Abstract
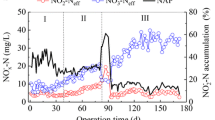
The aim of this study was to develop a simple operation strategy for the cultivation of partial nitrification granules (PNGs) treating an autotrophic medium. For this strategy, aerobic granular sludge adapted to high concentration organics removal was seeded in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) with a height/diameter ratio of 3.8, and the ratio of organics to the ammonia nitrogen-loading rate (C/N ratio) in the influent was employed as the main control parameter to start up the partial nitrification process. After 86 days of operation, the nitrite accumulation rate reached 1.44 kg/(m3 day) in the SBR, and the removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen (NH4 +-N) was over 95 %. The PNGs showed a dense and compact structure, with an excellent settling ability, a typical extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) composition, and a high ammonia oxidation activity. The high-throughput pyrosequencing results indicated that the microbial community structure in the granules was significantly influenced by the C/N ratio, and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), including the r-strategist Nitrosomonas and k-strategist Nitrosospira genre, which accounted for approximately 40 % of the total biomass at the end of operation. The effective suppression of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) growth was attributed to oxygen competition on the granular surface among functional bacteria, as well as the high free ammonia or free nitrous acid concentrations during the aeration period.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ (2008) Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J Hazard Mater 154:1120–1126
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2008) Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule. Water Res 42:1644–1650
Amato KR, Yeoman CJ, Kent A, Righini N, Carbonero F, Estrada A, Gaskins HR, Stumpf RM, Yildirim S, Torralba M, Gillis M, Wilson BA, Nelson KE, White BA, Leigh SR (2013) Habitat degradation impacts black howler monkey (Alouatta pigra) gastrointestinal microbiomes. Isme J 7:1344–1353
APHA (1998) Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater, 20th ed. American Public Health Association, New York
Bartroli A, Perez J, Carrera J (2010) Applying ratio control in a continuous granular reactor to achieve full nitritation under stable operating conditions. Environ Sci Technol 44:8930–8935
Bassin JP, Kleerebezem R, Dezotti M, van Loosdrecht MCM (2012a) Measuring biomass specific ammonium, nitrite and phosphate uptake rates in aerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 89:1161–1168
Bassin JP, Kleerebezem R, Rosado AS, van Loosdrecht MCM, Dezotti M (2012b) Effect of different operational conditions on biofilm development, nitrification, and nitrifying microbial population in moving-bed biofilm reactors. Environ Sci Technol 46:1546–1555
Chen FY, Liu YQ, Tay JH, Ning P (2015) Rapid formation of nitrifying granules treating high-strength ammonium wastewater in a sequencing batch reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:4445–4452
Chiu ZC, Chen MY, Lee DJ, Wang CH, Lai JY (2007) Oxygen diffusion and consumption in active aerobic granules of heterogeneous structure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:685–691
Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A, Wojnowska-Baryła I (2011) Nitrifying granules cultivation in a sequencing batch reactor at a low organics-to-total nitrogen ratio in wastewater. Folia Microbiol 56:201–208
Dennis KL, Wang Y, Blatner NR, Wang S, Saadalla A, Trudeau E, Roers A, Weaver CT, Lee JJ, Gilbert JA, Chang EB, Khazaie K (2013) Adenomatous polyps are driven by microbe-instigated focal inflammation and are controlled by IL-10-producing T cells. Cancer Res 73:5905–5913
Ford DL, Kachtick JW (1980) Comprehensive analysis of nitrification of chemical processing wastewaters. J Water Pollut Control Fed 52:2726–2746
Ganigué R, Volcke EIP, Puig S, Balaguer MD, Colprim J (2012) Impact of influent characteristics on a partial nitritation SBR treating high nitrogen loaded wastewater. Bioresour Technol 111:62–69
Grady CPL, Daigger GT, Love NG, Filipe CDM (2011) Biological wastewater treatment, 3rd ed. CRC Press, London, pp. 99–102
Groeneweg J, Sellner B, Tappe W (1994) Ammonia oxidation in nitrosomonas at NH3 concentrations near km: effects of pH and temperature. Water Res 28:2561–2566
Isanta E, Reino C, Carrera J, Perez J (2015) Stable partial nitritation for low-strength wastewater at low temperature in an aerobic granular reactor. Water Res 80:149–158
Jemaat Z, Suarez-Ojeda ME, Perez J, Carrera J (2014) Partial nitritation and o-cresol removal with aerobic granular biomass in a continuous airlift reactor. Water Res 48:354–362
Kim DJ, Seo DW, Lee SH, Shipin O (2012) Free nitrous acid selectively inhibits and eliminates nitrite oxidizers from nitrifying sequencing batch reactor. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35:441–448
Kishida N, Saeki G, Tsuneda S, Sudo R (2012) Rapid start-up of a nitrifying reactor using aerobic granular sludge as seed sludge. Water Sci Technol 65:581–588
Lackner S, Gilbert EM, Vlaeminck SE, Joss A, Horn H, van Loosdrecht MCM (2014) Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences—an application survey. Water Res 55:292–303
Li AJ, Yang SF, Li XY, Gu JD (2008) Microbial population dynamics during aerobic sludge granulation at different organic loading rates. Water Res 42:3552–3560
