlinson JA, Ostoja-Starzewska S, Adams IP, Miano DW, Abidrabo P, Kinyua Z, Alicai T, Dickinson MJ, Peters D, Boonham N (2013) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid detection of the causal agents of cassava brown streak disease. J Virol Methods 191:148–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2012.07.015
Torres GA, Sarria GA, Varon F, Coffey MD, Elliott ML, Martinez G (2010) First report of bud rot caused by Phytophthora palmivora on African oil palm in Colombia. Plant Dis 94:1163–1163. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-94-9-1163A
Torres GA, Sarria GA, Martinez G, Varon F, Drenth A, Guest DI (2016) Bud rot caused by Phytophthora palmivora: a destructive emerging disease of oil palm. Phytopathology 106:320–329. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-09-15-0243-RVW
Tri MV, Van Hoa N, Minh Chau N, Pane A, Faedda R, De Patrizio A, Schena L, Olsson CHB, Wright SAI, Ramstedt M, Cacciola SO (2015) Decline of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) incited by Phytophthora palmivora in Vietnam. Phytopathol Mediterr 54:275. https://doi.org/10.14601/Phytopathol_Mediterr-15008
Tsai HL, Huang LC, Ann PJ, Liou RF (2006) Detection of orchid Phytophthora disease by nested PCR. Bot Stud 47:379–387
Tsao PH, Ocana G (1969) Selective isolation of species of Phytophthora from natural soils on an improved antibiotic medium. Nature 223:636–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/223636a0
Türkölmez Ş, Çiftçi O, Serçe ÇU, Derviş S (2015) First report of Phytophthora crown and root rot of cherry caused by Phytophthora palmivora in eastern Turkey. Can J Plant Pathol 37:390–396. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060661.2015.1055517
Ward E, Foster SJ, Fraaije BA, Mccartney HA (2004) Plant pathogen diagnostics: Immunological and nucleic acid-based approaches. Ann Appl Biol 145:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2004.tb00354.x
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 315–322
Winkworth RC, Nelson BCW, Bellgard SE, Probst CM, McLenachan PA, Lockhart PJ (2020) A LAMP at the end of the tunnel: a rapid, field deployable assay for the kauri dieback pathogen, Phytophthora agathidicida. PLoS ONE 15:e0224007. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224007
Wongwan T, Cheewangkoon R, Haituk S, Senwanna C (2021) New host record of Phytophthora palmivora causing black rot on Rhynchostylis gigantea in Thailand. Chiang Mai J Sci 48:942–951
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Malaysian Cocoa Board (MCB), Malaysian Rubber Board (MRB), and CENIPALMA, for providing the isolates and materials for the study and our colleagues at the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom and the Malaysian Palm Oil Board, Malaysia for their help and support throughout the research. The study was carried out with the support from the Malaysian Palm Oil Board (MPOB), Malaysia.
Funding
The study was carried out with funding from the Malaysian Palm Oil Board, Malaysia and the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study and preparation of the manuscript. Study conception and design was done by MM and MD. Acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data was performed by MM, BA and MAZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MM and was critically revised by MD. MAZ and BA contributed to design of some table and graphic. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maizatul-Suriza, M., Dickinson, M., Al-Jaf, B. et al. Cross-pathogenicity of Phytophthora palmivora associated with bud rot disease of oil palm and development of biomarkers for detection. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 55 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03860-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03860-5