Abstract
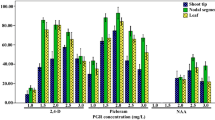
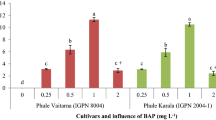
Spathoglottis plicata Blume is a vulnerable orchid species in various parts of the world, and the conventional propagation provides limited success to its cultivation and conservation. Therefore, present study deals with the direct induction of somatic embryos (SEs) from the leaf explants of S. plicata. Murashige and Skoog’s (MS) medium fortified with various types and concentrations of plant growth regulators were used to induce somatic embryogenesis and plantlet production. The highest percentage of somatic embryo formation (93.7 ± 0.56%) was achieved on MS medium supplemented with 1.0 mg L−1 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), whereas, maximum proliferation and increase in fresh weight (FW) of SEs (149.5 ± 0.24 mg/ 50 mg initial FW) was achieved on MS medium fortified with 2.0 mg L−1 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP) within 5 weeks of incubation. The light microscopic observation revealed that SEs emerged directly from the leaf surface. The viable synthetic seeds (SS) from SEs were prepared by encapsulating with gel matrix of 3% (w/v) sodium alginate and 100 mM calcium chloride. The SS were successfully stored for 60 days at − 4 °C with 97.4% germination frequency and shoot proliferation using MS medium with 2.0 mg L−1 BAP and 0.25 mg L−1 indole-3-acetic acid. The synergistic rooting frequency was observed on half-strength MS medium with 1.0 mg L−1 indole-3-butyric acid. The rooted shoots were acclimatized in a greenhouse with a 90% survival rate using soilrite® and vermicompost. This is an efficient short-term storage and regeneration protocol for S. plicata, which could help in reducing pressure on its wild population and could also be extended to the cryopreservation of this orchid species.
Key message
The somatic embryos were induced directly from the leaf explants of Spathoglottis plicata and an efficient short-term storage protocol was developed by encapsulating these somatic embryos. The light microscopic analysis confirmed the formation of somatic embryos. The protocol could be convenient for the commercial cultivation and conservation of S. plicata.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari S, Bandyopadhyay TK, Ghosha P (2014) Assessment of genetic stability of Cucumis sativus L. regenerated from encapsulated shoot tips. Sci Hortic 170:115–122
Aktar S, Nasiruddin KM, Huq H (2007) In vitro root formation in Dendrobium orchid plantlets with IBA. J Agric Rural Dev 5:48–51
Arditti J (1992) Fundamentals of orchid biology. Wiley, New York, p 691
Aswathi, Shibu S, Gopinath A, Mohan A (2017) In vitro propagation of Spathoglottis plicata Blume via asymbiotic seed germination. Int J Adv Res 5:431–438
Bhattacharyya P, Kumar V, Van Staden J (2018) In vitro encapsulation based short term storage and assessment of genetic homogeneity in regenerated Ansellia africana (Leopard orchid) using gene targeted molecular markers. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 133:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1382-0
Cardoso JC, Zanello CA, Chen JT (2020) An overview of orchid protocorm-like bodies: mass propagation, biotechnology, molecular aspects, and breeding. Int J Mol Sci 21:985. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030985
Chung H, Chen J, Chang W (2005) Cytokinins induce direct somatic embryogenesis of Dendrobium chiengmai pink and subsequent plant regeneration. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 41:765–769. https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2005702
Cueva-Agila A, Medina J, Concia L et al (2016) Effects of plant growth regulator, auxin polar transport inhibitors on somatic embryogenesis and CmSERK gene expression in Cattleya maxima (Lindl.). In: Mujib A (ed) Somatic embryogenesis in ornamentals and its applications. Springer, India, pp 255–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2683-3_16
Dagar HS, Dagar JC (2003) Plants used in ethnomedicine by the Nicobarese of Islands in Bay of Bengal, India. In: Singh V, Jain AP (eds) Ethnobotany and medicinal Plants of India and Nepal. Scientific Publishers (India), Jodhpur, pp 773–784
Deb CR, Pongener A (2011) Asymbiotic seed germination and in vitro seedling development of Cymbidium aloifolium (L.) Sw.: a multipurpose orchid. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 20:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-010-0031-4
Decruse WS, Gangaprasad A, Seeni S, Menon SV (2003) A protocol for shoot multiplication from foliar meristem of Vanda spathulata (L.) Spreng. Indian J Exp Biol 41:924–927
Dewir YH, El-Mahrouk ME, Murthy HN, Paek KY (2015) Micropropagation of Cattleya: improved in vitro rooting and acclimatization. Hort Environ Biotechnol 56:89–93
Dohling S, Das MC, Kumaria S, Tandon P (2007) Conservation of splendid orchids of North-East India. Biodiversity and its significance. IK Int Publishers, New Delhi, pp 354–365
Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act (1999) Spathoglottis plicata conservation advice, pp 1-3
Feng JH, Chen JT (2014) A novel in vitro protocol for inducing direct somatic embryogenesis in Phalaenopsis aphrodite without taking explants. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/263642
