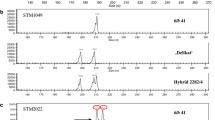
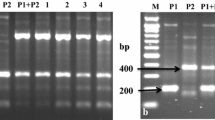
Abstract
Protoplast fusion may be used to introgress desirable traits from wild species into cultivated potato which are cross incompatible. However, none of commercial varieties have been developed from hyper-tetraploid somatic hybrids because of the unpredictable heredity associated with irregular chromosome segregation during meiosis. A pentaploid somatic hybrid (SH) from Solanum chacoense + S. tuberosum, 3C28-1, which carries bacterial wilt (BW) resistance from the wild species, was employed in the present research. Gamete genotypes and inheritance pattern of SH 3C28-1 were estimated by counting the chromosome numbers and detecting the parent-specific SSR alleles in a backcross population of SH 3C28-1 × E-Potato 1 (variety) which is BW susceptible. The SSR alleles retained from S. chacoense were analyzed for association with BW resistance and evaluation of wild species genetic background. Our results implied that SH 3C28-1 could produce viable gametes of n = 2x = 24 + a where a ≤ 6, which are compatible with a tetraploid pollen source to yield a high proportion of tetraploids and aneuploids with chromosome numbers between 48 and 54. Sixty-four of 83 SH 3C28-1-specific SSR alleles fit the tetrasomic or disomic/tetrasomic segregation ratio of a tetraploid, suggesting that the pentaploid mainly exhibits tetraploid inheritance pattern. Four (three positive and one negative) alleles were estimated to associate with BW resistance and backcross clones were selected for preserving less wild species genetic background and harboring the resistance. The present research elucidates the inheritance pattern of the pentaploid somatic hybrid to provide a theoretical and applied foundation for use of the pentaploid in potato breeding.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn YK, Park TH (2013) Resistance to common scab developed by somatic hybrids between Solanum brevidens and Solanum tuberosum. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 63:595–603
Barone A, Sebastiano A, Carputo D, della Rocca F, Frusciante L (2001) Molecular marker-assisted introgression of the wild Solanum commersonii genome into the cultivated S. tuberosum gene pool. Theor Appl Genet 102:900–907
Barone A, Li J, Sebastiano A, Cardi T, Frusciante L (2002) Evidence for tetrasomic inheritance in a tetraploid Solanum commersonii (+) S. tuberosum somatic hybrid through the use of molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:539–546
Butenko R, Kuchko A (1979) Somatic hybridization of Solanum tuberosum L. and Solanum chacoense Bitt. by protoplast fusion. In: Ferenczy L, Farkas GL (eds) Advances in protoplast research. Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, pp 293–300
Butenko R, Kuchko A, Komarnitsky I (1982) Some features of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum and Solanum chacoense and its F1 sexual progeny. In: Fujiwara A (ed) Plant tissue culture. Japanese Association for Plant Tissue Culture, Tokyo, pp 643–644
Cai X, Liu J, Xie C (2004) Mesophyll protoplast fusion of Solanum tuberosum and Solanum chacoense and their somatic hybrids analysis. Acta Hortic Sin 31:623–626
Carputo D (2003) Cytological and breeding behavior of pentaploids derived from 3x × 4x crosses in potato. Theor Appl Genet 106:883–888
Carputo D, Parisi M, Consiglio F, Iovene M, Caruso G, Monti L, Frusciante L (2003) Aneuploid hybrids from 5x–4x crosses in potato: chromosome number, fertility, morphology and yield. Am J Potato Res 80:93–101
Chen L, Guo X, Xie C, He L, Cai X, Tian L, Song B, Liu J (2013) Nuclear and cytoplasmic genome components of Solanum tuberosum + S. chacoense somatic hybrids and three SSR alleles related to bacterial wilt resistance. Theor Appl Genet 126:1861–1872
Cheng J, Saunders JA, Sinden SL (1995) Colorado potato beetle resistant somatic hybrid potato plants produced via protoplast electrofusion. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 31:90–95
Dellaporta S, Wood J, Hicks J (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Feingold S, Lloyd J, Norero N, Bonierbale M, Lorenzen J (2005) Mapping and characterization of new EST-derived microsatellites for potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Theor Appl Genet 111:456–466
Fock I, Collonnier C, Purwito A, Luisetti J, Souvannavong V, Vedel F, Servaes A, Ambroise A, Kodja H, Ducreux G, Sihachakr D (2000) Resistance to bacterial wilt in somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum and Solanum phureja. Plant Sci 160:165–176
Fock I, Collonnier C, Purwito A, Luisetti J, Souvannavong V, Vedel F, Servaes A, Ambroise A, Kodja H, Ducreux G (2001) Use of Solanum stenotomum for introduction of resistance to bacterial wilt in somatic hybrids of potato. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:899–908
Gavrilenko T, Thieme R, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2003) Fertile somatic hybrids of Solanum etuberosum (+) dihaploid Solanum tuberosum and their backcrossing progenies: relationships of genome dosage with tuber development and resistance to potato virus Y. Euphytica 131:323–332
Ghislain M, Nunez J, Herrera MR, Pignataro J, Guzman F, Bonierbale M, Spooner DM (2009) Robust and highly informative microsatellite-based genetic identity kit for potato. Mol Breed 23:377–388
Guo X, Xie C, Cai X, Song B, He L, Liu J (2010) Meiotic behavior of pollen mother cells in relation to ploidy level of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum and S. chacoense. Plant Cell Rep 29:1277–1285
Hayward AC (1994) Hosts of Pseudomonas solanacearum. In: Hayward AC, Hartman GL (eds) Bacterial wilt: the disease and its causative agent Pseudomonas solanacearum. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 9–23
