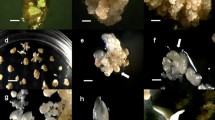
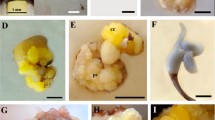
Abstract
An efficient in vitro plant regeneration method via somatic embryogenesis has been established in Ormosia henryi Prain, which is an important precious tree in the timber industry. Five types of explants, six types of basic media and different plant growth regulators (PGRs) were used for embryogenic callus (EC) initiation, EC proliferation, somatic embryo (SE) induction and SE germination. The EC and SE induction rates from mature zygotic embryos (MZE) were higher than those from stem segments, cotyledons, leaves and hypocotyls. MZE were used as explants, and the EC induction rate was greater than 30% on B5 medium supplemented with 1.0 mg/l 6-benzylaminopurine (BA) and 0.5 mg/l naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) or 0.2 mg/l BA and 2.0 mg/l 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). The highest induction rate (22.83%) for SE was obtained with B5 medium supplemented with 0.5 mg/l kinetin (KT) and 1.0 mg/l 2,4-D. The EC proliferation rate and SE number in the suspension culture were increased compared to those in the solid culture. Fifty-four percent of SE developed to the cotyledonary stage on B5 medium supplemented with 0.5 mg/l BA and 0.2 mg/l NAA. The number of cotyledon embryos was the highest on medium supplemented with 0.5 mg/l thidiazuron (TDZ) and 0.2 mg/l NAA. Histological analysis confirmed the bipolar organization of the somatic embryos, which were comprised of shoot and root meristems, and showed that SE was characterized by globular, heart-shaped, torpedo-shaped and cotyledon stages in O. henryi, the developmental process of which was similar to that of zygotic embryos.
Key Message
An efficient in vitro plant regeneration method via somatic embryogenesis has been established in Ormosia henryi Prain using mature zygotic embryos as explant.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrillaga I, Morcillo M, Zanón I et al (2019) New approaches to optimize somatic embryogenesis in maritime pine. Front Plant Sci 10:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00138
Asthana P, Rai MK, Jaiswal U (2017) Somatic embryogenesis from sepal explants in Sapindus trifoliatus, a plant valuable in herbal soap industry. Ind Crop Prod 100:228–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.02.034
Ballester A, Corredoira E, Vieitez AM (2016) Limitations of somatic embryogenesis in hardwood trees. In: Park Y-S, Bonga JM, Moon H-K (eds) Vegetative propagation of forest trees. National Institute of Forest Science (Nifos), Seoul, pp 56–74
Bartos PMC, Gomes HT, Amaral LIVD, Teixeira JB, Scherwinski-Pereira JE (2018) Biochemical events during somatic embryogenesis in Coffea arabica L. 3 Biotech 8:209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1238-7
Capelle SC, Mok DW, Kirchner SC, Mok MC (1983) Effects of thidiazuron on cytokinin autonomy and the metabolism of N-(delta-isopentenyl)[8-C]adenosine in callus tissues of Phaseolus lunatus L. Plant Physiol 73:796–802. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.73.3.796
Chen J, Shi J, Zhuge Q, Huang M (2003) Studies on the somatic embryogenesis of liriodendron hybrids (L. Chinense × L. Tulipifera). Sci Silvae Sinicae 39:49–53
Corredoira E, Ballester A, Ibarra M, Vieitez AM (2015) Induction of somatic embryogenesis in explants of shoot cultures established from adult Eucalyptus globulus and E. saligna × E. maidenii trees. Tree Physiol 35:678–690. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpv028
Corredoira E, Ballester A, Vieitez FJ, Vieitez AM (2006) Somatic embryogenesis in chestnut. In: Mujib A, Samaj J (eds) Somatic embryogenesis: plant cell monographs 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 177–199
Correia S, Lopes ML, Canhoto JM (2011) Somatic embryogenesis induction system for cloning an adult Cyphomandra betacea (Cav.) Sendt. (tamarillo). Trees-Struct Funct 25:1009–1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-011-0575-5
Dong Q, Xiaoli W, Qun L (2016) Establishment of sterile propagation system of different explant for rare species Ormosia henryi in tissue culture. Southwest China J Agric Sci 29:1719–1723
Fehér A (2005) Why somatic plant cells start to form embryos? In: Mujib A, Samaj J (eds) Plant cell monographs: somatic embryogenesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 85–101
Fehér A (2015) Somatic embryogenesis—stress-induced remodeling of plant cell fate. BBA-Gene Regul Mech 1849:385–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.07.005
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Gupta PK, Durzan DJ (1985) Shoot multiplication from mature trees of douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana). Plant Cell Rep 4:177–179