Gaintait S, Kundu S, Ali NC, Sahu NC (2015) Synthetic seed production of medicinal plants: a review on influence of explants, encapsulation agent and matrix. Acta Physiol Plant 37:98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1847-2
Govaerts R (2012) World checklist of orchidaceae. http://apps.kew.org/wcsp. Accessed on 11 July 2020
Haque MS, Ghosh B (2017) Regeneration of cytologically stable plants through dedifferentiation, redifferentiation and artificial seeds in Spathoglottis plicata Blume (Orchidaceae). Hortic Plant J 3:199–208
Horstman A, Bemer M, Boutilier K (2017) A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 4:201–216. https://doi.org/10.1002/reg2.91
Hossain MM, Dey R (2013) Multiple regeneration pathways in Spathoglottis plicata Blume—a study in vitro. S Afr J Bot 85:56–62
Johansen DA (1940) Plant microtechnique, 1st edn. McGraw Hill Book Co, New York, pp 182–197
Kaewubon P, Meesawat U (2016) Histological examination of callogenesis in bisected protocorm culture of pigeon orchid (Dendrobium crumenatum Swartz). Walailak J Schi Tech 13:745–756
Khor E, Ng WF, Loh CS (1998) Two-coat systems for encapsulation of Spathoglottis plicata (Orchidaceae) seeds and protocorms. Biotechnol Bioeng 59:635–639
Kulus D (2019) Application of synthetic seeds in propagation, storage, and preservation of Asteraceae plant species. In: Faisal M, Alatar A (eds) Synthetic Seeds. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24631-0_6
Kulus D, Tymoszuk A (2020) Induction of callogenesis, organogenesis, and embryogenesis in non-meristematic explants of bleeding heart and evaluation of chemical diversity of key metabolites from callus. Int J Mol Sci 21:5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165826
Mahendran G, Bai VN (2012) Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from seed derived protocorms of Cymbidium bicolor Lindl. Sci Hortic 135:40–44
Mahendran G, Bai VN (2016) Direct somatic embryogenesis of Malaxis densiflora (A. Rich.) Kuntze. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 14:77–81
Mahendran G, Muniappan V, Ashwini M, Muthukumar T, Narmatha Bai V (2013) Asymbiotic seed germination of Cymbidium bicolor Lindl. (Orchidaceae) and the influence of mycorrhizal fungus on seedling development. Acta Physiol Plant 35(3):829–840
Manokari M, Latha R, Priyadharshini S, Jogam P, Shekhawat MS (2020) Short-term cold storage of encapsulated somatic embryos and retrieval of plantlets in grey orchid (Vanda tessellata (Roxb.) Hook. ex G.Don). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01899-y
Martinez MT, San José MC, Vieitez AM, Cernadas MJ, Ballester A, Corredoira E (2017) Propagation of mature Quercus ilex L. (holm oak) trees by somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 131:321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1286-4
Mayer JLS, Stancato GC, AppezzatoDa-Gloria B (2010) Direct regeneration of protocorm-like bodies (PLB) from leaf apices of Oncidium flexuosum Sims (Orchidaceae). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 103:411–416
Micheli M, Standardi A (2016) From somatic embryo to synthetic seed in Citrus spp. through the encapsulation technology. In: Germana MA, Lambardi M (eds) In vitro embryogenesis in higher plants. Springer, New York, pp 515–522
Mohanraj R, Ananthan R, Bai VN (2009) Production and storage of synthetic seeds in Coelogyne breviscapa Lindl. Asian J Biotechnol 1:124–128
Mollik AH, Hossan S, Islam T, Jahan R, Rahmatullah M (2009) Medicinal plants used against rheumatoid arthritis by traditional medicinal practitioners of Bangladesh. Planta Med. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1234537
Moradi S, Daylami SD, Arab M, Vahdati K (2017) Direct somatic embryogenesis in Epipactis veratrifolia, a temperate terrestrial orchid. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 92:88–97
Mose W, Indrianto A, Purwantoro A, Semiarti E (2017) The influence of thidiazuron on direct somatic embryo formation from various types of explant in Phalaenopsis amabilis (L.) Blume Orchid. HAYATI J Biosci 24:201–205
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:495–497
Nawy T, Lukowitz W, Bayer M (2008) Talk global, act local-patterning the Arabidopsis embryo. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.10.007
Nongdam P, Tikendra L (2014) Establishment of an efficient in vitro regeneration protocol for rapid and mass propagation of Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl. using seed culture. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/740150
Novak O, Pencik A, Ljung K (2014) Identification and profiling of auxin and auxin metabolites. In: Zazímalová E, Petrásek J, Benková E (eds) Auxin and its role in plant development. Springer, Vienna, pp 39–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1526-8_3
Otero JT, Flanagan NS (2006) Orchid diversity: beyond deception. Trends Ecol Evol 21:64–65
Parthibhan S, Rao MV, Teixeira da Silva JA, Kumar ST (2018) Somatic embryogenesis from stem thin cell layers of Dendrobium aqueum. Biol Plant 62:439–450
Pradhan S, Tiruwa B, Subedee BR, Pant B (2014) In vitro germination and propagation of a threatened medicinal orchid, Cymbidium aloifolium (L.) Sw. through artificial seed. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 4:971–976
Recart W, Ackerman JD, Cuevas AA (2013) There goes the neighbourhood: apparent competition between invasive and native orchids mediated by a specialist florivorous weevil. Biol Invasions 15(2):283–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0283-0
