Abstract
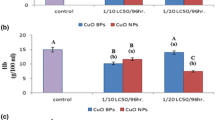
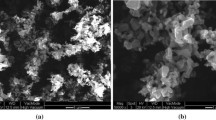
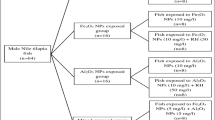
This study was carried out to comparatively evaluate the bioaccumulation potency of Zn bulk and nanoparticles in Oreochromis niloticus and to investigate the induced hematological and histological alterations. Fish were exposed to ½ LC50/96 h values of both bulk and nano Zn meal for 7, 14, and 28 days. Concerning metal bioaccumulation factor (BAF), the data displayed that zinc nanoparticles (Zn NPs) had more efficiency to penetrate the studied tissues such as the liver, kidneys, gills, skin, and muscle. Hematological parameters named red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin (Hb), and hematocrit (Hct) values were altered in Zn NPs treated groups after 14th and 28th days while these hematological parameters recovered to some extent in bulk particles (BPs) treated groups at the end of the experimental period. The changes in hematological parameters were found to be time dependent. Blood indices such as mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) revealed the presence of normocytic normochromic anemia in the studied groups at the most exposure periods except microcytic hypochromic anemia at the 7th day of bulk particles exposed fish. Based on histological end points, several alterations in the gills, liver, and kidney tissues were observed. Severely deformations were observed at NPs treated fish groups which varied between adaptive changes to tissue damage at the end of exposure period. The deformations were recorded to be increased in NPs exposed fish compared to BPs treated fish throughout the study periods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Khalek, A. A. (2015). Risk assessment, bioaccumulation of metals and histopathological alterations in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) facing degraded aquatic conditions. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 94, 77–83.
Abdel-Khalek, A. A., Kadry, M., Hamed, A., & Marie, M.-A. S. (2015). Ecotoxicological impacts of zinc metal in comparison to its nanoparticles in Nile tilapia; Oreochromis niloticus. Journal of Basic and Applied Zoology, 72, 113–125.
Affonso, E. G., Polez, V. L. P., Corrêa, C. F., Mazon, A. F., Araojo, M. R. R., Moraes, G., & Rantin, F. T. (2002). Blood parameters and metabolites in the teleost fish Colossoma macropomum exposed to sulfide or hypoxia. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 133, 375–382.
Al-Bairuty, G. A., Shaw, B. J., Handy, R. D., & Henry, T. B. (2013). Histopathological effects of waterborne copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on the organs of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquatic Toxicology, 126, 104–115.
Alkaladi, A., Nasr El-Deen, N. A. M., Afifim, M., & Abu Zinadah, O. A. (2015). Hematological and biochemical investigations on the effect of vitamin E and C on Oreochromis niloticus exposed to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 22, 556–563.
American Public Health Association (APHA). (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. New York: American Water Works Association.
Atli, G., Ariyurek, S. Y., Kanak, E. G., & Canli, M. (2015). Alterations in the serum biomarkers belonging to different metabolic systems of fish (Oreochromis niloticus) after Cd and Pb exposures. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 40, 508–515.
Auffan, M., Rose, J., Bottero, J. Y., Lowry, G. V., Jolivet, J. P., & Wiesner, M. (2009). Towards a definition of inorganic nanoparticles from an environmental, health and safety perspective. Nature Nanotechnology, 4, 634–641.
Bilberg, K., Malte, H., Wang, T., & Baatrup, E. (2010). Silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate cause respiratory stress in eurasian perch (Perca fluviatilis). Aquatic Toxicology, 96, 159–165.
Bour, A., Mouchet, F., Silvestre, J., Gauthier, L. & Pinelli, E. (2014). Environmentally relevant approaches to assess nanoparticles ecotoxicity: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1–44.
Carleton, M., Drary, Y., Wallington, E. A., & Cammeron, H. (1967). Carleton’s histological technique (4th ed.). New York, Toronto: Oxford Univ. Press.
Chang, Y., Zhang, M., Xia, L., Zhang, J., & Xing, G. (2012). The toxic effects and mechanisms of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Materials, 5, 2850–2871.
Ciji, P. P., & Nandan, S. B. (2014). Toxicity of copper and zinc to Puntius parrah (day, 1865). Marine Environmental Research, 93, 38–46.
Dacie, J. V., & Lewis, S. M. (1991). Practical hematology (Chap. 5 7th ed., p. 79). Edinburgh: Chuchill Livigstone.
Drabkin, D. L. (1964). Spectrophotometric studies: XIV. The crystallographic and optical properties of the hemoglobin of man in comparison with those of other species. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 164, 703–723.
Fahmy, S. R., Abdel-Ghaffar, F., Bakry, F. A., & Sayed, D. A. (2014). Ecotoxicological effect of sublethal exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles on freshwater snail Biomphalaria alexandrina. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67, 192–202.
Foulkes, E. C. (1990). Biological effects of heavy metals (Vol 1 and 2). Boca Raton: CRC press.
Garcia, A. J., Rodriguez, S. N., Misra, S. K., Valsami, J. E., Croteau, M. N., Luoma, S. N., & Rainbow, P. S. (2014). Toxicity and accumulation of silver nanoparticles during development of the marine polychaete platynereis dumerilii. Science of the Total Environment, 476, 688–695.
Ghosh, D., & Mandal, D. K. (2012). Histopathological effects and bioaccumulation of mercury in the kidney of an Indian major Carp, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 89, 479–483.
Gupta, P. K. (1977). Haematological techniques. 4th edn Syndicate, India, pp. 231.
Hseu, Z. Y. (2004). Evaluating heavy metal contents in nine composts using four digestion methods. Bioresource Technology, 95, 53–59.
