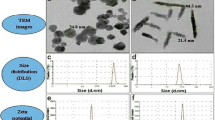
Abstract
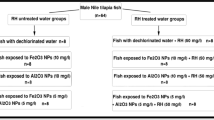
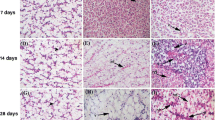
The present study was the first trial to use the adsorptive capacity of the rice husk to reduce the toxicological impacts of the iron and aluminum oxides nanoparticles on Oreochromis niloticus. The fish groups were subjected to a sub-lethal concentration (10 mg/l) of both metal oxides nanoparticles (in single and combined doses) with and without rice husk water treatment for 7 days. The bioaccumulation of iron and aluminum metals showed a significant increase (p < 0.05) compared with the control groups. The results revealed a tissue-specific distribution pattern as following: liver > kidney > gills > skin > muscles for iron and liver > gills > kidney > skin > muscles for aluminum. Moreover, the bioaccumulation potency of iron was greater than that of aluminum in all studied tissues. Both studied nanoparticles caused a decrease in the red blood cells count, hemoglobin content, hematocrit values, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, with an obvious increase in mean corpuscular volume and mean corpuscular hemoglobin. While all those parameters were restored more or less to that of control groups after rice husk water treatment. The histological studies of the gills, liver, and kidneys showed different histopathological alterations ranging from compensatory histological changes in the rice husk–treated groups to severe histopathological damage in the untreated groups. Based on the all studied biomarkers, the rice husk is a good absorbent for both studied nanoparticles individually or combined.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, S., Javed, M., Ahmad Khan, H., & Rahman, K. (2018). Toxicity And Bioaccumulation Of Metals (Al And Co) In Three Economically Important Carnivorous Fish Species Of Pakistan. International Journal Of Agriculture And Biology, 20(5), 1123–1128.
Abdel-Khalek, A. A. (2015). Antioxidant Responses And Nuclear Deformations In Freshwater Fish, Oreochromis Niloticus, Facing Degraded Environmental Conditions. Bulletin Of Environmental Contamination And Toxicology, 94(6), 701–708.
Abdel-Khalek, A. A. (2016). Comparative Evaluation Of Genotoxic Effects Induced By Cuo Bulk And Nano-Particles In Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus. Water, Air And Soil Pollution, 227, 35.
Abdel-Khalek, A. A. (2018). Chronic Exposure To Water Of Lake Qaroun Induced Metal-Related Testicular Damage And Endocrine Disruption In Male Fish. Biological Trace Element Research, 185(1), 197–204.
Abdel-Khalek, A. A., Badran, S. R., & Marie, M.-A. S. (2016a). Toxicity Evaluation Of Copper Oxide Bulk And Nanoparticles In Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis Niloticus, Using Hematological, Bioaccumulation And Histological Biomarkers. Fish Physiology And Biochemistry, 42, 1225–1236.
Abdel-Khalek, A. A., Hamed, A., & Marie, M.-A. S. (2016b). The Accumulation Potency Of Bulk And Nano Zinc Metal And Their Impacts On The Hematological And Histological Perturbations Of Oreochromis Niloticus. Water, Air And Soil Pollution, 227, 206.
Abdel-Khalek, A. A., Elhaddad, E., Mamdouh, S., & Marie, M. S. (2018). The Chronic Exposure To Discharges Of Sabal Drain Induces Oxidative Stress And Histopathological Alterations In Oreochromis Niloticus. Bulletin Of Environmental Contamination And Toxicology, 101(1), 92–98.
Adam, V., & Nowack, B. (2017). European country-specific probabilistic assessment of nanomaterial flows towards landfilling, incineration and recycling. Environmental Science: Nano, 4(10), 1961–1973.
Antunes, A. M., Rocha, T. L., Pires, F. S., de Freitas, M. A., Leite, V. R. M. C., Arana, S., Moreira, P. C., & Sabóia-Morais, S. M. T. (2017). Gender-specific histopathological response in guppies Poecilia reticulata exposed to glyphosate or its metabolite aminomethylphosphonic acid. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 37(9), 1098–1107.
