Abstract
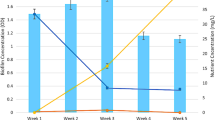
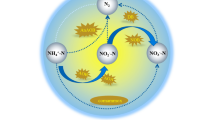
A mixed community of bacteria was enriched from groundwater contaminated with naphthalene as the sole carbon source. Based on the results of 16S rRNA sequences, Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas were the predominant species in the naphthalene-enriched culture. Different initial forms of nitrogen, including nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium, were beneficial to naphthalene degradation, which was considered second-order kinetics and naphthalene could be decreased by 94.68% during the incubation period of 30 days with an initial naphthalene concentration of 0.5 mg/L. These clear biogeochemical denitrification signals, the consumption and accumulation of nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium during the incubation period, suggested that naphthalene degradation may be coupled with denitrification and DNRA metabolism. Nitrate and nitrite were reduced mainly as electron acceptors, and ammonium was utilized by microorganisms as an important inorganic nutrient for their growth and reproduction, which promoted the degradation of naphthalene. The results of this study contributed to the removal pathway and transformational mechanism of nitrogen and reveal their involvement in the anaerobic biodegradation of naphthalene.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biache, C., Ouali, S., Cébron, A., Lorgeoux, C., Colombano, S., & Faure, P. (2017). Bioremediation of PAH-contamined soils: Consequences on formation and degradation of polar-polycyclic aromatic compounds and microbial community abundance. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 329, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.026.
Boyle, E. (2017). Nitrogen pollution knows no bounds. Science, 356(6339), 700. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan3242.
Cabral, L., & Júnior, G. V. L. (2018). Microbial functional responses to long-term anthropogenic impact in mangrove soils. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 160(30), 231–239.
Dagher, F., ., Déziel, E., ., Lirette, P., ., Paquette, G., ., Bisaillon, J. G., & Villemur, R., . (1997). Comparative study of five polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterial strains isolated from contaminated soils. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 43(4), 368–377.
Dan, M. N., Mihelcic, J. R., & Lueking, D. R. (1998). Biodegradation of three- and four-ring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons under aerobic and denitrifying conditions. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(17), 2633–2639.
Duc, H. D. (2016). Biodegradation of 3-chloroaniline by suspended cells and biofilm of Acinetobacter baumannii GFJ1. Applied Biological Chemistry, 59(5), 703–709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-016-0216-1.
Dutta, K., Shityakov, S., Khalifa, I., Mal, A., Moulik, S. P., Panda, A. K., et al. (2018). Effects of secondary carbon supplement on biofilm-mediated biodegradation of naphthalene by mutated naphthalene 1, 2-dioxygenase encoded by Pseudomonas putida strain KD9. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 357, 187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.05.024.
Gouveia, V., Almeida, C. M. R., Almeida, T., Teixeira, C., & Mucha, A. P. (2018). Indigenous microbial communities along the NW Portuguese coast: potential for hydrocarbons degradation and relation with sediment contamination. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 131, 620–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.04.063.
Hassanshahian, M., & Boroujeni, N. A. (2016). Enrichment and identification of naphthalene-degrading bacteria from the Persian Gulf. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 107(1), 59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.04.020.
Jegan, J., Vijayaraghavan, K., Senthilkumar, R., & Velan, M. (2010). Naphthalene degradation kinetics of Micrococcus sp., isolated from activated sludge. CLEAN: Soil, Air, Water, 38(9), 837–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.200900148.
Kong, F. X., Sun, G. D., & Liu, Z. P. (2018). Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil mesocosms by microbial/plant bioaugmentation: performance and mechanism. Chemosphere, 198, 83–91.
Li, C., Shuang, Z., Zhang, F., Zhi, W., Jiang, F., Wan, Y., et al. (2017). Response of microbial communities to supercritical CO 2 and biogeochemical influences on microbially mediated CO 2 -saline-sandstone interactions. Chemical Geology, 473, 1–9.
Napp, A. P., Pereira, J. E. S., Oliveira, J. S., Silva-Portela, R. C. B., Agnez-Lima, L. F., Peralba, M. C. R., et al. (2018). Comparative metagenomics reveals different hydrocarbon degradative abilities from enriched oil-drilling waste. Chemosphere, 209, 7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.068.
Oberoi, A. S., Philip, L., & Bhallamudi, S. M. (2015). Biodegradation of various aromatic compounds by enriched bacterial cultures: Part A–monocyclic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176(7), 1870–1888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1684-1.
Oudot, J., Merlin, F. X., & Pinvidic, P. (1998). Weathering rates of oil components in a bioremediation experiment in estuarine sediments. Marine Environmental Research, 45(2), 113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(97)00024-X.
Pathak, H., Kantharia, D., Malpani, A., & Madamwar, D. (2009). Naphthalene degradation by Pseudomonas sp. HOB1: In vitro studies and assessment of naphthalene degradation efficiency in simulated microcosms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(2), 1466–1473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.074.
Peng, R.-H., Xu, R.-R., Fu, X.-Y., Xiong, A.-S., Zhao, W., Tian, Y.-S., et al. (2011). Microarray analysis of the phytoremediation and phytosensing of occupational toxicant naphthalene. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189(1), 19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.114.
Ribeiro, H., Sousa, T. D., Santos, J. P., Sousa, A. G. G., Teixeira, C., Monteiro, M. R., et al. (2018). Potential of dissimilatory nitrate reduction pathways in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation. Chemosphere, 199, 54–67.
Rockne, K. J., Chee-Sanford, J. C., Sanford, R. A., Hedlund, B. P., Staley, J. T., & Strand, S. E. (2000). Anaerobic naphthalene degradation by microbial pure cultures under nitrate-reducing conditions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(4), 1595. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.4.1595-1601.2000.
Su, J. f., Zheng, S. C., Huang, T. l., Ma, F., Shao, S. C., Yang, S. F., et al. (2015). Characterization of the anaerobic denitrification bacterium Acinetobacter sp. SZ28 and its application for groundwater treatment. Bioresource Technology, 192, 654–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.020.
Sun, B., Zhang, L., Yang, L., Zhang, F., Norse, D., & Zhu, Z. (2012). Agricultural non-point source pollution in China: causes and mitigation measures. AMBIO, 41(4), 370–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-012-0249-6.
Wrenn Brian, A., Sarnecki Kathryn, L., Kohar Eugene, S., Lee, K., & Venosa Albert, D. (2006). Effects of nutrient source and supply on crude oil biodegradation in continuous-flow beach microcosms. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 132(1), 75–84. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2006)132:1(75).
Zafra, G., Taylor, T. D., Absalón, A. E., & Cortés-Espinosa, D. V. (2016). Comparative metagenomic analysis of PAH degradation in soil by a mixed microbial consortium. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 318, 702–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.060.
Zhang, X., Wu, Y., & Gu, B. (2015). Urban rivers as hotspots of regional nitrogen pollution. Environmental Pollution, 205, 139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.05.031.
Funding
This present work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41402207), and also supported by Science and Technology Project of Educational Department of Jilin Province for 13th Five Year Plan (JJKH20180159KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Zhang, F., Ma, Z. et al. Nitrogen Biogeochemistry of Anaerobic Biodegradation of Naphthalene. Water Air Soil Pollut 230, 222 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4276-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4276-9