Liang YH, Li D, Zeng HP, Zhang CD, Zhang J (2015) Rapid start-up and microbial characteristics of partial nitrification granular sludge treating domestic sewage at room temperature. Bioresour Technol 196:741–745
Liu YQ, Wu WW, Tay JH, Wang JL (2008) Formation and long-term stability of nitrifying granules in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour Technol 99:3919–3922
Ma B, Bao P, Wei Y, Zhu GB, Yuan ZG, Peng YZ (2015) Suppressing nitrite-oxidizing bacteria growth to achieve nitrogen removal from domestic wastewater via anammox using intermittent aeration with low dissolved oxygen. Sci Rep 5:13048–13057
Ma B, Wang SY, Cao SB, Miao YY, Jia FX, Du R, Peng YZ (2016) Biological nitrogen removal from sewage via anammox: recent advances. Bioresour Technol 200:981–990
Matsumoto S, Ishikawa D, Saeki G, Aoi Y, Tsuneda S (2010a) Microbial population dynamics and community structure during the formation of nitrifying granules to treat ammonia-rich inorganic wastewater. Microbes Environ 25:164–170
Matsumoto S, Katoku M, Saeki G, Terada A, Aoi Y, Tsuneda S, Picioreanu C, van Loosdrecht MCM (2010b) Microbial community structure in autotrophic nitrifying granules characterized by experimental and simulation analyses. Environ Microbiol 12:192–206
Mobarry BK, Wagner M, Urbain V, Rittmann BE, Stahl DA (1997) Phylogenetic probes for analyzing abundance and spatial organization of nitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:815–815
Mosquera-Corral A, González F, Campos JL, Méndez R (2005) Partial nitrification in a SHARON reactor in the presence of salts and organic carbon compounds. Process Biochem 40:3109–3118
Park S, Bae W, Rittmann BE (2010) Operational boundaries for nitrite accumulation in nitrification based on minimum/maximum substrate concentrations that include effects of oxygen limitation, pH, and free ammonia and free nitrous acid inhibition. Environ Sci Technol 44:335–342
Perez J, Lotti T, Kleerebezem R, Picioreanu C, van Loosdrecht MC (2014) Outcompeting nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in single-stage nitrogen removal in sewage treatment plants: a model-based study. Water Res 66:208–218
Rathnayake RM, Oshiki M, Ishii S, Segawa T, Satoh H, Okabe S (2015) Effects of dissolved oxygen and pH on nitrous oxide production rates in autotrophic partial nitrification granules. Bioresour Technol 197:15–22
Shi XY, Sheng GP, Li XY, Yu HQ (2010) Operation of a sequencing batch reactor for cultivating autotrophic nitrifying granules. Bioresour Technol 101:2960–2964
Show KY, Lee DJ, Tay JH (2012) Aerobic granulation: advances and challenges. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167:1622–1640
Sinha B, Annachhatre AP (2006) Partial nitrification—operational parameters and microorganisms involved. Rev Environ Sci Bio 6:285–313
Van H, Stijin WH, Vandeweyer HJP, Meesschaert BD, Vanrolleghem PA, Dejans P, Dumoulin A (2010) Engineering aspects and practical application of autotrophic nitrogen removal from nitrogen rich streams. Chem Eng J 162:1–20
Vázquez-Padín JR, Figueroa M, Campos JL, Mosquera-Corral A, Méndez R (2010) Nitrifying granular systems: a suitable technology to obtain stable partial nitrification at room temperature. Sep Purif Technol 74:178–186
Wan CL, Sun SP, Lee DJ, Liu X, Wang L, Yang X, Pan XL (2013) Partial nitrification using aerobic granules in continuous-flow reactor: rapid startup. Bioresour Technol 142:517–522
Wan CL, Zhang QL, Lee DJ, Wang YY, Li JN (2014) Long-term storage of aerobic granules in liquid media: viable but non-culturable status. Bioresour Technol 166:464–470
Wei D, Xue XD, Yan L, Sun M, Zhang G, Shi L, Du B (2014) Effect of influent ammonium concentration on the shift of full nitritation to partial nitrification in a sequencing batch reactor at ambient temperature. Chem Eng J 235:19–26
Wu L, Peng CY, Peng YZ, Li LY, Wang SY, Ma Y (2012) Effect of wastewater COD/N ratio on aerobic nitrifying sludge granulation and microbial population shift. J Environ Sci 24:234–241
Wu CY, Peng YZ, Wang SY, Ma Y (2010) Enhanced biological phosphorus removal by granular sludge: from macro- to micro-scale. Water Res 44:807–814
Wu DL, Shen YH, Ding AQ, Mahmood Q, Liu S, Tu QP (2013) Effects of nanoscale zero-valent iron particles on biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal and microorganisms in activated sludge. J Hazard Mater 262:649–655
Zhou Y, Oehmen A, Lim M, Vadivelu V, Ng WJ (2011) The role of nitrite and free nitrous acid (FNA) in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res 45:4672–4682
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (CN) (51308367, 51578353) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education (14KJB610009, 15KJB610013). We also acknowledge the support from the Preponderant Discipline Construction Project in higher education of Jiangsu Province, China. Jianfang Wang received the Jiangsu Government Scholarship for overseas studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 287 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Qian, F., Liu, X. et al. Cultivation and characteristics of partial nitrification granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor inoculated with heterotrophic granules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 9381–9391 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7797-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7797-9