American Public 439 Health Association (APHA). (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. New York: American Water Works Association.
Arosio, P., & Levi, S. (2010). Cytosolic and mitochondrial ferritins in the regulation of cellular iron homeostasis and oxidative damage. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1800, 783–792.
Ates, M., Demir, V., Arslan, Z., Kaya, H., Yılmaz, S., & Camas, M. (2016). Chronic exposure of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) to iron oxide nanoparticles: effects of particle morphology on accumulation, elimination, hematology and immune responses. Aquatic Toxicology, 177, 22–32.
Barbier, O., Jacquillet, G., Tauc, M., Cougnon, M., & Poujeol, P. (2005). Effect of heavy metals on, and handling by, the kidney. Nephron Physiology, 99, 105–110.
Benavides, M., Fernández-Lodeiro, J., Coelho, P., Lodeiro, C., & Diniz, M. S. (2016). Single and combined effects of aluminum (Al2O3) and zinc (ZnO) oxide nanoparticles in a freshwater fish, Carassius auratus. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 24578–24591.
Bernet, D., Schmidt, H., Meier, W., Burkhardt-Holm, P., & Wahli, T. (1999). Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. Journal of Fish Diseases, 22(1), 25–34.
Canli, E. G., Dogan, A., & Canli, M. (2018). Serum biomarker levels alter following nanoparticle (Al2O3, CuO, TiO2) exposures in freshwater fish (Oreochromis niloticus). Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 62, 181–187.
Capaldo, A., Gay, F., & Laforgia, V. (2019). Changes in the gills of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla) after chronic exposure to environmental cocaine concentration. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 169, 112–119.
Chen, P. J., Tan, S. W., & Wu, W. L. (2012). Stabilization or oxidation of nanoscale zerovalent iron at environmentally relevant exposure changes bioavailability and toxicity in medaka fish. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(15), 8431–8439.
Chupani, L., Niksirat, H., Velíšek, J., Stará, A., Hradilová, Š., Kolařík, J., Panáček, A., & Zusková, E. (2018). Chronic dietary toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.): tissue accumulation and physiological responses. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 147, 110–116.
Ciji, P. P., & Nandan, S. B. (2014). Toxicity of copper and zinc to Puntius parrah (day, 1865). Marine Environmental Research, 93, 38–46.
Dacie, J. V. & Lewis, S. M. (1991). Practical hematology. chuchill. Livigstone, Chap.5, 79.
Dar, Z. A., & Borana, K. (2014). Effect of sublethal doses of copper sulphate on certain haematological parameters of common carp, Cyprinus carpio. International Journal of Recent Scientific Research, 5(2), 332–335.
Drabkin, D. L. (1964). Spectrophotometric studies: XIV. The crystallographic and optical properties of the hemoglobin of man in comparison with those of other species. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 164, 703–723.
Feng, Q., Liu, Y., Huang, J., Chen, K., Huang, J., & Xiao, K. (2018). Uptake, distribution, clearance, and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles with different sizes and coatings. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 2082–2094.
Gupta, P. K. (1977). Haematological Techniques. 4th edition Syndicate, India, pp.231.
Gupta, Y. R., Sellegounder, D., Kannan, M., Deepa, S., Senthilkumaran, B., & Basavaraju, Y. (2016). Effect of copper nanoparticles exposure in the physiology of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio): biochemical, histological and proteomic approaches. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 1, 15–23.
Hadi, A. A., & Alwan, S. F. (2012). Histopathological changes in gills, liver and kidney of fresh water fish, Tilapia zillii, exposed to aluminum. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences, 3(11), 2071–2081.
Hao, L., Chen, L., Hao, J., & Zhong, N. (2013). Bioaccumulation and sub-acute toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles in juvenile carp (Cyprinus carpio): a comparative study with its bulk counterparts. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 91, 52–60.
Hermenean, A., Damache, G., Albu, P., Ardelean, A., Ardelean, G., Ardelean, D. P., Horge, M., Nagy, T., Braun, M., Zsuga, M., & Kéki, S. (2015). Histopatological alterations and oxidative stress in liver and kidney of Leuciscus cephalus following exposure to heavy metals in the Tur River, North Western Romania. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 119, 198–205.
