Abstract
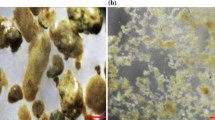
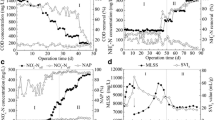
Batch experiment at COD/NO3 −-N ratio of 8.0 was conducted to investigate the initial performance of the simultaneous denitrification and methanogenesis (SDM) process and corresponding granular sludge (SDMGS). The results showed a high level of inhibition of methanogenesis activity with nitrate addition, and the particle size, settling performance, and morphologies of the SDMGS were also different from conventional methanogenesis granular sludge. The structure and succession of bacterial communities of the granular sludge during the initial stage of the SDM process were determined using the high-throughput sequencing method. Sequence analysis indicated that diversity of bacterial communities was significantly decreased due to nitrate addition. Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Spirochaetes were identified to be the dominant bacterial communities (96.06%) of the SDMGS samples, and microbes associated with anaerobic fermentation were reorganized. Alpha-, Beta- and Gamma-proteobacteria, and Bacteroides might be the sources of denitrificans. Lastly, species associated with animal and human infections, such as Enterobacteriaceae, Bacteroides, and other common human enteric pathogens, were found to be recovered during the initial stage. Short-term assessment of bacterial communities of the SDMGS would strengthen understandings of the effects of nitrate contamination in water bodies and provide vital guidance for operation of nitrate-containing wastewater treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akunna, J. C., Bizeau, C., & Moletta, R. (1992). Denitrification in anaerobic digesters: possibilities and influence of wastewater COD/N–NOX ratio. Environmental Technology, 13, 825–836. doi:10.1080/09593339209385217.
Akunna, J. C., Bizeau, C., & Moletta, R. (1993). Nitrate and nitrite reductions with anaerobic sludge using various carbon sources: glucose, glycerol, acetic acid, lactic acid and methanol. Water Research, 27, 1303–1312. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(93)90217-6.
Andalib, M., Nakhla, G., McIntee, E., & Zhu, J. (2011). Simultaneous denitrification and methanogenesis (SDM): review of two decades of research. Desalination, 279, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.06.018.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Chen, J., Taniguchi, M., Liu, G., Miyaoka, K., Onodera, S.-i., Tokunaga, T., & Fukushima, Y. (2007). Nitrate pollution of groundwater in the Yellow River delta, China. Hydrogeology Journal, 15, 1605–1614. doi:10.1007/s10040-007-0196-7.
Chen, S., Sun, D., & Chung, J.-S. (2009). Simultaneous methanogenesis and denitrification of aniline wastewater by using anaerobic–aerobic biofilm system with recirculation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169, 575–580. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.03.132.
Collado, L., et al. (2010). Occurrence and diversity of Arcobacter spp. along the Llobregat River catchment, at sewage effluents and in a drinking water treatment plant. Water Research, 44, 3696–3702. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.04.002.
Del Pozo, R., & Diez, V. (2003). Organic matter removal in combined anaerobic–aerobic fixed-film bioreactors. Water Research, 37, 3561–3568. doi:10.1016/s0043-1354(03)00273-2.
Hendriksen, H. V., & Ahring, B. K. (1996a). Combined removal of nitrate and carbon in granular sludge: substrate competition and activities. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 69, 33–39. doi:10.1007/bf00641609.
Hendriksen, H. V., & Ahring, B. K. (1996b). Integrated removal of nitrate and carbon in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor: operating performance. Water Research, 30, 1451–1458. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(96)00041-3.
Herlemann, D. P., et al. (2009). Genomic analysis of “Elusimicrobium minutum”, the first cultivated representative of the phylum “Elusimicrobia” (formerly termite group 1). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 2841–2849. doi:10.1128/AEM.02698-08.
Huws, S. A., et al. (2011). As yet uncultured bacteria phylogenetically classified as Prevotella, Lachnospiraceae incertae sedis and unclassified Bacteroidales, Clostridiales and Ruminococcaceae may play a predominant role in ruminal biohydrogenation. Environmental Microbiology, 13, 1500–1512. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02452.x.
Karim, K., & Gupta, S. K. (2003). Continuous biotransformation and removal of nitrophenols under denitrifying conditions. Water Research, 37, 2953–2959. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00073-3.
Liao, R., Shen, K., Li, A. M., Shi, P., Li, Y., Shi, Q., & Wang, Z. (2013). High-nitrate wastewater treatment in an expanded granular sludge bed reactor and microbial diversity using 454 pyrosequencing analysis. Bioresource Technology, 134, 190–197. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.057.