Hazubska-Przybył T, Kalemba EM, Ratajczak E, Bojarczuk K (2016) Effects of abscisic acid and an osmoticum on the maturation, starch accumulation and germination of Picea spp. somatic embryos. Acta Physiol Plant 38:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2078-x
Heringer AS, Santa-Catarina C, Silveira V (2018) Insights from proteomic studies into plant somatic embryogenesis. Proteomics 18:17002655. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201700265
Hu R, Sun Y, Wu B, Duan H, Zheng H, Hu D et al (2017) Somatic embryogenesis of immature Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) hook zygotic embryos. Sci Rep UK 7:56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00156-1
Ikeuchi M, Iwase A, Rymen B, Harashima H, Shibata M, Ohnuma M et al (2015) PRC2 represses dedifferentiation of mature somatic cells in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 1:15089. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.89
Jiménez VM (2005) Involvement of plant hormones and plant growth regulators on in vitro somatic embryogenesis. Plant Growth Regul 47:91–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-3478-x
Jun Y, Hong-Lin L, Bo Y (2007) Tissue culture and rapid propagation of Ormosia henryi Prain. Plant Physiol J 111:123–124
Keshvari T, Najaphy A, Kahrizi D, Zebarjadi A (2018) Callus induction and somatic embryogenesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni as a medicinal plant. Cell Mol Biol 64:46–49
Kim DH, Kang KW, Sivanesan I (2019) Influence of auxins on somatic embryogenesis in Haworthia retusa Duval. Biologia 74:25–33. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-018-0151-1
Leljak-Levanić D, Bauer N, Mihaljević S, Jelaska S (2004) Somatic embryogenesis in pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.): control of somatic embryo development by nitrogen compounds. J Plant Physiol 161:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-01055
Lloyd GB, McCown BH (1980) Commercially feasible micropropagation of mountain laurel (Kalmia latifolia) by use of shoot tip culture. Proc Int Plant Prop Soc 30:421–437
Lu D, Wei W, Zhou W, Mcguigan LD, Ji FY, Li X et al (2017) Establishment of a somatic embryo regeneration system and expression analysis of somatic embryogenesis-related genes in Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume). Plant Cell Tissue Org 130:601–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1250-3
Manivannan A, Jana S, Soundararajan P, Chungho K, Byoungryong J (2015) Antioxidant enzymes metabolism and cellular differentiation during the developmental stages of somatic embryogenesis in Torilis japonica (Houtt.) DC. Plant Omics 8:461–471
Martínez MT, San José MC, Vieitez AM, Cernadas MJ, Ballester A, Corredoira E (2017) Propagation of mature Quercus ilex L. (holm oak) trees by somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Org 131:321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1286-4
Martínez MT, Vieitez AM, Corredoira E (2015) Improved secondary embryo production in Quercus alba and Q. rubra by activated charcoal, silver thiosulphate and sucrose: influence of embryogenic explant used for subculture. Plant Cell Tissue Org 121:531–546
Merkle SA, Neu KA, Battle PJ, Bailey RL (1998) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from immature and mature tissues of sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua). Plant Sci 132:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-9452(98)00007-7
Mikuła A, Pożoga M, Grzyb M, Rybczyński JJ (2015) An unique system of somatic embryogenesis in the tree fern Cyathea delgadii Sternb.: the importance of explant type, and physical and chemical factors. Plant Cell Tissue Org 123:467–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0850-z
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nawy T, Lukowitz W, Bayer M (2008) Talk global, act local—patterning the Arabidopsis embryo. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.10.007
Neuman MC, Preece JE, Van SJ, Gaffney GR, Van Sambeek JW (1993) Somatic embryogenesis and callus production from cotyledon explants of eastern black walnut. Plant Cell Tiss Org 32:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00040110
Nunes S, Marum L, Farinha N, Pereira VT, Almeida T, Sousa D et al (2018) Somatic embryogenesis of hybrid Pinus elliottii var. elliottii × P. caribaea var. hondurensis and ploidy assessment of somatic plants. Plant Cell Tiss Org 132:71–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1311-7
Peng P (2017) Somatic embryogenesis and cytological observation of Picea mongolica. Dissertation, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University.
