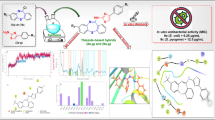
Abstract
The MurD enzyme of Staphylococcus aureus is an attractive drug target as it is essential and ubiquitous in bacteria but absent in mammalian cells. In the present study, we performed in silico high-throughput virtual screening with small molecule library of 1.60 million compounds to identify potential hits. We used S. aureus modeled MurD protein for this purpose and to find the best leads, dock complexes were further subjected to the extra-precision docking and binding free energy calculations by MM-GBSA approach. It is evident that van der Waals and Coulomb energy terms are major favorable contributors while electrostatic solvation energy term strongly disfavors the binding of ligands to the S. aureus MurD enzyme. The inhibitory activity of two selected virtual hits H5 and H10 was performed against S. aureus MurD enzyme using malachite green assay. In in vitro antibacterial screening, compound H5 inhibited the growth of S. aureus NCIM 5021, S. aureus NCIM 5022, and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA strain 43300) at high concentrations while the other tested compound H10 was inactive against all the tested strains. In order to validate the stability of inhibitor-protein complex, compound H5 with the highest inhibitory against S. aureus MurD and lowest binding free energy was subjected to 30-ns molecular dynamics simulation. Further, ADMET predictions showed the favorable pharmacokinetic profile of compounds H5 and H10.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAP:
-
2,6-diaminopimelic acid
- d-Glu:
-
d-glutamic acid
- MurC:
-
UDP-N-acetylmuramate:l-Ala ligase
- MRSA:
-
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- MIC:
-
minimum inhibitory concentration
- MBC:
-
minimum bactericidal concentration
- MurD:
-
UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-l-Ala:d-Glu ligase
- MurE:
-
UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-l-Ala-d-Glu:meso-DAP ligase
- MurF:
-
UDPN-acetylmuramoyl-l-Ala-g-d-Glu-meso-DAP (or l-Lys):d-Ala-d-Ala ligase
- MurNAc:
-
N-acetylmuramic acid
- UDP:
-
uridine-5′-diphosphate
- RMSD:
-
root mean square deviation
- UMA:
-
uridine-5′-diphosphate-N-acetylmueamoyl-l-alanine
- UMAG:
-
UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine-d-glutamat
References
World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. (2014), http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/112647/1/WHO_HSE_PED_AIP_2014.2_eng.pdf?ua=1. Accessed 20 Jan 2018
Nambiar S, Laessig K, Toerner J, Farley J, Cox E (2014) Antibacterial drug development: challenges, recent developments, and future considerations. Clin Pharmacol Ther 96:147–149
Duval X, Delahaye F, Alla F, Tattevin P, Obadia JF, Le Moing V, Doco-Lecompte T, Celard M, Poyart C, Strady C, Chirouze C, Bes M, Cambau E, Iung B, Selton-Suty C, Hoen B (2012) Temporal trends in infective endocarditis in the context of prophylaxis guideline modifications: three successive population-based surveys. J Am Coll Cardiol 59:1968–1976
Fedeli U, Schievano E, Buonfrate D, Pellizzer G, Spolaore P (2011) Increasing incidence and mortality of infective endocarditis: a population-based study through a record-linkage system. BMC Infect Dis 11:48
Barreteau H, Kovac A, Boniface A, Sova M, Gobec S, Blanot D (2008) Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:168–207
Smith CA (2006) Structure, function and dynamics in the mur family of bacterial cell wall ligases. J Mol Biol 362:640–655
Bouhss A, Dementin S, van Heijenoort J, Parquet C, Blanot D (2002) MurC and MurD synthetases of peptidoglycan biosynthesis: borohydride trapping of acylphosphate intermediates. Methods Enzymol 354:189–196
Eveland SS, Pompliano DL, Anderson MS (1997) Conditionally lethal Escherichia coli murein mutants contain point defects that map to regions conserved among murein and folyl poly-g-glutamate ligases: identification of a ligase superfamily. Biochem 36:6223–6229
Bouhss A, Dementin S, Parquet C, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Bertrand JA, Le Beller D, Dideberg O, van Heijenoort J, Blanot D (1999) Role of the ortholog and paralog amino acid invariants in the active site of the UDP-MurNAc-l-alanine:D-glutamate ligase (MurD). Biochem 38:12240–12247
van Heijenoort J (2001) Recent advances in the formation of the bacterial peptidoglycan monomer unit. Nat Prod Rep 18:503–519
Skedelj V, Tomasic T, Masic LP, Zega A (2011) ATP-binding site of bacterial enzymes as a target for antibacterial drug design. J Med Chem 54:915–929
Walsh AW, Falk PJ, Thanassi J, Discotto L, Pucci MJ, Ho HT (1999) Comparison of the D-glutamate-adding enzymes from selected gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 181:5395–5401
El Zoeiby A, Sanschagrin F, Levesque RC (2003) Structure and function of the Mur enzymes: development of novel inhibitors. Mol Microbiol 47:1–12