Hua, J., Peijnenburg, W. J., & Vijver, M. G. (2016). TiO2 nanoparticles reduce the effects of ZnO nanoparticles and Zn ions on zebra fish embryos (Danio rerio). NanoImpact, 2, 45–53.
Jahanbakhshi, A., Hedayati, A., & Pirbeigi, A. (2015). Determination of acute toxicity and the effects of sub-acute concentrations of CuO nanoparticles on blood parameters in Rutilus rutilus. Nanomedicine Journal, 2(3), 195–202.
Javed, M., Ahmad, I., Usmani, N., & Ahmad, M. (2016). Bioaccumulation, oxidative stress and genotoxicity in fish (Channa punctatus) exposed to a thermal power plant effluent. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 127, 163–169.
Joshi, P. K., Bose, M., & Harish, D. (2002). Changes in certain haematological parameters in a siluroid catfish Clarias batrachus (Linn) exposed to cadmium chloride. Pollution Research, 21(2), 129–131.
Kadar, E., Tarran, G. A., Jha, A. N., & Al-Subiai, S. N. (2011). Stabilization of engineered zero-valent nano iron with Na-acrylic copolymer enhances spermiotoxicity. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(8), 3245–3251.
Kanwal, Z., Raza, M. A., Manzoor, F., Riaz, S., Jabeen, G., Fatima, S., & Naseem, S. (2019). A comparative assessment of nanotoxicity induced by metal (silver, nickel) and metal oxide (cobalt, chromium) nanoparticles in Labeo rohita. Nanomaterials, 9, 309–329.
Karthikeyeni, S., Vijayakumar, T. S., Vasanth, S., Ganesh, A., Manimegalai, M., & Subramanian, P. (2013). Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles and its haematological effects on fresh water fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Journal of Academia and Industrial Research, 1(10), 645–649.
Kaur, S., Khera, K. S., & Kondal, J. K. (2018). Effect of water contaminated with heavy metals on histopathology of freshwater catfish, Clarias batrachus. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 6(4), 3103–3108.
Kaviani, E. F., Naeemi, A. S., & Salehzadeh, A. (2019). Influence of copper oxide nanoparticle on hematology and plasma biochemistry of Caspian trout (Salmo trutta caspius), following acute and chronic exposure. Pollution, 5(1), 225–234.
Khabbazi, M., Harsij, M., Hedayati, S. A. A., Gholipoor, H., Gerami, M. H., & Farsani, H. G. (2015). Effect of CuO nanoparticles on some hematological indices of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and their potential toxicity. Nanomedicine Journal, 2, 67–73.
Khosravi-Katuli, K., Shabani, A., Paknejad, H., & Imanpoor, M. R. (2018). Comparative toxicity of silver nanoparticle and ionic silver in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio): accumulation, physiology and histopathology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 359, 373–381.
Kori-Siakpere, O., & Ubogu, E. O. (2008). Sublethal haematological effects of zinc on the freshwater fish, Heteroclarias sp. (Osteichthyes: Clariidae). African Journal of Biotechnology, 7(12), 2068–2073.
Krishnani, K. K., & Ayyappan, S. (2006). Heavy metals remediation of water using plants and lignocellulosic agrowastes. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 188, 59–84.
Lata, S., & Samadder, S. R. (2014). Removal of heavy metals using rice husk: a review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Development, 4(2), 165–170.
Lavanya, S., Ramesh, M., Kavitha, C., & Malarvizhi, A. (2011). Hematological, biochemical and ionoregulatory responses of Indian major carp Catla catla during chronic sublethal exposure to inorganic arsenic. Chemosphere, 82(7), 977–985.
Lewis, W. K., Harruff, B. A., Gord, J. R., Rosenberger, A. T., Sexton, T. M., Guliants, E. A., & Bunker, C. E. (2010). Chemical dynamics of aluminum nanoparticles in ammonium nitrate and ammonium perchlorate matrices: enhanced reactivity of organically capped aluminum. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115, 70–77.
