Abstract
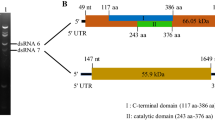
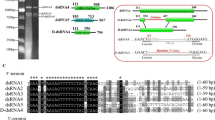
Protozoa double-stranded (ds) RNA viruses have been described in Trichomonas, Giardia, and Leishmania. In this study, dsRNA and virus-like particles (approximately 30 nm in diameter) were discovered in Eimeria tenella sporulated oocysts. The complete genome of this novel dsRNA virus was sequenced using a three-step strategy. The sequencing results showed that the complete genome sequence was 6006 bp containing two open reading frames (ORFs) (2367 bp for ORF1 and 3216 bp for ORF2) with a five-nucleotide overlap (UGA/UG). The predicted ORF1 and ORF2 encoded a putative capsid protein of 788 amino acids (84.922 kDa) and a putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) protein of 1071 amino acids (118.190 kDa). BLASTp analysis showed that the amino acid sequences for the E. tenella virus shared similarity with the E. brunetti RNA virus, with 29% homology in capsid proteins and 36% in RDRP proteins. The two untranslated regions were 349 bp (5′ UTR) and 78 bp (3′ UTR). The complete genome sequence of the E. tenella virus resembled characteristics of the Totiviridae family, indicating that this virus was a novel member of Totiviridae. Surprisingly, phylogenetic analysis showed that the E. tenella virus, E. brunetti RNA virus 1, and Mycoviruses were clustered into the genus Victorivirus and separated from the reported protozoa viruses, strongly suggesting a novel Eimeriaviruses subgenus. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report for the complete genome sequence of the E. tenella virus. Using the nomenclature generally adopted for viruses, this new isolate was named E. tenella RNA virus 1. This study provides a foundation basis for further research on the biological characteristics of Eimeriaviruses.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
ICTV 2014 Master Species List (MSL)
L.S. Diamond, C.F. Mattern, I.L. Bartgis, Viruses of Entamoeba histolytica. I. Identification of transmissible virus-like agents. J. Virol. 9, 326–341 (1972)
A.L. Wang, C.C. Wang, The double-stranded RNA in Trichomonas vaginalis may originate from virus-like particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 7956–7960 (1986)
A.L. Wang, C.C. Wang, Discovery of a specific double-stranded RNA virus in Giardia lamblia. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 21, 269–276 (1986)
R.L. Miller, A.L. Wang, C.C. Wang, Purification and characterization of the Giardia lamblia double-stranded RNA virus. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 28, 189–195 (1988)
P.I. Tarr, R.F. Aline, B.L. Smiley, J. Scholler, J. Keithly, K. Stuart, LR1: a candidate RNA virus of Leishmania. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 9572–9575 (1988)
K. Stuart, R. Week, C. Tripp, B. Smiley, J.R. Aline, Virus and Episomes of Leishmania Immune Recognition and Evasion: Molecular Aspects of Host Parasite Interaction (Academic Press, London, 1990), pp. 269–278
H. Revets, D. Dekegel, W. Deleersnijder, J. Jonckheere, J. Peeters, E. Leysen, R. Hamers, Identification of virus-like particles in Eimeria stiedae. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 36, 209–215 (1989)
T. Sepp, R. Entzeroth, J. Mertsching, P.H. Hofschneider, R. Kandolf, Novel ribonucleic acid species in Eimeria nieschulzi are associated with RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity. Parasitol. Res. 77, 581–584 (1991)
I. Roditi, T. Wyler, N. Smith, R. Braun, Virus-like particles in Eimeria nieschulzi are associated with multiple RNA segments. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 63, 275–282 (1994)
J. Ellis, H. Revets, Eimeria species which infect the chicken contain virus-like RNA molecules. Parasitology 101, 163–169 (1990)
Q. Han, J. Li, P. Gong, J. Gai, S. Li, X. Zhang, Virus-like particles in Eimeria tenella are associated with multiple RNA segments. Exp. Parasitol. 127, 646–650 (2011)
S. Lee, M.A. Fernando, E. Nagy, dsRNA associated with virus-like particles in Eimeria spp. of the domestic fowl. Parasitol. Res. 82, 518–523 (1996)
N.V. Khramtsov, K.M. Woods, M.V. Nesterenko, C.C. Dykstra, S.J. Upton, Virus-like, double-stranded RNAs in the parasitic protozoan Cryptosporidium parvum. Mol. Microbiol. 26, 289–300 (1997)