Lin, Y.-F., & Chen, K.-C. (1995). Denitrification and methanogenesis in a co-immobilized mixed culture system. Water Research, 29, 35–43. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(94)00144-v.
Liu, X., et al. (2013). Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature, 494, 459–462. doi:10.1038/nature11917.
Logares, R., Haverkamp, T. H., Kumar, S., Lanzen, A., Nederbragt, A. J., Quince, C., & Kauserud, H. (2012). Environmental microbiology through the lens of high-throughput DNA sequencing: synopsis of current platforms and bioinformatics approaches. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 91, 106–113. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2012.07.017.
Nishiyama, T., Ueki, A., Kaku, N., Watanabe, K., & Ueki, K. (2009). Bacteroides graminisolvens sp. nov., a xylanolytic anaerobe isolated from a methanogenic reactor treating cattle waste. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 59, 1901–1907. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.008268-0.
Pohlschroeder, M., Leschine, S. B., & Canale-Parola, E. (1994). Spirochaeta caldaria sp. nov., a thermophilic bacterium that enhances cellulose degradation by Clostridium thermocellum. Archives of Microbiology, 161, 17–24. doi:10.1007/bf00248889.
Qu, J., & Fan, M. (2010). The current state of water quality and technology development for water pollution control in China. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 519–560. doi:10.1080/10643380802451953.
Ruiz, G., Jeison, D., & Chamy, R. (2006). Development of denitrifying and methanogenic activities in USB reactors for the treatment of wastewater: effect of COD/N ratio. Process Biochemistry, 41, 1338–1342. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.01.007.
Show, K. Y., Lee, D. J., & Pan, X. (2013). Simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen-sulfur-carbon: recent advances and challenges. Biotechnology Advances, 31, 409–420. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.12.006.
Su, X., Wang, H., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Health risk assessment of nitrate contamination in groundwater: a case study of an agricultural area in Northeast China. Water Resources Management, 27, 3025–3034. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0330-3.
Sun, H., Peng, Y., & Shi, X. (2015). Advanced treatment of landfill leachate using anaerobic-aerobic process: organic removal by simultaneous denitritation and methanogenesis and nitrogen removal via nitrite. Bioresource Technology, 177, 337–345. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.152.
Sun, Y., Zuo, J., Chen, L., & Wang, Y. (2008). Eubacteria and Archaea community of simultaneous methanogenesis and denitrification granular sludge. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 20, 626–631. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62104-X.
Tugtas, A. E., & Pavlostathis, S. G. (2007). Inhibitory effects of nitrogen oxides on a mixed methanogenic culture. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 96, 444–455. doi:10.1002/bit.21105.
Ueki, A., Akasaka, H., Suzuki, D., & Ueki, K. (2006). Paludibacter propionicigenes gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel strictly anaerobic, Gram-negative, propionate-producing bacterium isolated from plant residue in irrigated rice-field soil in Japan. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 56, 39–44. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.63896-0.
Wang, F., Jin, X., Yang, S., Liu, Y., & Chen, X. (2014). A control strategy for promoting the stability of denitrifying granular sludge in upflow sludge blankets. Environmental Technology, 35, 52–59. doi:10.1080/09593330.2013.808250.
Wolinska, A., Szafranek-Nakonieczna, A., Banach, A., Blaszczyk, M., & Stepniewska, Z. (2016). The impact of agricultural soil usage on activity and abundance of ammonifying bacteria in selected soils from Poland. Springerplus, 5, 565. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-2264-8.
Yamada, T., Sekiguchi, Y., Imachi, H., Kamagata, Y., Ohashi, A., & Harada, H. (2005). Diversity, localization, and physiological properties of filamentous microbes belonging to Chloroflexi subphylum I in mesophilic and thermophilic methanogenic sludge granules. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 7493–7503. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.11.7493-7503.2005.
Zhang, T., Shao, M. F., & Ye, L. (2012). 454 pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity of activated sludge from 14 sewage treatment plants. The ISME Journal, 6, 1137–1147. doi:10.1038/ismej.2011.188.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31570568), the State Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Engineering in China (No. 201535), and Guangdong High-level Talent Project (No. 201339). The authors are thankful to the editors and all the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, XH., Wan, J., Ma, Y. et al. Structure and Succession of Bacterial Communities of the Granular Sludge during the Initial Stage of the Simultaneous Denitrification and Methanogenesis Process. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3168-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3168-5