Mela, M., Randi, M. A. F., Ventura, D. F., Carvalho, C. E. V., Pelletier, E., & Ribeiro, C. O. (2007). Effects of dietary methyl mercury on liver and kidney histology in the neotrophical fish Hoplias malabaricus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 68, 426–435.
Murali, M., Suganthi, P., Athif, P., Bukhari, A. S., Mohamed, S. H. E., Basu, H., & Singhal, R. K. (2017). Histological alterations in the hepatic tissues of Al2O3 nanoparticles exposed freshwater fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 44, 125–131.
Murali, M., Athif, P., Suganthi, P., Bukhari, A. S., Mohamed, H. S., Basu, H., & Singhal, R. K. (2018). Toxicological effect of Al2O3 nanoparticles on histoarchitecture of the freshwater fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 59, 74–81.
Murugan, S. S., Karuppasamy, R., Poongodi, K., & Puvaneswari, S. (2008). Bioaccumulation pattern of zinc in freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch) after chronic exposure. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 8, 55–59.
Saravanan, M., Suganya, R., Ramesh, M., Poopal, R. K., Gopalan, N., & Ponpandian, N. (2015). Iron oxide nanoparticles induced alterations in haematological, biochemical and ionoregulatory responses of an Indian major carp Labeo rohita. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 17, 274–285.
Shaluei, F., Hedayati, A., Jahanbakhshi, A., Kolangi, H., & Fotovat, M. (2013). Effect of subacute exposure to silver nanoparticle on some hematological and plasma biochemical indices in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Human and Experimental Toxicology, 32(12), 1270–1277.
Sivakumar, S., Khatiwada, C. P., & Sivasubramanian, J. (2012). Bioaccumulations of aluminum and the effects of chelating agents on different organs of Cirrhinus mrigala. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 34(3), 791–800.
Sobhanardakani, S., Parvizimosaed, H., & Olyaie, E. (2013). Heavy metals removal from wastewaters using organic solid waste-rice husk. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 20(8), 5265–5271.
Thophon, S., Kruatrachue, M., Upatham, E. S., Pokethitiyook, P., Sahaphong, S., & Jaritkhuan, S. (2003). Histopathological alterations of white sea bass, Later calcarifer, in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environmental Pollution, 121, 307–320.
Vidya, P. V., & Chitra, K. C. (2019). Irreversible histopathological modifications induced by iron oxide nanoparticles in the fish, Oreochromis mossambicus (Peters, 1852). Biological Forum Journal, 11(1), 01–06.
Wang, D., Lin, Z., Wang, T., Yao, Z., Qin, M., Zheng, S., & Lu, W. (2016). Where does the toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles come from: the nanoparticles, the ions, or a combination of both? Journal of Hazardous Materials, 308, 328–334.
Wang, M., Liu, R. R., Wang, C. J., Kang, W., Yang, G. H., Zhong, W. N., & Lai, Y. R. (2015). Combined histological and hematological assessment of iron-induced organ damage in a gerbil model of iron overload. American Journal of Translational Research, 7(2), 385–392.
Wu, Y., & Zhou, Q. (2013). Silver nanoparticles cause oxidative damage and histological changes in medaka (Oryzias latipes) after 14 days of exposure. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 32, 165–173.
Zhu, B., He, W., Hu, S., Kong, R., & Yang, L. (2019). The fate and oxidative stress of different sized SiO2 nanoparticles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Chemosphere, 225, 705–712.
Acknowledgment
The authors extend their appreciation to the Faculty of Science, Cairo University, Egypt for supporting the current work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in the present study involving animals (fish) were approved (approval no. CUFS F ECO 4615) and were in accordance with the ethical standards of Faculty of Science, Cairo University, Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Khalek, A.A., Badran, S.R. & Marie, MA.S. The Efficient Role of Rice Husk in Reducing the Toxicity of Iron and Aluminum Oxides Nanoparticles in Oreochromis niloticus: Hematological, Bioaccumulation, and Histological Endpoints. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 53 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4424-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4424-2