Rittirat S, Thammasiri K, Te-chato S (2012) Effect of media and sucrose concentrations with or without activated charcoal on the plantlet growth of Phalaenopsis cornucervi (Breda) Blume & Rchb. F. J Agr Tech 8:2077–2087
Riva SS, Islam A, Hoque ME (2016) In vitro regeneration and rapid multiplication of Dendrobium bensoniae, an indigenous ornamental orchid. Agriculturalists 14:24–31
Saiprasad GVS, Polisetty R (2003) Propagation of three orchid genera using encapsulated protocorm-like bodies. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1079/IVP2002360
Sebastinraj J, Muhirkuzhali S (2014) Asymbiotic seed germination and micropropagation of Spathoglottis plicata Blume. I J Adv Pharm Biol Chem 3:495–501
Shen HJ, Chen JT, Chung HH, Chang WC (2018) Plant regeneration via direct somatic embryogenesis from leaf explants of Tolumnia Louise Elmore ‘Elsa.’ Bot Stud. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-018-0220-3
Sherif AN, Benjamin FJH, Kumar ST, Rao MV (2018) Somatic embryogenesis, acclimatization and genetic homogeneity assessment of regenerated plantlets of Anoectochilus elatus Lindl., an endangered terrestrial jewel orchid. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 132:303–316
Sinha P, Hakim LM, Alam FM (2009) In vitro mass clonal propagation of Spathoglottis plicata Blume. Plant Tissue Cult Biotechnol 19:151–160
Soonthornkalump S, Yamamoto S, Nakkanong K, Meesawat U (2019) The investigation of condition for cryopreservation of Snow-White Venus’s Slipper orchid protocorm [Paphiopedilum niveum (Rchb.f.) Stein] using V cryo-plate method. Songklanakarin J Plant Sci 6:10–18
Stella RY, Priya MT, Begam MFK, Manimekalai V (2015) In vitro seed germination, somatic embryogenesis and protocorm based micropropagation of a terrestrial ornamental orchid—Spathoglottis plicata Blume. Eur J Biotechnol Biosci 3:20–23
Stevens PF (2012) Angiosperm phylogeny. http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb. Accessed on 9 June 2020
Su YH, Zhang XS (2009) Auxin gradients trigger de novo formation of stem cells during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Signal Beh 4:547–576
Teixeira da Silva JA, Winarto B (2016) Somatic embryogenesis in two orchid genera (Cymbidium, Dendrobium). In: Germana M, Lambardi M (eds) In vitro embryogenesis in higher plants. Methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3061-6_18
Teixeira da Silva JA, Hossain MM, Sharma M, Dobranszki J, Cardoso JC, Songjun Z (2017) Acclimatization of in vitro derived Dendrobium. Hortic Plant J 3:110–124
Teng W, Nicholson L, Teng M (1997) Micropropagation of Spathoglottis plicata. Plant Cell Rep 16:831–835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050329
Teng W, Nicholson L, Yu YY (1997) Clonal propagation of Spathoglottis plicata from young plants. Acta Hortic 447:193–198. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.1997.447.37
Teoh ES (2016) Medicinal orchids of Asia. Springer, Singapore, pp 644–646
Vondrakova Z, Eliasova K, Fischerova L, Vágner M (2011) The role of auxins in somatic embryogenesis of Abies alba. Open Life Sci 6:587–596. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-011-0035-7
Wagner WI, Herbst DR, Sohmer SH (1999) Manual of the Flowering Plants of Hawaii. Revised edition. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu
Wu G-Y, Wei X-L, Wang X, Wei Y (2020) Induction of somatic embryogenesis in different explants from Ormosia henryi Prain. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01822-5
Yang X, Zhang X (2010) Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in higher plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29:36–57
Zavattieri MA, Frederico AM, Lima M et al (2010) Induction of somatic embryogenesis as an example of stress-related plant reactions. Electron J Biotechnol 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol13-issue1-fulltext-4
Zhao P, Wang W, Sun M (2011) Characterization and expression pattern analysis of DcNAC gene in somatic embryos of Dendrobium candidum Wall ex Lindl. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9968-9
Acknowledgements
Authors MSS and PS are grateful to the National Medicinal Plants Board, Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India for providing financial support to their laboratory (grant number NMPB/IFD/GIA/NR/PL/2018-19/187).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MSS and MM: Conceptualization, investigation, methodology. PS and MM: Conducted experiments. MM and MSS: Writing the original draft. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from all individual participants for whom identifying information is included in this article.
Research involving human and/or animal participants
This research did not involve experiments with human or animal participants.
Additional information
Communicated by So-Young Park.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manokari, M., Priyadharshini, S. & Shekhawat, M.S. Direct somatic embryogenesis using leaf explants and short term storage of synseeds in Spathoglottis plicata Blume. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 145, 321–331 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02010-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02010-9