Rai MK, Shekhawat NS (2014) Recent advances in genetic engineering for improvement of fruit crops. Plant Cell Tiss Org 116:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0389-9
Satish L, Rathinapriya P, Rency AS, Ceasar SA, Pandian S, Rameshkumar R et al (2016) Somatic embryogenesis and regeneration using Gracilaria edulis and Padina boergesenii seaweed liquid extracts and genetic fidelity in finger millet (Eleusine coracana). J Appl Phycol 28:2083–2098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0696-0
Solorzano-Cascante P, Sanchez-Chiang N, Jimenez VM (2018) Explant type, culture system, 6-benzyladenine, meta-topolin and encapsulation affect indirect somatic embryogenesis and regeneration in Carica papaya L. Front Plant Sci 9:1769. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01769
Thomas JC, Katterman FR (1986) Cytokinin activity induced by thidiazuron. Plant Physiol 81:681–683. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.81.2.681
Vasil V, Vasil IK (1984) Preparation of cultured tissues for scanning electron microscopy. In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell culture and somatic cell genetics of plants, vol I. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 738–743
Vesco L, Guerra M, Dal-Vesco L (2001) The effectiveness of nitrogen sources in Feijoa somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Org 64:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1010635926146
Von Arnold S, Sabala I, Bozhkov P, Dyachok J, Filonova L (2002) Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Org 69:233–249. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1015673200621
Von Arnold S (2008) Somatic embryogenesis. In: George EF, Hall MA, De Klerk G-J (eds) Plant propagation by tissue culture. Vol. 1. The background, 3rd edn. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 335–354
Wang X, Lei S, Lin G, Xiao P, Chen H, Wu X et al (2013) A systematic comparison of embryogenic and non-embryogenic cells of banana (Musa spp. AAA): ultrastructural, biochemical and cell wall component analyses. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 159:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.05.008
Wang YG, Ye Z, Liu H, Liu QL, Zhang B, Hao YY (2014) Studies of paraffin section manufaction for apple fruits in different development stages. J Fruit Sci 5:973–976
Wu H, Chen B, Fiers M, Wróbel-Marek J, Kodde J, Groot SPC et al (2019) Seed maturation and post-harvest ripening negatively affect arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Org 139:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01658-8
Xiaoli W, Xianshuai M, Zhao D (2014) Relation between being endangered and seed reproductive ecology of a rare species Ormosia henryi. Seed 33:82–86
Yong WK, Yang Y, Noh ER, Kim JC (1998) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of Japanese larch (Larix leptolepis). Plant Cell Tissue Org 55:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006120302512
Zhang C, Li Q, Kong L (2007) Induction, development and maturation of somatic embryos in Bunge's pine (Pinus bungeana Zucc. ex Endl.). Plant Cell Tissue Org 91:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9294-4
Zhongxiong L, Liangzhen P, Zhenguang C (1997) Establishment and maintenance of longan embryogenic cell lines. J Fujian Agric Univ 2:33–40
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the members of the research group for their help. We thank the first-class disciplines of forestry and ecology for offering good experimental conditions for this work.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460193) and the High Level Innovative Talents Training Programme of Guizhou Province ([2016]5661).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Communicated by Maria Margarida Oliveira.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, GY., Wei, XL., Wang, X. et al. Induction of somatic embryogenesis in different explants from Ormosia henryi Prain. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 142, 229–240 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01822-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01822-5