Helgeson J, Pohlman J, Austin S, Haberlach G, Wielgus S, Ronis D, Zambolim L, Tooley P, McGrath J, James R (1998) Somatic hybrids between Solanum bulbocastanum and potato: a new source of resistance to late blight. Theor Appl Genet 96:738–742
Hermsen JGT, Bradshaw JE, Mackay GR (1994) Introgression of genes from wild species, including molecular and cellular approaches. In: Bradshaw JE, Mackay GR (eds) Potato genetics. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 515–538
Iovene M, Barone A, Frusciante L, Monti L, Carputo D (2004) Selection for aneuploid potato hybrids combining a low wild genome content and resistance traits from Solanum commersonii. Theor Appl Genet 109:1139–1146
Jackson SA, Hanneman REJ (1999) Crossability between cultivated and wild tuber- and non-tuber-bearing Solanums. Euphytica 109:51–67
Johnston SA, den Nijs TPM, Peloquin SJ, Hanneman REJ (1980) The significance of genic balance to endosperm development in interspecific crosses. Theor Appl Genet 57:5–9
Kim-Lee HY, Moon JS, Hong YJ, Kim MS, Cho HM (2005) Bacterial wilt resistance in the progenies of the fusion hybrids between haploid of potato and Solanum commersonii. Am J Potato Res 82:129–137
Laferriere LT, Helgeson JP, Allen C (1999) Fertile Solanum tuberosum + S. commersonii somatic hybrids as sources of resistance to bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum. Theor Appl Genet 98:1272–1278
Lamm R (1941) Varying cytological behaviour in reciprocal Solanum crosses. Hereditas 27:202–208
Li YH, Han ZH, Xu X (2004) Segregation patterns of AFLP markers in F1 hybrids of a cross between tetraploid and diploid species in genus Malus. Plant Breed 123:316–320
Li J, Lindqvist-Kreuze H, Tian Z, Liu J, Song B, Landeo J, Portal L, Gastelo M, Frisancho J, Sanchez L (2012) Conditional QTL underlying resistance to late blight in a diploid potato population. Theor Appl Genet 124:1339–1350
Liu J, Xu X, Deng X (2005) Intergeneric somatic hybridization and its application to crop genetic improvement. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 82:19–44
Murakami N, Matsunaga H, Senda K, Okuyama Y, Iritani M, Asama K, Mitsui Y, Shimizu K (1995) A new potato variety “Konamuso (=Sakurafubuki)”. Bull Hokkaido Prefect Agric Exp Stn 68:1–16
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Orczyk W, Przetakiewicz J, Nadolska-Orczyk A (2003) Somatic hybrids of Solanum tuberosum—application to genetics and breeding. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74:1–13
Sarkar D, Tiwari JK, Sharma S, Poonam Sharma S, Gopal J, Singh BP, Luthra SK, Pandey SK, Pattanayak D (2011) Production and characterization of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum L. and S. pinnatisectum Dun. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 107:427–440
Thieme R, Rakosy-Tican E, Gavrilenko T, Antonova O, Schubert J, Nachtigall M, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2008) Novel somatic hybrids (Solanum tuberosum L. + Solanum tarnii) and their fertile BC1 progenies express extreme resistance to potato virus Y and late blight. Theor Appl Genet 116:691–700
Thieme R, Rakosy-Tican E, Nachtigall M, Antonova O, Gavrilenko T, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2010) Characterization of the multiple resistance traits of somatic hybrids between Solanum cardiophyllum Lindl. and two commercial potato cultivars. Plant Cell Rep 29:1187–1201
Tiwari JK, Poonam B, Sarkar D, Pandey SK, Gopal J, Kumar SR (2010) Molecular and morphological characterization of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum L. and S. etuberosum Lindl. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103:175–187
Toppino L, Mennella G, Rizza F, D’Alessandro A, Sihachakr D, Rotino GL (2008) ISSR and isozyme characterization of and rogenetic dihaploids reveals tetrasomic inheritance in tetraploid somatic hybrids between Solanum melongena and Solanum aethiopicum group Gilo. J Hered 99:304–315
Winstead NN, Kelman A (1952) Inoculation techniques for evaluating resistance to Pseudomonas solanacearum. Phytopathology 42:628–634
Yamada T, Hosaka K, Kaide N, Nakagawa K, Misoo S, Kamijima O (1998) Cytological and molecular characterization of BC1 progeny from two somatic hybrids between dihaploid Solanum acaule and tetraploid S. tuberosum. Genome 41:743–750
Yu Y, Ye W, He L, Cai X, Liu T, Liu J (2013) Introgression of bacterial wilt resistance from eggplant to potato via protoplast fusion and genome components of the hybrids. Plant Cell Rep 32:1687–1701
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (nycytx-15), the special fund for agro-scientific research in the public interest from the Ministry of Agriculture, China (201303007) and the Ministry of Education of China (IRT13065).
Authors’ contributions
LC conducted the SSR marker selection, bacterial wilt assessment and paper drafting; XG constructed the backcrossing population and investigated the agronomic traits; HW and LH conducted the chromosome counting; JZ assisted on genetic analysis; XC reviewed the progress of the experiments; CX advised on data analysis and paper drafting; JL designed and supervised the study. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Lin Chen and Xianpu Guo have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Flowers of the parents: a. The pentaploid somatic hybrid Solanum chacoense (+) S. tuberosum, 3C28-1, b Tetraploid potato cv. E1 and c. Genotype BC1.17 of the progeny (2n = 52)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Guo, X., Wang, H. et al. Tetrasomic inheritance pattern of the pentaploid Solanum chacoense (+) S. tuberosum somatic hybrid (resistant to bacterial wilt) revealed by SSR detected alleles. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 127, 315–323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1051-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1051-0