R.B. Williams, Epidemiological aspects of the use of live anticoccidial vaccines for chickens. Int. J. Parasitol. 28, 1089–1098 (1998)
P. Scott, Leishmania-a parasitized parasite. New. Engl. J. Med. 364, 1773–1774 (2011)
A. Ives, C. Ronet, F. Prevel, G. Ruzzante, S. Fuertes-Marraco, F. Schutz, H. Zangger, M. Revaz-Breton, L.F. Lye, S.M. Hickerson, S.M. Beverley, H. Acha-Orbea, P. Launois, N. Fasel, S. Masina, Leishmania RNA virus controls the severity of mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Science 331, 775–778 (2011)
H. Attoui, F. Billoir, J.F. Cantaloube, P. Biagini, P. Micco, X. Lamballerie, Strategies for the sequence determination of viral dsRNA genomes. J. Virol. Methods 89, 147–158 (2000)
S. Maan, S. Rao, N.S. Maan, S.J. Anthony, H. Attoui, A.R. Samuel, P.P. Mertens, Rapid cDNA synthesis and sequencing techniques for the genetic study of bluetongue and other dsRNA viruses. J. Virol. Methods 143, 132–139 (2007)
A.C. Potgieter, N.A. Page, J. Liebenberg, I.M. Wright, O. Landt, A.A. van Dijk, Improved strategies for sequence-independent amplification and sequencing of viral double-stranded RNA genomes. J. Gen. Virol. 90, 1423–1432 (2009)
F.T. Vreede, M. Cloete, G.B. Napier, A.A. Dijk, G.J. Viljoen, Sequence-independent amplification and cloning of large dsRNA virus genome segments by poly(dA)-oligonucleotide ligation. J. Virol. Methods 72, 243–247 (1998)
M.W. Shirley, A.C. Bushell, J.E. Bushell, V. McDonald, B. Roberts, A live attenuated vaccine for the control of avian coccidiosis: trials in broiler breeders and replacement layer flocks in the United Kingdom. Vet. Rec. 137, 453–457 (1995)
A.E. Bashar, J. Cai, M. Xie, G. Li, Z. Qin, H. Wu, X. Peng, W. Wei, Characterization of microneme-2 (EtMIC-2) gene of Eimeria tenella Guangdong strain. Int. J. Poultry. Sci. 113, 133–138 (2003)
Anita Haug, R.B. Williams, S. Larsen, Counting coccidial oocysts in chicken faeces: a comparative study of a standard McMaster technique and a new rapid method[J]. Vet. Parasitol. 13, 233–242 (2006)
J.L. Dale, D.A. Phillips, J.N. Parry, Double-stranded RNA in Banana plants with bunchy top disease[J]. J. Gen. Virol. 67(2), 371–375 (1986)
J.A. Dodds, M. Bar-Joseph, Double-stranded RNA from plants infected with closteroviruses. Phytopathology. 73, 419–423 (1983)
P.L. Hunst, F.M. Latterell, A.E. Rossi, Variation in double stranded RNA from isolates of Pyricularia oryzae. Phytopathology. 76, 674–678 (1986)
V.K. Singh, A.K. Mangalam, S. Dwivedi, S. Naik, Primer premier: program for design of degenerate primers from a protein sequence. Biotechniques 24, 318–319 (1998)
H. Telenius, N.P. Carter, C.E. Bebb, M. Nordenskjo, B.A. Ponder, A. Tunnacliffe, Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics 13, 718–725 (1992)
D.J. Korbie, J.S. Mattick, Touchdown PCR for increased specificity and sensitivity in PCR amplification. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1452–1456 (2008)
D.S. Prestridge, Predicting Pol II promoter sequences using transcription factor binding sites. J. Mol. Biol. 249, 923–932 (1995)
J.D. Thompson, D.G. Higgins, T.J. Gibson, CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680 (1994)
F. Felsenstein, PHYLIP (phylogeny inference package) version 3.67. Distributed by the author. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, USA (2007)
A. Rambaut, FigTree: Tree figure drawing tool, version 1.0. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh (2006). http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/
S.A. Ghabrial, M.L. Nibert, Victorivirus, a new genus of fungal viruses in the family Totiviridae[J]. Arch. Virol. 154(2), 373–379 (2009)
P. Mertens, The dsRNA viruses. Virus Res. 101, 3–13 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31072123, 31272550, and 31372425), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by A. Lorena Passarelli.
Bin Wu, Xichen Zhang, and Pengtao Gong have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Zhang, X., Gong, P. et al. Eimeria tenella: a novel dsRNA virus in E. tenella and its complete genome sequence analysis. Virus Genes 52, 244–252 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-016-1295-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-016-1295-0