El-Sherbeini M, Geissler WM, Pittman J, Yuan X, Wong KK, Pompliano DL (1998) Cloning and expression of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes murD genes encoding uridine diphosphate N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine:D-glutamate ligases. Gene 210:117–125
Bertrand JA, Auger G, Martin L, Fanchon E, Blanot D, Le Beller D, van Heijenoort J, Dideberg O (1999) Determination of the MurD mechanism through crystallographic analysis of enzyme complexes. J Mol Biol 289:579–590
Gordon E, Flouret B, Chantalat L, van Heijenoort J, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Dideberg O (2001) Crystal structure of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate: meso-diaminopimelate ligase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 276:10999–11006
Yan Y, Munshi S, Leiting B, Anderson MS, Chrzas J, Chen Z (2000) Crystal structure of Escherichia coli UDPMurNAc-tripeptide d-alanyl-d-alanine-adding enzyme (MurF) at 2.3 A resolution. J Mol Biol 304:435–445
Perdih A, Kotnik M, Hodoscek M, Solmajer T (2007) Targeted molecular dynamics simulation studies of binding and conformational changes in E. coli MurD. Proteins 68:243–254
Bouhss A, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Blanot D, van Heijenoort J, Parquet C (1997) Invariant amino acids in the Mur peptide synthetases of bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis and their modification by site-directed mutagenesis in the UDP-MurNAc:L-alanine ligase from Escherichia coli. Biochem 36:11556–11563
Barreteau H, Sosic I, Turk S, Humljan J, Tomasic T, Zidar N, Herve M, Boniface A, Peterlin-Masic L, Kikelj D, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Gobec S, Blanot D (2012) MurD enzymes from different bacteria: evaluation of inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol 84:625–632
Gegnas LD, Waddell ST, Chabin RM, Reddy S, Wong KK (1998) Inhibitors of the bacterial cell wall biosynthesis enzyme MurD. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8:1643–1648
Gobec S, Urleb U, Auger G, Blanot D (2001) Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of some novel N-acyl phosphono- and phosphinoalanine derivatives as potential inhibitors of the D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme. Die Pharmazie 56:295–297
Strancar K, Blanot D, Gobec S (2006) Design, synthesis and structure–activity relationships of new phosphinate inhibitors of MurD. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:343–348
Auger G, van Heijenoort J, Blanot D (1995) Synthesis of N-Acetylmuramic acid derivatives as potential inhibitors of the D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme. J Prakt Chem 337:351–357
Kotnik M, Humljan J, Contreras-Martel C, Oblak M, Kristan K, Hervé M, Blanot D, Urleb U, Gobec S, Dessen A, Solmajer T (2007) Structural and functional characterization of enantiomeric glutamic acid derivatives as potential transition state analogue inhibitors of MurD ligase. J Mol Biol 370:107–115
Humljan J, Kotnik M, Contreras-Martel C, Blanot D, Urleb U, Dessen A, Solmajer T, Gobec S (2008) Novel naphthalene-N-sulfonyl-D-glutamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of MurD, a key peptidoglycan biosynthesis enzyme. J Med Chem 51:7486–7494
Pratviel-Sosa F, Acher F, Trigalo F, Blanot D, Azerad R, van Heijenoort J (1994) Effect of various analogues of D-glutamic acid on the D-glutamate-adding enzyme from Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 115:223–228
Perdih A, Bren U, Solmajer T (2009) Binding free energy calculations of N-sulphonyl-glutamic acid inhibitors of MurD ligase. Mol Model 15:983–996
Sova M, Kovac A, Turk S, Hrast M, Blanot D, Gobec S (2009) Phosphorylated hydroxyethylamines as novel inhibitors of the bacterial cell wall biosynthesis enzymes MurC to MurF. Bioorg Chem 37:217–222
Zidar N, Tomasic T, Sink R, Rupnik V, Kovac A, Turk S, Patin D, Blanot D, Contreras Martel C, Dessen A, Müller Premru M, Zega A, Gobec S, Peterlin Masic L, Kikelj D (2010) Discovery of novel 5-benzylidenerhodanine and 5-benzylidenethiazolidine-2,4-dione inhibitors of MurD ligase. J Med Chem 53:6584–6594
Zidar N, Tomasic T, Sink R, Kovac A, Patin D, Blanot D, Contreras-Martel C, Dessen A, Premru MM, Zega A, Gobec S, Masic LP, Kikelj D (2011) New 5-benzylidenethiazolidin-4-one inhibitors of bacterial MurD ligase: design, synthesis, crystal structures, and biological evaluation. Eur J Med Chem 46:5512–5523
Sosic I, Barreteau H, Simcic M, Sink R, Cesar J, Zega A, Grdadolnik SG, Contreras-Martel C, Dessen A, Amoroso A, Joris B, Blanot D, Gobec S (2011) Second-generation sulfonamide inhibitors of D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme: activity optimisation with conformationally rigid analogues of D-glutamic acid. Eur J Med Chem 46:2880–2894