Issac, R. A., & Kerber, J. D. (1971). Atomic absorption and flame photometry. Techniques and uses in soil, plant and water analysis. In L. M. Walsh (Ed.), Instrumental methods for analysis of soil and plant tissue (pp. 17–37). Madison: Soil Science Society of America-Agronomy Society of America Inc.
Joshi, P. K., Bose, M., & Harish, D. (2002). Haematological changes in the blood of Clarias batrachus exposed to mercuric chloride. Journal of Ecotoxicology and Environmental Monitoring, 12, 119–122.
Kim, J.-H., & Kang, J.-C. (2015). The lead accumulation and hematological findings in juvenile rock fish Sebastes schlegelii exposed to the dietary lead (II) concentrations. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 115, 33–39.
Kori-Siakpere, O., & Ubogu, E. O. (2008). Sublethal haematological effects of zinc on the freshwater fish, Heteroclarias sp. (Osteichthyes: Clariidae). African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 2068–2073.
Lee, S.-W., Kim, S.-M., & Choi, J. (2009). Genotoxicity and ecotoxicity assays using the freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna and the larva of the aquatic midge Chironomus riparius to screen the ecological risks of nanoparticle exposure. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 28, 86–91.
Luoma, S. N., Cain, D. J., & Rainbow, P. S. (2010). Calibrating biomonitors to ecological disturbance: a new technique for explaining metal effects in natural waters. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 6, 199–209.
Mela, M., Randi, M. A. F., Ventura, D. F., Carvalho, C. E. V., Pelletier, E., & Oliveira Ribeiro, C. A. (2007). Effects of dietary methylmercury on liver and kidney histology in the neotropical fish Hoplias malabaricus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 68, 426–435.
Moiseenko, T. I., & Kudryavtseva, L. P. (2001). Trace metal accumulation and fish pathologies in areas affected by mining and metallurgical enterprises in the Kola region, Russia. Environmental Pollution, 114, 285–297.
Muñoz, L., Weber, P., Dressler, V., Baldisserotto, B., & Vigliano, F. A. (2015). Histopathological biomarkers in juvenile silver catfish (Rhamdia quelen) exposed to a sublethal lead concentration. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 241–247.
Ostaszewska, T., Chojnacki, M., Kamaszewski, M., & Sawosz-Chwalibóg, E. (2016). Histopathological effects of silver and copper nanoparticles on the epidermis, gills, and liver of Siberian sturgeon. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 23(2), 1621–1633.
Pacheco, M., & Santos, M. A. (2002). Biotransformation, genotoxic and histopathological effects of environmental contaminants in European eel, Anguilla anguilla L. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 53, 331–347.
Rundle, A., Robertson, A. B., Blay, A. M., Butler, K. M. A., Callaghan, N. I., Dieni, C. A., Tyson, J., & MacCormack, T. J. (2016). Cerium oxide nanoparticles exhibit minimal cardiac and cytotoxicity in the freshwater fish Catostomus commersonii. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C, 181–182, 19–26.
Sanchez-Valle, V., Chavez-Tapia, N. C., Uribe, M., & Mendez-Sanchez, N. (2012). Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: a review. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 19, 4850–4860.
Saravanan, M., Kumar, K. P., & Ramesh, M. (2011). Haematological and biochemical responses of freshwater teleost fish Cyprinus carpio (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes) during acute and chronic sublethal exposure to lindane. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 100, 206–211.
Shaluei, F., Hedayati, A., Jahanbakhshi, A., Kolangi, H., & Fotovat, M. (2013). Effect of subacute exposure to silver nanoparticle on some hematological and plasma biochemical indices in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Human and Experimental Toxicology, 32(12), 1270–1277.
Singhal, R. N., & Jain, M. (1997). Cadmium induced changes in the histology of Kidneys of common carp, Cyprinus carpio (Cyprinidae). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 58, 456–461.
Sirelkhatim, A., Mahmud, S., Seeni, A., Kaus, N. H. M., Ann, L. C., Bakhori, S. K. M., Hasan, H., & Mohamad, D. (2015). Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Letters, 7(3), 219–242.
Tabassum, H., Ashafaq, M., Khan, J., Shah, M. Z., Raisuddin, S., & Parvez, S. (2016). Short term exposure of pendimethalin induces biochemical and histological perturbations in liver, kidney and gill of freshwater fish. Ecological Indicators, 63, 29–36.
Uysal, K., Köse, E., Bülbül, M., Dönmez, M., Erdoğan, Y., Koyun, M., Ömeroğlu, Ç., & Özmal, F. (2009). The comparison of heavy metal accumulation ratios of some fish species in Enne Dame Lake (Kütahya/Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 157, 355–362.
Velma, V., & Tchounwou, P. B. (2010). Chromium induced biochemical, genotoxic and histopathologic effects in liver and kidney of goldfish, Carassius auratus. Mutation Research, 698, 43–51.
Witeska, M., & Kościuk, B. (2003). The changes in common carp blood after short-term zinc exposure. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 10, 284–286.
Zauke, G. P., Savinov, V. M., Ritterhoff, J., & Savinova, T. (1999). Heavy metals in fish from the Barents Sea (summer, 1994). Science of the Total Environment, 227, 161–173.
Zhang, L., Shi, Z., Jiang, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, F., & Huang, X. (2015). Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in marine organisms in east and west Guangdong coastal regions, South China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101, 930–937.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the Faculty of Science, Cairo University for their partly financial support of this work through the provision of chemicals necessary to complete this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This manuscript complies with the ethical rules applicable for this journal.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that he has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Khalek, A.A., Hamed, A. & Marie, MA. The Accumulation Potency of Bulk and Nano Zinc Metal and Their Impacts on the Hematological and Histological Perturbations of Oreochromis niloticus . Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 206 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2908-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2908-x