Perdih A, Hrast M, Barreteau H, Gobec S, Wolber G, Solmajer T (2014) Benzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid 2,5-dimethylpyrrole derivatives as multiple inhibitors of bacterial Mur ligases (MurC-MurF). Bioorg Med Chem 22:4124–4134
Perdih A, Kovac A, Wolber G, Blanot D, Gobec S, Solmajer T (2009) Discovery of novel benzene 1,3-dicarboxylic acid inhibitors of bacterial MurD and MurE ligases by structure-based virtual screening approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:2668–2673
Turk S, Kovac A, Boniface A, Bostock JM, Chopra I, Blanot D, Gobec S (2009) Discovery of new inhibitors of the bacterial peptidoglycan biosynthesis enzymes MurD and MurF by structure-based virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem 17:1884–1889
Kotnik M, Anderluh PS, Prezelj A (2007) Development of novel inhibitors targeting intracellular steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Curr Pharm Des 13:2283–2309
Tomasic T, Zidar N, Sink R, Kovac A, Blanot D, Contreras-Martel C, Dessen A, Muller-Premru M, Zega A, Gobec S, Kikelj D, Masic LP (2011) Structure-based design of a new series of D-glutamic acid based inhibitors of bacterial UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine:D-glutamate ligase (MurD). J Med Chem 54:4600–4610
Tomasic T, Sink R, Zidar N, Fic A, Contreras-Martel C, Dessen A, Patin D, Blanot D, Muller-Premru M, Gobec S, Zega A, Kikelj D, Masic LP (2012) Dual inhibitor of MurD and MurE ligases from Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Med Chem Lett 3:626–630
Azam MA, Jupudi S, Saha N, Paul RK (2018) Combining molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies for modelling Staphylococcus aureus MurD inhibitory activity. SAR QSAR Environ Res 30:1–20
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Sanschagrin PC, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196
Jacobson MP, Pincus DL, Rapp CS, Day TJ, Honig B, Shaw DE, Friesner RA (2004) A hierarchical approach to all-atom protein loop prediction. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf 55:351–367
Li J, Abel R, Zhu K, Cao Y, Zhao S, Friesner RA (2011) The VSGB 2.0 model: a next generation energy model for high resolution protein structure modelling. Proteins 79:2794–2812
Guo Z, Mohanty U, Noehre J, Sawyer TK, Sherman W, Krilov G (2010) Probing the α-helical structural stability of stapled p53 peptides: molecular dynamics simulations and analysis. Chem Biol Drug Des 75:348–359
Harder E, Damm W, Maple J, Wu C, Reboul M, Xiang JY, Wang L, Lupyan D, Dahlgren MK, Knight JL, Kaus JW, Cerutti DS, Krilov G, Jorgensen WL, Abel R, Friesner RA (2016) OPLS3: a force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins. J Chem Theory Comput 12:281–296
Jorgensen WJ, Madura JD (1985) Temperature and size dependence for Monte Carlo simulations of TIP4P water. Mol Phys 56:1381–1392
Lawrence CP, Skinner JL (2003) Flexible TIP4P model for molecular dynamics simulation of liquid water. Chem Phys Lett 372:842–847
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowit ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593
Martyna GJ, Klein ML, Tuckerman M (1992) Nose-Hoover chains: the canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics. J Chem Phys 97:2635–2643
Martyna GJ, Tobias DJ, Klein ML (1994) Constant-pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J Chem Phys 101:4177–4189
Auger G, Martin L, Bertrand J, Ferrari P, Fanchon E, Vaganay S, Petillot Y, van Heijenoort J, Blanot D, Dideberg O (1998) Large-scale preparation, purification, and crystallization of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine: D-glutamate ligase from Escherichia coli. Prot Express Purif 13:23–29
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia OA (1979) An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem 100:95–97
Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) (2007) Methods for dilution antibacterial susceptibility test for Bacteria that grow aerobically, 7th ed. Approved Standard (MA7-A7); Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute: Wayne. 27:133
Tomasic T, Kovac A, Simcic M, Blanot D, Grdadolnik SG, Gobec S, Kikelj D, Peterlin Masic L (2011) Novel 2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one inhibitors of bacterial MurD ligase targeting D-Glu- and diphosphate-binding sites. Eur J Med Chem 46:3964–3975
Funding
We would like to thank the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Government of India, for the financial support (No. EMR/2016/002981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3382 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azam, M.A., Jupudi, S. Structure-based virtual screening to identify inhibitors against Staphylococcus aureus MurD enzyme. Struct Chem 30, 2123–2133 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-019-01330-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-019-01330-z